Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study was to clarify the reason for the high rate of false-negative cases for offending vessels determined by magnetic resonance tomographic angiography (MRTA) in trigeminal neuralgia (TN) patients before microvascular decompression (MVD).
Methods
Preoperative MRTA imaging was performed in 115 patients with TN. The characteristics of the offending vessels were determined by MRTA prior to MVD. The relationships between TN and surrounding vessels were classified into two types, MRTA-positive (contact or compressing) and MRTA-negative (near or distant), and compared with the surgical findings.
Results
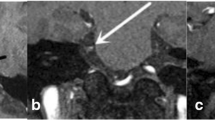
According to the surgical findings in the 100 MRTA-positive patients, vascular compression was found in 90 patients, vascular contact without compression was found in six patients, and no contact between vessels and the root of TN was found in three patients. Bony compression was found in one patient. In the 15 MRTA-negative patients, small artery compression (one with arterial wall stiffening) was found in seven patients, venous compression was found in two patients, arachnoid thickening and adhesion were found in three patients, and no vessel compression was found in three patients. MRTA showed sensitivity of 91.4 % (96/105) and specificity of 60 % (6/10).
Conclusions
Preoperative MRTA is valuable for determining the offending vessels in TN patients. However, owing to its inability to distinguish offending vessels such as small arteries, small veins, and vessels with wall calcification in addition to abnormal blood flow, the false-negative rate is comparably high.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
MacDonald BK, Cockerell OC, Sander JW, Shorvon SD. The incidence and lifetime prevalence of neurological disorders in a prospective community-based study in the UK. Brain. 2000;123:665–76.
Emril DR, Ho KY. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: role of radiofrequency ablation. J Pain Res. 2010;3:249–54.
Katusic S, Beard CM, Bergstralh E, Kurland LT. Incidence and clinical features of trigeminal neuralgia, Rochester, Minnesota, 1945–1984. Ann Neurol. 1990;27:89–95.
Love S, Coakham HB. Trigeminal neuralgia: pathology and pathogenesis. Brain. 2001;124:2347–60.
Miller JP, Acar F, Burchiel KJ. Classification of trigeminal neuralgia: clinical, therapeutic, and prognostic implications in a series of 144 patients undergoing microvascular decompression. J Neurosurg. 2009;111:1231–4.
Nurmikko TJ, Eldridge PR. Trigeminal neuralgia–pathophysiology, diagnosis and current treatment. Br J Anaesth. 2001;87:117–32.
Sweet WH, Wepsic JG. Controlled thermocoagulation of trigeminal ganglion and rootlets for differential destruction of pain fibers. 1. Trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 1974;40:143–56.
Skirving DJ, Dan NG. A 20-year review of percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal ganglion. J Neurosurg. 2001;94:913–7.
Zakrzewska JM, Lopez BC, Kim SE, Coakham HB. Patient reports of satisfaction after microvascular decompression and partial sensory rhizotomy for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery. 2005;56:1304–11 (discussion 1311–2).
Broggi G, Ferroli P, Franzini A, Servello D, Dones I. Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: comments on a series of 250 cases, including 10 patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000;68:59–64.
Barker FG, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD. The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:1077–83.
Zhang L, Zhang Y, Li C, Zhu S. Surgical treatment of primary trigeminal neuralgia: comparison of the effectiveness between MVD and MVD + PSR in a series of 210 patients. Turk Neurosurg. 2012;22:32–8.
Meaney JF, Eldridge PR, Dunn LT, Nixon TE, Whitehouse GH, Miles JB. Demonstration of neurovascular compression in trigeminal neuralgia with magnetic resonance imaging. Comparison with surgical findings in 52 consecutive operative cases. J Neurosurg. 1995;83:799–805.
Han-Bing S, Wei-Guo Z, Jun Z, Jian-Kang S, Yu C. Predicting the outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia using magnetic resonance tomographic angiography. J Neuroimaging. 2010;20:345–9.
Leandri M, Eldridge P, Miles J. Recovery of nerve conduction following microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurology. 1998;51:1641–6.
Sindou M, Howeidy T, Acevedo G. Anatomical observations during microvascular decompression for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia (with correlations between topography of pain and site of the neurovascular conflict). Prospective study in a series of 579 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2002;144:1–12 (discussion 12–3).
Rhoton AL Jr. The cerebellopontine angle and posterior fossa cranial nerves by the retrosigmoid approach. Neurosurgery. 2000;47:S93–129.
Cai J, Xin ZX, Zhang YQ, Sun J, Lu JL, Xie F. Diagnostic value of 3D time-of-flight MRA in trigeminal neuralgia. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22:1343–8.
Boecher-Schwarz HG, Bruehl K, Kessel G, Guenthner M, Perneczky A, Stoeter P. Sensitivity and specificity of MRA in the diagnosis of neurovascular compression in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. A correlation of MRA and surgical findings. Neuroradiology. 1998;40:88–95.
Fukuda H, Ishikawa M, Okumura R. Demonstration of neurovascular compression in trigeminal neuralgia and hemifacial spasm with magnetic resonance imaging: comparison with surgical findings in 60 consecutive cases. Surg Neurol. 2003;59:93–9 (discussion 99–100).
Korogi Y, Nagahiro S, Du C, Sakamoto Y, Takada A, Ushio Y, et al. Evaluation of vascular compression in trigeminal neuralgia by 3D time-of-flight MRA. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1995;19:879–84.
Leal PR, Hermier M, Froment JC, Souza MA, Cristino-Filho G, Sindou M. Preoperative demonstration of the neurovascular compression characteristics with special emphasis on the degree of compression, using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging: a prospective study, with comparison to surgical findings, in 100 consecutive patients who underwent microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir. 2010;152:817–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Haitao Huang, Zhihui Wang, Yi Ma, Yanfeng Li, Lei Wang, Guofei Wang, Qiang Ma, and Xin Liang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human rights statements and informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Wang, Z., Ma, Y. et al. Analysis of magnetic resonance tomographic angiography false negatives in trigeminal neuralgia before microvascular decompression. Oral Radiol 33, 45–50 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-016-0247-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-016-0247-7