Abstract
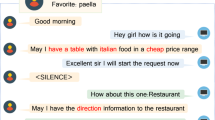
Conversation Recommender System (CRS) engage in multi-turn conversations with users and provide recommendations through responses. As user preferences evolve dynamically during the course of the conversation, it is crucial to understand natural interaction utterances to capture the user’s dynamic preference accurately. Existing research has focused on obtaining user preference at the entity level and natural language level, and bridging the semantic gap through techniques such as knowledge augmentation, semantic fusion, and prompt learning. However, the representation of each level remains under-explored. At the entity level, user preference is typically extracted from Knowledge Graphs, while other modal data is often overlooked. At the natural language level, user representation is obtained from a fixed language model, disregarding the relationships between different contexts. In this paper, we propose User-augmented Conversation Recommendation via Multi-modal graph learning and Context Mining (UaMC) to address above limitations. At the entity level, we enrich user preference by leveraging multi-modal knowledge. At the natural language level, we employ contrast learning to extract user preference from similar contexts. By incorporating the enhanced representation of user preference, we utilize prompt learning techniques to generate responses related to recommended items. We conduct experiments on two public CRS benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach in both the recommendation and conversation subtasks.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of supporting data
All datasets used in this paper are open datasets.
References
Chen, Q., Lin, J., Zhang, Y., Ding, M., Cen, Y., Yang, H., Tang, J.: Towards knowledge-based recommender dialog system. In: EMNLP-IJCNLP, pp. 1803–1813 (2019). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D19-1189
Wang, X., Zhou, K., Wen, J., Zhao, W.X.: Towards unified conversational recommender systems via knowledge-enhanced prompt learning. In: KDD, pp. 1929–1937 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3534678.3539382
Zhou, Y., Zhou, K., Zhao, W.X., Wang, C., Jiang, P., Hu, H.: C\({^2}\)-crs: Coarse-to-fine contrastive learning for conversational recommender system. In: WSDM, pp. 1488–1496 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3488560.3498514
Lu, Y., Bao, J., Song, Y., Ma, Z., Cui, S., Wu, Y., He, X.: Revcore: Review-augmented conversational recommendation. In: ACL/IJCNLP, pp. 1161–1173 (2021). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.findings-acl.99
Zhou, J., Wang, B., He, R., Hou, Y.: CRFR: improving conversational recommender systems via flexible fragments reasoning on knowledge graphs. In: EMNLP, pp. 4324–4334 (2021). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.emnlp-main.355
Zhou, K., Zhao, W.X., Bian, S., Zhou, Y., Wen, J., Yu, J.: Improving conversational recommender systems via knowledge graph based semantic fusion. In: KDD, pp. 1006–1014 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3394486.3403143
Wang, L., Hu, H., Sha, L., Xu, C., Jiang, D., Wong, K.: Recindial: A unified framework for conversational recommendation with pretrained language models. In: AACL/IJCNLP, pp. 489–500 (2022). https://aclanthology.org/2022.aacl-main.37
Fan, S., Wang, Y., Li, J., Zhang, Z., Shang, S., Han, P.: Interactive information extraction by semantic information graph. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 2022, Vienna, Austria, 23-29 July 2022, pp. 4100–4106 (2022). https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2022/569
Fan, S., Zhang, B., Zhou, S., Wang, M., Li, K.: Few-shot relation extraction towards special interests. Big Data Res. 26, 100273 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bdr.2021.100273
Li, J., Shang, S., Shao, L.: Metaner: Named entity recognition with meta-learning. In: WWW ’20: The web conference 2020, Taipei, Taiwan, April 20-24, 2020, pp. 429–440 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3366423.3380127
Li, J., Han, P., Ren, X., Hu, J., Chen, L., Shang, S.: Sequence labeling with meta-learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 35(3), 3072–3086 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2021.3118469
Li, J., Ye, D., Shang, S.: Adversarial transfer for named entity boundary detection with pointer networks. In: Kraus, S. (ed.) Proceedings of the 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 2019, Macao, China, August 10-16, 2019, pp. 5053–5059. ijcai.org, ??? (2019). https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2019/702
Gao, C., Lei, W., He, X., Rijke, M., Chua, T.: Advances and challenges in conversational recommender systems: Asurvey. AI Open, pp. 100–126 (2021)
Jannach, D., Manzoor, A., Cai, W., Chen, L.: A survey on conversational recommender systems. ACM Comput. Surv. 54(5), 105–110536 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3453154
Sharma, A., Lin, I.W., Miner, A.S., Atkins, D.C., Althoff, T.: Towards facilitating empathic conversations in online mental health support: A reinforcement learning approach. In: WWW ’21: The Web Conference 2021, pp. 194–205 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3442381.3450097
Christakopoulou, K., Radlinski, F., Hofmann, K.: Towards conversational recommender systems. In: SIGKDD, pp. 815–824 (2016)
Mirzadeh, N., Ricci, F., Bansal, M.: Feature selection methods for conversational recommender systems. In: IEEE, pp. 772–777 (2005)
Sun, Y., Zhang, Y.: Conversational recommender system. In: SIGIR, pp. 235–244 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3209978.3210002
Lei, W., He, X., Miao, Y., Wu, Q., Hong, R., Kan, M., Chua, T.: Estimation-action-reflection: Towards deep interaction between conversational and recommender systems. In: WSDM, pp. 304–312 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3336191.3371769
Deng, Y., Li, Y., Sun, F., Ding, B., Lam, W.: Unified conversational recommendation policy learning via graph-based reinforcement learning. In: SIGIR, pp. 1431–1441 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3404835.3462913
Lei, W., Zhang, G., He, X., Miao, Y., Wang, X., Chen, L., Chua, T.: Interactive path reasoning on graph for conversational recommendation. In: KDD, pp. 2073–2083 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3394486.3403258
Li, R., Kahou, S.E., Schulz, H., Michalski, V., Charlin, L., Pal, C.: Towards deep conversational recommendations. In: NeurIPS, pp. 9748–9758 (2018). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2018/hash/800de15c79c8d840f4e78d3af937d4d4-Abstract.html
Pang, X., Wang, Y., Fan, S., Chen, L., Shang, S., Han, P.: Empmff: A multi-factor sequence fusion framework for empathetic response generation. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, WWW 2023, Austin, TX, USA, 30 April 2023 - 4 May 2023, pp. 1754–1764. https://doi.org/10.1145/3543507.3583438
Rao, X., Chen, L., Liu, Y., Shang, S., Yao, B., Han, P.: Graph-flashback network for next location recommendation. In: KDD ’22: The 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Washington, DC, USA, August 14 - 18, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3534678.3539383
Han, P., Shang, S., Sun, A., Zhao, P., Zheng, K., Kalnis, P.: AUC-MF: point of interest recommendation with AUC maximization. In: 35th IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, ICDE 2019, Macao, China, April 8-11, pp. 1558–1561 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2019.00141
Han, P., Li, Z., Liu, Y., Zhao, P., Li, J., Wang, H., Shang, S.: Contextualized point-of-interest recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI, pp. 2484–2490 (2020) . https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2020/344
Chen, L., Shang, S., Jensen, C.S., Yao, B., Zhang, Z., Shao, L.: Effective and efficient reuse of past travel behavior for route recommendation. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, KDD 2019, Anchorage, AK, USA, August 4-8, pp. 488–498 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3292500.3330835
Han, P., Shang, S.: Scene re-ranking for recommendation. In: 24th IEEE International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, MMSP 2022, Shanghai, China, September 26-28, pp. 1–6 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/MMSP55362.2022.9949116
Han, P., Shang, S., Sun, A., Zhao, P., Zheng, K., Zhang, X.: Point-of-interest recommendation with global and local context. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 34(11), 5484–5495 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2021.3059744
Feng, S., Chen, L., Zhao, K., Wei, W., Li, F., Shang, S.: Node2lv: Squared lorentzian representations for node proximity. In: 37th IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, ICDE 2021, Chania, Greece, April 19-22, 2021, pp. 2015–2020 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE51399.2021.00193
Zhu, S., Wang, Y., Shang, S., Zhao, G., Wang, J.: Probabilistic routing using multimodal data. Neurocomputing. 253, 49–55 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.08.138
Lehmann, J., Isele, R., Jakob, M., Jentzsch, A., Kontokostas, D., Mendes, P.N., Hellmann, S., Morsey, M., Kleef, P., Auer, S., Bizer, C.: Dbpedia - A large-scale, multilingual knowledge base extracted from wikipedia. Semantic Web. 6(2), 167–195 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3233/SW-140134
Lin, Y., Liu, Z., Sun, M., Liu, Y., Zhu, X.: Learning entity and relation embeddings for knowledge graph completion. In: AAAI, pp. 2181–2187 (2015). http://www.aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI15/paper/view/9571
Han, P., Yang, P., Zhao, P., Shang, S., Liu, Y., Zhou, J., Gao, X., Kalnis, P.: GCN-MF: disease-gene association identification by graph convolutional networks and matrix factorization. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, KDD 2019, Anchorage, AK, USA, August 4-8, 2019, pp. 705–713 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3292500.3330912
Chen, L., Shang, S., Yang, C., Li, J.: Spatial keyword search: a survey. GeoInformatica. 24(1), 85–106 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10707-019-00373-y
Zhou, S., Zhang, J., Chen, L., Shang, S.: Multiple behaviors recommendation with graph learning. In: 24th IEEE International workshop on multimedia signal processing, MMSP 2022, Shanghai, China, September 26-28, pp. 1–6 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/MMSP55362.2022.9949145
Chen, L., Shang, S., Jensen, C.S., Xu, J., Kalnis, P., Yao, B., Shao, L.: Top-k term publish/subscribe for geo-textual data streams. VLDB J. 29(5), 1101–1128 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00778-020-00607-8
Chen, L., Shang, S.: Approximate spatio-temporal top-k publish/subscribe. World Wide Web. 22(5), 2153–2175 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-018-0564-3
Chen, L., Shang, S., Zhang, Z., Cao, X., Jensen, C.S., Kalnis, P.: Location-aware top-k term publish/subscribe. In: 34th IEEE International conference on data engineering, ICDE 2018, Paris, France, April 16-19, 2018, pp. 749–760. IEEE Computer Society, ??? (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDE.2018.00073
Wang, X., He, X., Cao, Y., Liu, M., Chua, T.: KGAT: knowledge graph attention network for recommendation. In: KDD, pp. 950–958 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3292500.3330989
Reimers, N., Gurevych, I.: Sentence-bert: Sentence embeddings using siamese bert-networks. In: EMNLP-IJCNLP, pp. 3980–3990 (2019). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D19-1410
Henderson, M.L., Al-Rfou, R., Strope, B., Sung, Y., Lukács, L., Guo, R., Kumar, S., Miklos, B., Kurzweil, R.: Efficient natural language response suggestion for smart reply (2017). arXiv:1705.00652
Liang, Z., Hu, H., Xu, C., Miao, J., He, Y., Chen, Y., Geng, X., Liang, F., Jiang, D.: Learning neural templates for recommender dialogue system. In: EMNLP, pp. 7821–7833 (2021). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.emnlp-main.617
Li, X.L., Liang, P.: Prefix-tuning: Optimizing continuous prompts for generation. In: ACL/IJCNLP, pp. 4582–4597 (2021). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.acl-long.353
Hayati, S.A., Kang, D., Zhu, Q., Shi, W., Yu, Z.: INSPIRED: toward sociable recommendation dialog systems. In: EMNLP, pp. 8142–8152 (2020). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.emnlp-main.654
Montazeralghaem, A., Allan, J.: Extracting relevant information from user’s utterances in conversational search and recommendation. In: KDD, pp. 1275–1283 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3534678.3539471
Zhou, K., Wang, X., Zhou, Y., Shang, C., Cheng, Y., Zhao, W.X., Li, Y., Wen, J.: Crslab: An open-source toolkit for building conversational recommender system. In: ACL, pp. 185–193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.acl-demo.22
Li, J., Chiu, B., Shang, S., Shao, L.: Neural text segmentation and its application to sentiment analysis. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 34(2), 828–842 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2020.2983360
Acknowledgements
We also acknowledge the editorial committee’s support and all anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions, which improved the content and presentation of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the NSFC (U2001212, U22B2037, U21B2046, 62032001, and 61932004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and model design. Siqi Fan and Yequan Wang worked on the full manuscript. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Siqi Fan and Yequan Wang. Lisi Chen and Shuo Shang wrote the Sections 1–2. Peng Han and Xiaobing Pang prepared the Sections 3–5. The expermental study was conducted by Siqi Fan. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors proof-read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval and Consent to participate
Not applicable
Human and Animal Ethics
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: Special Issue on Advancing recommendation systems with foundation models.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, S., Wang, Y., Pang, X. et al. UaMC: user-augmented conversation recommendation via multi-modal graph learning and context mining. World Wide Web 26, 4109–4129 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-023-01219-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-023-01219-2