Abstract
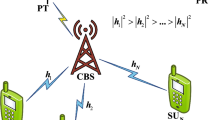
Spectrum sensing is the active research area in the Cognitive radio networks that initiates the effective data sharing between the licensed and the unlicensed users of Cognitive Network. Maximizing the detection probability for a provided false alarm rate is a hectic challenge of most of the spectral sensing methods. The paper proposes a spectral sensing method, termed as Krill-Herd Whale optimization-based actor critic neural network. The unoccupied spectrum is optimally determined using the proposed method that allocates the free spectrum bands to the primary users instantly such that the delay is minimized due to the effective functioning of the fusion center. For the effective sensing, the Eigen-value-based cooperative sensing is activated in the cognitive radio. The analysis of the proposed method is progressed based on the performance metrics, such as false alarm probability and detection probability. The proposed spectral sensing method outperforms the existing methods that yield a maximum probability of detection and minimum probability of false alarm at a rate of 0.9805 and of 0.009.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pandi, N., & Kumar, A. (2017). A review on cognitive radio for next generation cellular network and its challenges. American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 10(2), 334–347.
Marinho, J., Granjal, J., & Monteiro, E. (2015). A survey on security attacks and countermeasures with primary user detection in cognitive radio networks. EURASIP Journal on Information Security, 2015, 1–14.
Zhang, D., Chen, Z., Ren, J., Zhang, N., Awad, M. K., Zhou, H., & Shen, X. (2015). Energy harvesting-aided spectrum sensing and data transmission in heterogeneous cognitive radio sensor network. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66(1), 831–843.
Supraja, P., & Jayashri, S. (2016). Optimized neural network for spectrum prediction scheme in cognitive radio. Wireless Personal Communication, 94(4), 2597–2611.
Roy, P., & Muralidhar, M. (2015). Channel state prediction in a cognitive radio network using neural network Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm. International Journal of Wireless Communications and Networking Technologies, 4(2), 24–29.
Venkatesan, M., & Kulkarni, A. V. (2014). Spectrum predictor model for cognitive radio. In International conference on advances in engineering & technology (ICAET) (pp. 10–14).
Sadough, S. S., & Ivrigh, S. S. (2012). Spectrum sensing for cognitive radio systems through primary user activity prediction. Radio Engineering, 21(4), 1092–1100.
Gavrilovska, L., & Atanasovski, V. (2011). Spectrum sensing framework for cognitive radio networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 59(3), 447–469.
Christopher Clement, J., Bharath Reddy, B., & Emmanuel, D. S. (2016). An energy-efficient cooperative spectrum sensing strategy with robustness against noise uncertainty for cognitive radio networks. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 41(9), 3399–3405.
Chen, H., Zhou, M., Xie, L., & Jin, X. (2013). Fault-tolerant cooperative spectrum sensing scheme for cognitive radio networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 71(4), 2379–2397.
Yu, H., Tang, W., & Li, S. (2011). Optimization of cooperative spectrum sensing with sensing user selection in cognitive radio networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking. https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1499-2011-208.
Akyildiz, I., Lo, B., & Balakrishnan, R. (2011). Cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks: A survey. Physical Communication, 4(1), 40–62.
Li, H., Xing, X., Zhu, J., Cheng, X., Li, K., Bie, R., Jing, T. (2015). Utility-based cooperative spectrum sensing scheduling in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66(1), 645–655.
Alom, Md. Z., Godder, T. K., Morshed, M. N., & Maali, A. (2017). Enhanced spectrum sensing based on energy detection in cognitive radio network using adaptive threshold. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Networking, Systems and Security (NSysS).
Tumuluru, V. K., Wang, P., & Niyato, D. (2010). A neural network based spectrum prediction scheme for cognitive radio. In IEEE international conference on communications (ICC) (pp. 1–5).
Ferreira, P. V. R., Paffenrothy, R., Wyglinski, A. M., Hackettz, T. M., Bilénz, S. G., Reinhartx, R. C., & Mortensenx, D. J. (2017). Multi-objective reinforcement learning-based deep neural networks for cognitive space communications. In Proceedings of cognitive communications for aerospace applications workshop (CCAA) (pp. 1–8).
Surampudi, A., & Kalimuthu, K. (2016). An adaptive decision threshold scheme for the matched filter method of spectrum sensing in cognitive radio using artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of information processing (IICIP) (pp. 1–5).
Ratre, A., & Pankajakshan, V. (2017). Tucker visual search-based hybrid tracking model and Fractional Kohonen self-organizing map for anomaly localization and detection in surveillance videos. The Imaging Science Journal, 66, 1–16.
Dhumane, A. V., & Prasad, R. S. (2017). Multi-objective fractional gravitational search algorithm for energy efficient routing in IoT. Wireless Networks, 1–15.
Nipanikar, S. I., Hima Deepthi, V., & Kulkarni, N. (2017). A sparse representation based image steganography using particle swarm optimization and wavelet transform. Alexandria Engineering Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2017.09.005.
Shelke, P. M., & Prasad, R. S. (2018). An improved anti-forensics JPEG compression using least Cuckoo search algorithm. The Imaging Science Journal, 66(3), 169–183.
Krishnamoorthy, N., & Asokan, R. (2014). Optimized resource selection to promote grid scheduling using hill climbing algorithm. International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications, 5(2), 14–19.
Liu, K. (2016). Optimization algorithm of cognitive radio spectrum sensing based on quantum neural network. Automatic Control and Computer Sciences, 50(5), 324–331.
Sun, M., Zhao, C., Yan, S., & Li, B. (2017). A novel spectrum sensing for cognitive radio networks with noise uncertainty. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66(5), 4424–4429.
Yang, H., Liang, Y., Miao, J., & Zhao, D. (2017). Radio spectrum management for cognitive radio based on fuzzy neural methodology. Part of the Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing book series (AISC), 611, 609–616.
Huang, H., & Yuan, C. (2018). Cooperative spectrum sensing over generalized fading channels based on energy detection. China Communications, 15(5), 128–137.
Lee, K., Yoon, C., Jo, O., & Lee, W. (2018). Joint optimization of spectrum sensing and transmit power in energy harvesting-based cognitive radio networks. IEEE Access, 6, 30653–30662.
Ivanov, A., Mihovska, A., & Tonchev, K. (2018). Real-time adaptive spectrum sensing for cyclostationary and energy detectors. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 33(5–6), 20–33.
Zhao, D., Wang, B., & Liu, D. (2013). A supervised actor–critic approach for adaptive cruise control. Soft Computing, 17(11), 2089–2099.
Du, D., & Fei, M. (2008). A two-layer networked learning control system using actor–critic neural network. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 205(1), 26–36.
Gandomi, A. H., & Alavi, A. H. (2012). Krill herd: A new bio-inspired optimization algorithm. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 17, 4831–4845.
Mirjalili, S., & Lewis, A. (2016). The Whale optimization algorithm. Advances in Engineering Software, 95, 51–67.
Guimarães, D. A., da Silva, C. R. N., & de Souza, R. A. A. (2013). Cooperative spectrum sensing using eigenvalue fusion for OFDMA and other wideband signals. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, 2, 1–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhowmik, M., Malathi, P. Spectrum Sensing in Cognitive Radio Using Actor–Critic Neural Network with Krill Herd-Whale Optimization Algorithm. Wireless Pers Commun 105, 335–354 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-6115-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-6115-5