Abstract
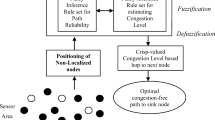
Congestion management in a wireless sensor network (WSN) is a key determinant of the quality of service. Congestion in a network causes data loss, a reduced transmission rate, increased delays, and excess energy consumption. The latter has a direct impact on tiny sensor devices with limited resources and processing, buffering, and transmitting capabilities. In addition, a WSN relies on multiple packet relays between nodes, which inevitably results in network congestion near the base station, whose neighboring nodes incur crowded traffic from multisource deliveries. Thus, this paper proposes a novel routing method that minimizes congestion. The adaptive routing strategy consists of 3 main modules. First, an optimal notification level for queue control is specified by using multistage fuzzy logic (MFL). The resulting weights evaluated from congestion-related parameters are then passed onto the subsequent modules. The second module adjusts the congestion notification, which makes the module more flexible to improve its routing discovery efficiency and to reduce the chance of loss during the rerouting stage. Finally, we propose a routing adjustment and control mechanism by using a novel navigation technique based on linear and angular distances and MFL to create weights for path assessment. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of the packet loss ratio, average hop count, network lifetime, and energy consumption metrics.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Telecommunication Union. (2016). Harnessing the Internet of Things for global development. Geneva.
Laurence, G. (2019). Gartner says 5.8 billion enterprise and automotive IoT endpoints will be in use in 2020. Gartner Inc. [Online]. Retrieved January 25, 2020 from https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2019-08-29-gartner-says-5-8-billion-enterprise-and-automotive-io.
Riaz, A. (2018). IoTs—overview of the ecosystem. Retrieved January 25, 2020 from https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-D/Regional-Presence/AsiaPacific/Documents/Events/2018/IoT-BDG/Day1-IoT-Aamir.pdf.
Lopez, J., Rios, R., Bao, F., & Wang, G. (2017). Evolving privacy: From sensors to the Internet of Things. Future Generation Computing Systems, 75, 46–57.
Yetgin, H., Cheung, K. T. K., El-Hajjar, M., & Hanzo, L. (2017). A survey of network lifetime maximization techniques in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 19(2), 828–854.
Pham, Q. V., & Hwang, W. J. (2017). Network utility maximization-based congestion control over wireless networks: a survey and potential directives. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 19(2), 1173–1200.
Kobo, H. I., Abu-Mahfouz, A. M., & Hancke, G. P. (2017). A survey on software-defined wireless sensor networks: challenges and design requirements. IEEE Access, 5, 1872–1899.
Modieginyane, K. M., Letswamotse, B. B., Malekian, R., & Abu-Mahfouz, A. M. (2018). Software defined wireless sensor networks application opportunities for efficient network management: A survey. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 66, 274–287.
Rault, T., Bouabdallah, A., & Challal, Y. (2014). Energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks: A top-down survey. Computer Networks Journal, 67, 104–122.
Jan, M. A., Jan, S. R. U., Alam, M., Akhunzada, A., & Rahman, I. U. (2018). A comprehensive analysis of congestion control protocols in wireless sensor networks. Mobile Networks and Applications, 23(3), 456–468.
Rashid, B., & Rehmani, M. H. (2016). Applications of wireless sensor networks for urban areas: A survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 60, 192–219.
Ghaffari, A. (2015). Congestion control mechanisms in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 52, 101–115.
Shah, S. A., Nazir, B., & Khan, I. A. (2017). Congestion control algorithms in wireless sensor networks: Trends and opportunities. Journal of King Saud University, 29(3), 236–245.
Al-Saadi, R., Armitage, G., But, J., & Branch, P. (2019). A survey of delay-based and hybrid TCP congestion control algorithms. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 21(4), 3609–3638.
Xu, C., Zhao, J., & Muntean, G. M. (2016). Congestion control design for multipath transport protocols: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 18(4), 2948–2969.
Sergiou, C., Antoniou, P., & Vassiliou, V. (2014). A comprehensive survey of congestion control protocols in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 16(4), 1839–1859.
Bohloulzadeh, A., & Rajaei, M. (2020). A survey on congestion control protocols in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, 27(3), 365–384.
Gherbi, C., Aliouat, Z., & Benmohammed, M. (2017). A survey on clustering routing protocols in wireless sensor networks. Sensor Review, 37(1), 12–25.
Pratama, A., Munadi, R., & Mayasari, R. (2018). Design and implementation of flood detector using wireless sensor network with mamdani’s fuzzy logic method. In Proceedings—2017 2nd international conferences on information technology, information systems and electrical engineering, ICITISEE 2017 (vol. 2018-January, pp. 192–197).
Aguirre, E., Lopez-Iturri, P., Azpilicueta, L., Astrain, J. J., Villadangos, J., Santesteban, D., & Falcone, F. (2016). Implementation and analysis of a wireless sensor network-based pet location monitoring system for domestic scenarios. Sensors, 16(9), 1–20.
Yu, F., He, Z., & Xu, N. (2019). Autonomous navigation for GPS using inter-satellite ranging and relative direction measurements. Acta Astronautica, 160, 646–655.
Stegagno, P., Cognetti, M., Oriolo, G., Bulthoff, H. H., & Franchi, A. (2016). Ground and Aerial mutual localization using anonymous relative-bearing measurements. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 32(5), 1133–1151.
Ren, F., He, T., Das, S. K., & Lin, C. (2011). Traffic-aware dynamic routing to alleviate congestion in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 22(9), 1585–1599.
Woo, A., Tong, T., & Culler, D. (2003). Taming the underlying challenges of reliable multihop routing in sensor networks. In SenSys’03: Proceedings of international conference on embedded network sensor systems (pp. 14–27).
Tan, D. D., Dinh, N. Q., & Kim, D. S. (2013). GRATA: Gradient-based traffic-aware routing for wireless sensor networks. IET Wireless Sensor Systems, 3(2), 104–111.
Gholipour, M., Haghighat, A. T., & Meybodi, M. R. (2015). Hop-by-hop traffic-aware routing to congestion control in wireless sensor networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2015(1), 15.
Farzaneh, N., & Yaghmaee, M. H. (2015). An adaptive competitive resource control protocol for alleviating congestion in wireless sensor networks: An evolutionary game theory approach. Wireless Personal Communications, 82(1), 123–142.
Ding, W., Tang, L., & Ji, S. (2016). Optimizing routing based on congestion control for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 22(3), 915–925.
Tang, L., Liu, H., & Yan, J. (2017). Gravitation theory based routing algorithm for active wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 97(1), 269–280.
Raman, C. J., & James, V. (2019). FCC: Fast congestion control scheme for wireless sensor networks using hybrid optimal routing algorithm. Cluster Computing, 22, 12701–12711.
Izadi, D., Abawajy, J., & Ghanavati, S. (2013). Fuzzy logic optimized wireless sensor network routing protocol. Journal of High Speed Networks, 19(2), 115–128.
Hatamian, M., Bardmily, M. A., Asadboland, M., Hatamian, M., & Barati, H. (2016). Congestion-aware routing and fuzzy-based rate controller for wireless sensor networks. Radioengineering, 25(1), 114–123.
Sangeetha, G., Vijayalakshmi, M., Ganapathy, S., & Kannan, A. (2020). An improved congestion-aware routing mechanism in sensor networks using fuzzy rule sets. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 13(3), 890–904.
Chen, F., Wang, N., German, R., & Dressler, F. (2010). Simulation study of IEEE 802.15.4 LR-WPAN for industrial applications. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 10(5), 609–621.
Heinzelman, W. B., Chandrakasan, A. P., & Balakrishnan, H. (2002). An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 1(4), 660–670.
Tamandani, Y. K., & Bokhari, M. U. (2016). SEPFL routing protocol based on fuzzy logic control to extend the lifetime and throughput of the wireless sensor network. Wireless Network, 22(2), 647–653.
Taheri, H., Neamatollahi, P., Younis, O. M., Naghibzadeh, S., & Yaghmaee, M. H. (2012). An energy-aware distributed clustering protocol in wireless sensor networks using fuzzy logic. Ad Hoc Networks, 10(7), 1469–1481.
Hosseini, S. S., & Noorossana, R. (2018). Performance evaluation of EWMA and CUSUM control charts to detect anomalies in social networks using average and standard deviation of degree measures. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 34(4), 477–500.
Tang, A., Castagliola, P., Sun, J. S., & Hu, X. L. (2018). The effect of measurement errors on the adaptive EWMA chart. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 34(4), 609–630.
Luo, J., Panchard, J., Piórkowski, M., Grossglauser, M., & Hubaux, J. P. (2006). MobiRoute: Routing towards a mobile sink for improving lifetime in sensor networks. In Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics) (Vol. 4026, pp. 480–497). LNCS.
Kim, Y. H., Ahn, S. C., & Kwon, W. H. (2000). Computational complexity of general fuzzy logic control and its simplification for a loop controller. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 111(2), 215–224.
Fall, K., & Varadhan, K. (2007). The network simulator NS-2. Retrieved January 25, 2020 from https://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/doc/index.html.
Manna Research Group. (2010). Mannasim framework [Online]. Retrieved January 25, 2020 from http://www.mannasim.dcc.ufmg.br/index.htm.
Eaton, J. W., Bateman, D., & Hauberg, S. (1997). Gnu octave. London: Network Theory.
DataSheet, MICAz. (2009). Crossbow technology inc. Retrieved January 25, 2020 from http://www.openautomation.net/uploadsproductos/micaz_datasheet.pdf.
Naeve, M., et al. (2002). Home networking with IEEE 802.15.4: A developing standard for low-rate wireless personal area networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 40(8), 70–77.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Thailand Science Research and Innovation (TSRI) and the National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT) via the International Research Network Program (IRN61W0006) and by Khon Kaen University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aimtongkham, P., Horkaew, P. & So-In, C. Multistage fuzzy logic congestion-aware routing using dual-stage notification and the relative barring distance in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Netw 27, 1287–1308 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02513-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02513-x