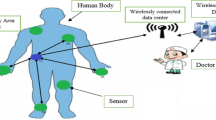
Abstract
Wireless body area network (WBAN) routing protocols are primarily designed for improvement of network performance parameters such as network lifetime, throughput and latency. However, these designs do not take into account the health hazards posed due to WBAN radiation. The focus of implementing IEEE 802.15.6 standards is to develop an energy-efficient, reliable and health-conscious wireless communication system around human body. This paper presents the implementation of a clustering-based routing protocol for WBAN that targets in achieving overall optimization of WBAN performance parameters including network lifetime, throughput, latency, node signal power and specific absorption rate (SAR) of human body for emf radiation. The suggested protocol applies a multi-objective NSGA-II optimization heuristic for cluster formation while taking into account various IEEE 802.15.6 standard constraints. A unique chromosome structure has been proposed for NSGA-II population in which each chromosome represents a random network topology for determining the node clusters, cluster heads and node transmission power. Furthermore, three system-level models for conducting multi-objective fitness evaluation of each chromosome have been proposed. These models predict the global transmission energy consumption; the average received signal strength (RSSI) and end to end network latency respectively. The developed NSGA-II model evolves into a non-dominated set of Pareto-optimal network topologies that renders the desired objectives of minimization of network energy consumption and network latency besides maximization of average RSSI. Enhancement in RSSI further leads to a tremendous improvement in the throughput rate. The node transmission power specifications of Pareto-optimal network topologies meet the standard SAR constraints too. The performance results shows that the suggested protocol strictly meets IEEE 802.15.6 compliance.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are included within the article.
Code availability
The authors confirm that the custom codes supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Cavallari, R., Martelli, F., Rosini, R., Buratti, C., & Verdone, R. (2014). A survey on wireless body area networks: technologies and design challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials. https://doi.org/10.1109/SURV.2014.012214.00007.
Latré, B., Braem, B., Moerman, I., et al. (2011). A survey on wireless body area networks. Wireless Networks,17, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-010-0252-4.
Khan, R. A., Mohammadani, K. H., Soomro, A. A., Hussain, J., Khan, S., Arain, T. H., et al. (2018). An energy efficient routing protocol for wireless body area sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communication. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5285-5.
Javaid, N., Ahmad, A., Nadeem, Q., Imran, M., & Haider, N. (2015). iMSIMPLE: iMproved stable increased-throughput multi-hop link efficient routing protocol for wireless body area networks. Computers in Human Behavior. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.10.005.
Choudhary, A., Nizamuddin, M., Singh, M. K., et al. (2019). Energy budget based multiple attribute decision making (EB-MADM) algorithm for cooperative clustering in wireless body area networks. Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-018-00006-8.
Ullah, Z., Ahmed, I., Razzaq, K., Naseer, M. K., & Ahmed, N. (2017). DSCB: Dual sink approach using clustering in body area network. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Appllications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-017-0587-z.
Kaur, N., & Singh, S. (2017). Optimized cost effective and energy efficient routing protocol for wireless body area networks. Ad Hoc Networks. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2017.03.008.
Wu, T., Wu, F., Redoute, J. M., & Yuce, M. R. (2017). An autonomous wireless body area network implementation towards IoT connected healthcare applications. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2716344.
Salehi, S. A., Razzaque, M. A., Tomeo-Reyes, I., & Hussain, N. (2016). IEEE 802.15.6 standard in wireless body area networks from a healthcare point of view. In 22nd Asia-Pacific conference on communications (APCC), Yogyakarta. https://doi.org/10.1109/APCC.2016.7581523.
Smith, D. B., & Hanlen, L. W. (2015). Channel modeling for wireless body area networks. In P. Mercier & A. Chandrakasan (Eds.), Ultra-low-power short-range radios: Integrated circuits and systems. Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14714-7_2.
Wu, T., & Lin, C. (2015). Low-SAR path discovery by particle swarm optimization algorithm in wireless body area networks. IEEE Sensors Journal. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2014.2354983.
Tuovinen, T., Berg, M., Yazdandoost, K. Y., Hämäläinen, M., & Iinatti, J. (2013). On the evaluation of biological effects of wearable antennas on contact with dispersive medium in terms of SAR and bio-heat by using FIT technique. In 7th international symposium on medical information and communication technology (ISMICT), Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISMICT.2013.6521719.
Cicioğlu, M., & Çalhan, A. (2019). Dynamic HUB selection process based on specific absorption rate for WBANs. IEEE Sensors Journal. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2019.2906044.
Zuhra, F. T., Bakar, K. B. A., Arain, A. A., & Tunio, M. A. (2017). Routing protocols in wireless body sensor networks: A comprehensive survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2017.10.002.
Choudhary, A., Nizamuddin, M., & Sachan, V. K. (2019). A hybrid fuzzy-genetic algorithm for performance optimization of cyber physical wireless body area networks. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00751-6.
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., & Meyarivan, T. (2002). A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.996017.
Korkmaz, T., & Sarac, K. (2010). Characterizing link and path reliability in large-scale wireless sensor networks. In IEEE 6th international conference on wireless and mobile computing, networking and communications (WiMob). https://doi.org/10.1109/WIMOB.2010.5644996.
Sample Data. (2018). Sample Shimmer3 ECG data. Retrieved February 25, 2019 from http://www.shimmersensing.com/images/uploads/docs/Shimmer3_ECG_Sample_Data.zip.
Ahmed, S., Javaid, N., Yousaf, S., Ahmad, A., Sandhu, M. M., Imran, M., et al. (2015). Co-LAEEBA: Cooperative link aware and energy efficient protocol for wireless body area networks. Computers in Human Behavior. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.12.051.
Maskooki, A., Soh, C., Gunawan, E., & Low, K. (2014). Adaptive routing for dynamic on-body wireless sensor networks. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2014.2313343.
Bangash, J., Khan, A., & Abdullah, H. (2015). Data-centric routing for intra wireless body sensor networks. Journal of Medical Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0268-5.
Ullah, F., Ullah, Z., Ahmad, S., Islam, I., & Iqbal, J. (2019). Traffic priority based delay-aware and energy efficient path allocation routing protocol for wireless body area network. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01343-w.
Abidi, B., Jilbab, A., & Mohamed, E. H. (2018). An energy efficiency routing protocol for wireless body area networks. Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology. https://doi.org/10.1080/03091902.2018.1483440.
El Azhari, M., El Moussaid, N., Toumanari, A., & Latif, R. (2017). Equalized energy consumption in wireless body area networks for a prolonged network lifetime. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4157858.
Yang, G., Wu, X., Li, Y., et al. (2020). Energy efficient protocol for routing and scheduling in wireless body area networks. Wireless Networks,26, 1265–1273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-019-02150-z.
Li, Z., Chen, M., & Zhang, G. (2015). Variable-rate transmission method with coordinator election for wireless body area networks. Wireless Networks,21, 2169–2180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-0917-0.
Khan, Z., Sivakumar, S., Phillips, W., & Robertson, B. (2014). QPRR: QoS-aware peering routing protocol for reliability sensitive data in body area network communication. The Computer Journal. https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/bxu114.
Javaid, N., Abbas, Z., Fareed, M. S., Khan, Z. A., & Alrajeh, N. (2013). M-ATTEMPT: A new energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless body area sensor networks. Elsevier Procedia Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2013.06.033.
Zhang, Yu., Zhang, Bing, & Zhang, Shi. (2017). A lifetime maximization relay selection scheme in wireless body area networks. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17061267.
Elhoseny, M., Yuan, X., Yu, Z., Mao, C., El-Minir, H. K., & Riad, A. M. (2015). Balancing energy consumption in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks using genetic algorithm. IEEE Communications Letters. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2381226.
Zhang, Q.-Y., Sun, Z.-M., & Zhang, F. (2014). A clustering routing protocol for wireless sensor networks based on type-2 fuzzy logic and ACO. In IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems. https://doi.org/10.1109/FUZZ-IEEE.2014.6891584.
Deb, K. (2011). Multi-objective optimisation using evolutionary algorithms: An introduction. In L. Wang, A. Ng, & K. Deb (Eds.), Multi-objective evolutionary optimisation for product design and manufacturing. London: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-85729-652-8_1.
Heinzelman, W. R., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2000). Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd Hawaii international conference on system sciences (HICSS ‘00), Washington DC, USA. https://doi.org/10.1109/HICSS.2000.926982.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank department of electronics and communication engineering, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi for providing the opportunity and guidance for research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary, A., Nizamuddin, M., Zadoo, M. et al. Multi-objective optimization framework complying IEEE 802.15.6 communication standards for wireless body area networks. Wireless Netw 26, 4339–4362 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02342-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02342-y