Abstract
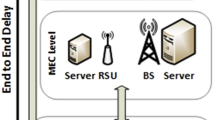
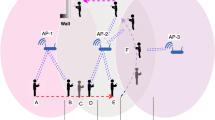
In Proxy Mobile IP (PMIPv6) networks, proxy-registrations are performed even for idle MNs, resulting in unnecessary signaling traffic. Although there have been many IP paging techniques aimed at reducing the unnecessary location update, they focus only on Mobile IP (MIP) since they had been developed before PMIPv6 was proposed. Thus, adopting existing IP paging support is not sufficient to support mobility in PMIPv6 networks. For more efficient support, we propose a dynamic multi-step paging scheme that pages an MN in multiple incremental steps instead of flooding paging messages to a whole paging area to significantly reduce the signaling traffic caused by the proxy location updates in the PMIPv6 networks. In addition, to improve the paging delay performance that may be deteriorated by the multi-step paging, the proposed scheme configures paging area dynamically to raise the efficiency of locating MNs. The size of a paging area is designed to be determined based on the speed of an MN. We also develop a thorough analytical model for evaluating the performance of the proposed scheme compared with a static paging scheme in terms of the signaling cost and the paging delay. Thorough analysis and simulation demonstrate that in the PMIPv6 network, our paging scheme can significantly reduce the signaling cost for IP paging, achieving a shorter paging delay, compared to that of a paging scheme with a fixed paging area.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I. F., Xie, J., & Mohanty, S. (2004). A survey of mobility management in next-generation all-IP-based wireless systems. Wireless Communications, IEEE, 11(4), 16–28.
Johnson, D., Perkins, C., & Arkko, J. (2004). Mobility support in IPv6. IETF RFC 3775, June 2004.
Soliman, H., Castellucci, C., Malki, K. E., & Bellier, L. (2005). Hierarchical mobile IPv6 mobility management (HMIPv6). IETF RFC 4140.
Koodli, R. (Ed.). (2009). Mobile IPv6 fast handovers. IETF RFC 5568.
Gundavelli, S. (Ed.). (2008). Proxy Mobile IPv6. RFC5213, August 2008.
Kaaranen, H., Ahtiainen, A., Laitinen, L., Naghian, S., & Niemi, V. (2005). UMTS networks: Architecture, mobility and services, (2nd Ed.). London: Wiley.
Campbell, A. T., Gomez, J., Kim, S., Wan, C.-Y., Turanyi, Z. R., & Valko, A. G. (2002). Comparison of IP micromobility protocols. Wireless Communications, IEEE , 9(1), 72–82.
Zhang, X., Castellanos, J. G., & Campbell, A. T. (2002). P-MIP: Paging extension for mobile IP. ACM Mobile Networks and Applications, 7(2), 127–141.
Kempf, J. (2001). Dormant mode host alerting (IP paging) problem statement. IETF RFC 3132, June 2001.
Do, H. T., & Onozato, Y. (2005). Merit of adaptability to mobile user parameters in IP paging. In IEEE proceedings of wireless on-demand network systems and services (WONS’05) (pp. 246–251).
Le, D., Lei, J., & Fu, X. (2007). A new decentralized mobility management service architecture for IPv6-based networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd ACM workshop on wireless multimedia networking and performance modeling (WMuNeP).
Xie, J. (2006). User-independent paging scheme based on mobility rate for mobile IP. Wireless Networks, 12, 145–158.
Ramjee, R., Li, L., Porta, T. L., & Kasera, S. (2002). IP paging service for mobile hosts. Wireless Networks, 8(5), 332–344.
Pack, S., Kim, K., & Choi, Y. (2006). A cost-effective approach to selective IP paging scheme using explicit multicast. Computer Networks, 50(15), 2577–2594.
Do, H. T., & Onozato, Y. (2007). A comparison of different paging mechanisms for mobile IP. Wireless Networks, 13:(3), 379–395.
Lee, J., Chung, J., Pack, S., & Gundavelli, S. (2008). Shall we apply paging technologies to proxy mobile IPv6?. In The 3rd international workshop on MobiArch.
Bettstetter, C. (2001). Mobility modeling in wireless networks: Categorization, smooth movement, and border effects. SIGMOBILE Mobility Computer and Communication Review, 5,(3), 55-66.
Makaya, C., & Pierre, S. (2008). An analytical framework for performance evaluation of IPv6-Based mobility management protocols. IEEE Transaction on Wireless Communication 7(3).
Guan, J., Zhou, H., Yan, Z., Qin, Y., & Zhang, H. (2011). Implementation and analysis of proxy MIPv6. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 11(4), 477–490.
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2011-0004733).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, K., Lee, S. Dynamic multi-step paging scheme in PMIPv6-based wireless networks. Wireless Netw 18, 33–44 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-011-0385-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-011-0385-0