Abstract
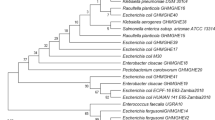
Propolis presents many biological properties, including antibacterial activities, and has been proposed as an additive in ruminant nutrition. Twenty bacterial strains, previously isolated from enrichments of Brazilian cow rumen contents in the presence of different propolis extracts (LLOS), were characterized using phenotyping and 16S rRNA identification. Seven strains were assigned to Streptococcus sp., most likely S. bovis, and were all degrading starch. One amylolytic lactate-utilizing strain of Selenomonas ruminantium was also found. Two strains of Clostridium bifermentans were identified and showed proteolytic activity. Two strains were assigned to Mitsuokella jalaludinii and were saccharolytic. One strain belonged to a Bacillus species and seven strains were affiliated with Escherichia coli. All of the 20 strains were able to use many sugars, but none of them were able to degrade the polysaccharides carboxymethylcellulose and xylans. The effect of three propolis extracts (LLOS B1, C1 and C3) was tested on the in vitro growth of four representative isolates of S. bovis, E. coli, M. jalaludinii and C. bifermentans. The growth of S. bovis, E. coli and M. jalaludinii was not affected by the three propolis extracts at 1 mg ml−1. C. bifermentans growth was completely inhibited at this LLOS concentration, but this bacterium was partially resistant at lower concentrations. LLOS C3, with the lower concentration of phenolic compounds, was a little less inhibitory than B1 and C1 on this strain.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar SC, Zeoula LM, Moura LPP, Prado IN, Paula EM, Samensari RB (2012) Performance, digestibility, microbial production and carcass characteristics of feedlot young bulls fed diets containing propolis. Acta Sci Anim Sci 34:393–400
Aguiar SC, Zeoula LM, Franco SL, Peres LP, Arcuri PB, Forano E (2013) Antimicrobial activity of Brazilian propolis extracts against rumen bacteria in vitro. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:1951–1959
Balcells J, Aris A, Serrano A, Seradj AR, Crespo J, Devant M (2012) Effects of an extract of plant flavonoids (Bioflavex) on rumen fermentation and performance in heifers fed high-concentrate diets. J Anim Sci 90:4975–4984
Bankova V, Marcucci MC, Castro SL (2000) Propolis: recent advances in chemistry and plant origin. Apidologie 31:3–15
Bonvehí JS, Gutiérrez AL (2012) The antimicrobial effects of propolis collected in different regions in the Basque Country (Northern Spain). World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:1351–1358
Broudiscou LP, Papon Y, Broudiscou AF (2000) Effects of dry plant extracts on fermentation and methanogenesis in continuous culture of rumen microbes. Anim Feed Sci Technol 87:263–277
Broussolle V, Forano E, Gaudet G, Ribot Y (1994) Gene sequence and analysis of protein domains of EGB, a novel family E endoglucanase from Fibrobacter succinogenes S85. FEMS Microbiol Lett 124:439–447
Chassard C, Scott KP, Marquet P, Martin JC, Del’homme C, Dapoigny M, Flint HJ, Bernalier-Donadille A (2008) Assessment of metabolic diversity within the intestinal microbiota from healthy humans using combined molecular and cultural approaches. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66:496–504
Chaucheyras-Durand F, Masséglia S, Fonty G (2005) Effect of the microbial feed additive Saccharomyces cerevisiae CNCM I-1077 on protein and peptide degrading activities of rumen bacteria grown in vitro. Curr Microbiol 50:96–101
Cole JR, Wang Q, Fish JA, Chai B, McGarrell DM, Sun Y, Brown CT, Porras-Alfaro A, Kuske CR, Tiedje JM (2014) Ribosomal database project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucl Acids Res 41(Database issue):D633–D642
Costa JBG Jr, Zeoula LM, Franco SL, de Moura LPP, Valero MV, Simioni FL, da Paula EM, Samensari RB (2012) Effect of propolis product on digestibility and ruminal parameters in buffaloes consuming a forage-based diet. Ital J Anim Sci 11:441–448
Cui K, Lu W, Zhu L, Shen X, Huang J (2013) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), an active component of propolis, inhibits Helicobacter pylori peptide deformylase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 435:289–294
Cushnie TP, Lamb AJ (2005) Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Int J Antimicrob Agents 26:343–356
Cushnie TP, Lamb AJ (2011) Recent advances in understanding the antibacterial properties of flavonoids. Int J Antimicrob Agents 38:99–107
Devillard E, Newbold CJ, Scott KP, Forano E, Wallace RJ, Jouany JP, Flint HJ (1999) A xylanase produced by the rumen anaerobic protozoan Polyplastron multivesiculatum shows close sequence similarity to family 11 xylanases from Gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 181:145–152
Ferens WA, Hovde CJ (2011) Escherichia coli O157:H7: Animal reservoir and sources of human infection. Foodborne Pathog Dis 8:465–487
Flythe M, Kagan I (2010) Antimicrobial effect of red clover (Trifolium pratense) phenolic extract on the ruminal hyper ammonia-producing bacterium, Clostridium sticklandii. Curr Microbiol 61:125–131
Franco SL, Bueno JHF (1999) Otimização de processo extrativo de própolis. Infarma 11:48–51
Hernandez JD, Scott PT, Shephard RW, Al Jassim RAM (2008) The characterization of lactic acid producing bacteria from the rumen of dairy cattle grazing on improved pasture supplemented with wheat and barley grain. J Appl Microbiol 104:1754–1763
Jami E, Israel A, Kotser A, Mizrahi I (2013) Exploring the bovine rumen bacterial community from birth to adulthood. ISME J 7:1069–1079
Jurd L, Stevens KL, King AD Jr, Mihara K (1971) Antimicrobial properties of natural phenols and related compounds. II. Cinnamylated phenols and their hydrogenation products. J Pharm Sci 60:1753–1755
Kasana RC, Salwan R, Dhar H, Dutt S, Gulati A (2008) A rapid and easy method for the detection of microbial cellulases on agar plates using gram’s iodine. Curr Microbiol 57:503–507
Lan GQ, Ho YW, Abdullah N (2002) Mitsuokella jalaludinii sp nov., from the rumens of cattle in Malaysia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:713–718
Leedle JA, Hespell RB (1980) Differential carbohydrate media and anaerobic replica plating techniques in delineating carbohydrate-utilizing subgroups in rumen bacterial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 39:709–719
Mamuad LL, Kim SH, Lee SS, Cho KK, Jeon CO, Lee S-S (2012) Characterization, metabolites and gas formation of fumarate reducing bacteria isolated from Korean native goat (Capra hircus coreanae). J Microbiol 50:925–931
Netíková L, Bogusch P, Heneberg P (2013) Czech ethanol-free propolis extract displays inhibitory activity against a broad spectrum of bacterial and fungal pathogens. J Food Sci 78:M1421–M1429
Odenyo AA, Osuji PO (1998) Tannin-tolerant ruminal bacteria from east African ruminants. Can J Microbiol 44:905–909
Oeztuerk H, Emre B, Sagmanligil V, Piskin I, Fidanci UR, Pekcan M (2010) Effects of nisin and propolis on ruminal fermentation in vitro. J Anim Vet Adv 9:2752–2758
Oliveira MG, Feitosa Brito JR, Carvalho RR, Guth BEC, Gomes TAT, Vieira MAM, Kato MAMF, Ramos II, Vaz TMI, Irino K (2007) Water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) identified as an important reservoir of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in Brazil. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5945–5948
Parkar SG, Trower TM, Stevenson DE (2013) Fecal microbial metabolism of polyphenols and its effects on human gut microbiota. Anaerobe 23:12–19
Prado OPP, Zeoula LM, Moura LPP, Franco SL, Prado IN, Gomes HCC (2010a) Digestibilidade e parâmetros ruminais de dietas à base de forragem com adição de própolis e monensina sódica para bovinos. Rev Bras Zootec 39:1336–1345
Prado OPP, Zeoula LM, Moura LPP, Franco SL, Prado IN, Jacobi G (2010b) Efeito da adição de própolis e monensina sódica na digestibilidade e características ruminais em bubalinos alimentados com dieta à base de forragem. Rev Bras Zootec 39:2055–2065
Prado OPP, Zeoula LM, Moura LPP, Franco SL, Paiva SB, Arcuri PB (2010c) Isolation and expeditious morphological, biochemical and kinetic characterization of propolis-tolerant ruminal bacteria. Rev Bras Zootec 39:2048–2054
Ríspoli TB, Rodrigues IL, Martins Neto RG, Kazama R, Prado OPP, Zeoula LM, Arcuri PB (2009) Protozoários ciliados do rúmen de bovinos e bubalinos alimentados com dietas suplementadas com monensina ou própolis. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 44:92–97
Russell JB, Bottje WG, Cotta MA (1981) Degradation of protein by mixed cultures of rumen bacteria: identification of Streptococcus bovis as an actively proteolytic rumen bacterium. J Anim Sci 53:242–252
Sankar M, Delgado O, Mattiasson B (2003) Isolation and characterization of solventogenic, cellulase-free xylanolytic Clostridia from cow rumen. Water Sci Technol 48:185–188
Santana HF, Teixeira Barbosa AA, Ferreira SO, Mantovani HC (2012) Bactericidal activity of ethanolic extracts of propolis against Staphylococcus aureus isolated from mastitic cows. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:485–491
Scazzocchio F, D’Auria FD, Alessandrini D, Pantanella F (2006) Multifactorial aspects of antimicrobial activity of propolis. Microbiol Res 161:327–333
Schlegel L, Grimont F, Ageron E, Grimont PAD, Bouvet A (2003) Reappraisal of the taxonomy of the Streptococcus bovis Streptococcus equinus complex and related species: description of Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp gallolyticus subsp nov., S-gallolyticus subsp macedonicus subsp nov and S-gallolyticus subsp pasteurianus subsp nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:631–645
Sforcin JM, Fernandes A, Lopes CAM, Bankova V, Funari SRC (2000) Seasonal effect on Brazilian propolis antibacterial activity. J Ethnopharmacol 73:243–249
Souza RL, Nishimura LS, Guth BEC (2007) Uncommon Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli serotype O165:HNM as cause of hemolytic uremic syndrome in São Paulo, Brazil. Diag Microbiol Infec Dis 59:223–225
Stepanovic S, Antic N, Dakic I, Svabic-Vlahovic M (2003) In vitro antimicrobial activity of propolis and synergism between propolis and antimicrobial drugs. Microbiol Res 158:353–357
Stradiotti Júnior D, Queiroz AC, Lana RP, Pacheco CG, Eifert EC, Nunes PMM (2004) Ação da própolis sobre a desaminação de aminoácidos e a fermentação ruminal. R Bras Zootec 33:1086–1092
Sundset MA, Praesteng KE, Cann IKO, Mathiesen SD, Mackie RI (2007) Novel rumen bacterial diversity in two geographically separated sub-species of reindeer. Microb Ecol 54:424–438
Taghavi-Nezhad M, Alipour D, Flythe MD, Zamani P, Khodakaramian G (2013) The effect of essential oils of Zataria multiflora and Mentha spicata on the in vitro rumen fermentation, and growth and deaminative activity of amino acid-fermenting bacteria isolated from Mehraban sheep. Animal Prod Sci. http://dx.doi.org/10.1071/AN12244
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Wallace RJ (2004) Antimicrobial properties of plant secondary metabolites. Proc Nutr Soc 63:621–629
Wallace RJ, Onodera R, Cotta MA (1997) Metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds. In: Hobson PN, Stewart CS (eds) The rumen microbial ecosystem, 2nd edn. Chapman Hall, London, pp 283–328
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naïve bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 73(16):5261–5267. doi:10.1128/AEM.00062-07
Acknowledgments
The authors thank G. Andant and G. Lopes for excellent technical assistance and the Brazilian agencies Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária (Embrapa) for granting the scholarship to S.C. Aguiar (CNPq/Labex Embrapa 201720/2010-8).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Aguiar, S.C., Zeoula, L.M., do Prado, O.P.P. et al. Characterization of rumen bacterial strains isolated from enrichments of rumen content in the presence of propolis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30, 2917–2926 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1719-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1719-8