Abstract
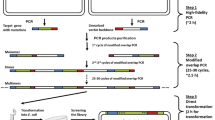
Saturation mutagenesis is a powerful tool in protein engineering. Even though QuikChange site-directed mutagenesis method is dominantly used in laboratories, it could not be successfully applied to the generation of a focused mutant library of human glutathione transferase A2-2. In the present study, we further developed an improved versatile dual-tube approach of randomizing difficult-to-amplify targets, exhibiting significant improvement towards equal distribution of nucleotides at randomized sites compared to other published methods.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- QCM:
-
QuikChange site-directed mutagenesis method
- GST:
-
Glutathione transferase
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
References
Hogrefe HH, Cline J, Youngblood GL, Allen RM (2002) Creating randomized amino acid libraries with the QuikChange Multi Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit. Biotechniques 33(5):1158–1160, 1162, 1164–1155
Inoue H, Nojima H, Okayama H (1990) High efficiency transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. Gene 96(1):23–28
Kirsch RD, Joly E (1998) An improved PCR-mutagenesis strategy for two-site mutagenesis or sequence swapping between related genes. Nucleic Acids Res 26(7):1848–1850
Kurtovic S, Moden O, Shokeer A, Mannervik B (2008) Structural determinants of glutathione transferases with azathioprine activity identified by DNA shuffling of alpha class members. J Mol Biol 375(5):1365–1379
Sanchis J, Fernandez L, Carballeira JD, Drone J, Gumulya Y, Hobenreich H, Kahakeaw D, Kille S, Lohmer R, Peyralans JJ, Podtetenieff J, Prasad S, Soni P, Taglieber A, Wu S, Zilly FE, Reetz MT (2008) Improved PCR method for the creation of saturation mutagenesis libraries in directed evolution: application to difficult-to-amplify templates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81(2):387–397
Tseng WC, Lin JW, Wei TY, Fang TY (2008) A novel megaprimed and ligase-free, PCR-based, site-directed mutagenesis method. Anal Biochem 375(2):376–378
Tseng WC, Lin JW, Hung XG, Fang TY (2010) Simultaneous mutations up to six distal sites using a phosphorylation-free and ligase-free polymerase chain reaction-based mutagenesis. Anal Biochem 401(2):315–317
Zhang W, Moden O, Tars K, Mannervik B (2012) Structure-based redesign of GST A2-2 for enhanced catalytic efficiency with azathioprine. Chem Biol 19(3):414–421
Zheng L, Baumann U, Reymond JL (2004) An efficient one-step site-directed and site-saturation mutagenesis protocol. Nucleic Acids Res 32(14):e115
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council and the Swedish Cancer Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Mannervik, B. An improved dual-tube megaprimer approach for multi-site saturation mutagenesis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29, 667–672 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1222-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1222-z