Abstract
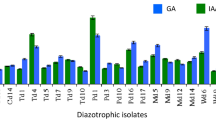
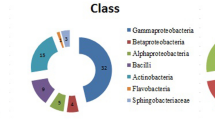
In this study, a total of 80 rhizobacteria was isolated from coastal agricultural ecosystem of cultivated vegetable rhizosphere soils. The isolates were screened for antagonistic activity against Sclerotium rolfsii and Colletotrichum capsici and plant growth promoting traits. The results revealed that 15.0 and 43.7% isolates showed statistically significant inhibition of mycelial growth of S. rolfsii and C. capsici respectively, while 48.7% isolates produced siderophore, 57.5% isolates solubilized phosphate and 21.1% isolates produced indole-3-acetic acid more than 20 μg/mL. However, only three isolates PfS1, PfR2 and BL5 were found positive to all properties tested. The identification of potential bacterial isolates through Microbial Identification System (BIOLOG) and 16S rDNA sequencing of the isolates revealed Bacillus species were dominant in the cultivated vegetable rhizosphere soil of Neil and Havelock Islands, India.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S (1995) Agriculture-fertilization interface in Asia issue of growth and sustainability. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co, New Delhi
Chen WP, Kuo TT (1993) A simple and rapid method for the preparation of gram negative bacterial genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 21:2260
Ding Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Chen S (2005) Isolation and identification of nitrogen fixing bacilli from plant rhizospheres in Beijing region. J Appl Microbiol 99:1271–1281
Edwards U, Rogall T, Blocker H, Emde M, Bottger EC (1989) Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 17:7843–7853
Garbeva P, van Veen JA, van Elsas JD (2003) Predominant Bacillus spp. in agricultural soil under different management regimes detected via PCR-DGGE. Microb Ecol 45:302–316
Glick BR (1995) The Enhancement of plant growth by free living bacteria. Can J Microbiol 41:109–117
Glick BR, Bashan Y (1997) Genetic manipulation of plant growth-promoting bacteria to enhance biocontrol of phytopathogens. Biotechnol Adv 15:353–378
Glick BR, Penrose DM, Li J (1998) A model for the lowering of plant ethylene concentrations by plant growth–promoting bacteria. J Theor Biol 190:63–68
Gordon SA, Paleg LG (1957) Quantitative measurement of indole acetic acid. Physiol Plant Pathol 10:347–348
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein 242 metabolism. Academic Press, New York, pp 21–132
King EO, Ward MK, Raney DE (1954) Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med 44:301–307
Kloepper JW (1993) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria as biocontrol agents. In: Metting FB Jr (ed) Soil microbial ecology-applications in agricultural and environmental management. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 255–274
Laguerre G, Allard MR, Revoy F, Amarger N (1994) Rapid identification of rhizobia by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of PCR amplifies 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:56–63
Nishijima T, Toyota K, Mochizuki M (2005) Predominant culturable Bacillus species in Japanese arable soils and their potential as biocontrol agents. Microb Environ 20:61–68
Patten CL, Glick BR (1996) Bacterial biosynthesis of Indole-3-Acetic Acid. Can J Microbiol 42:207–220
Principe A, Alvarez FA, Castro MG, Zachi L, Fischer SE, Mori GB, Jofre E (2007) Biocontrol and PGPR features in native strain isolated from saline soils of Argentina. Curr Microbiol 55:314–322
Rosch C, Mergel A, Bothe H (2002) Biodiversity of denitrifying and dinitrogen-fixing bacteria in an acid forest soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3818–3829
Ross IL, Alami Y, Harvey PR, Achouak W, Ryder MH (2000) Genetic diversity and biological control activity of novel species closely related Pseudomonads isolated from wheat field soils in South Australia. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1609–1616
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Ann Biochem 160:47–56
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4888
Verma SC, Ladha JK, Tripathi AK (2001) Evaluation of plant growth promoting and colonization ability of endophytic diazotrophs from deep water rice. J Biotechnol 91:127–141
Wang YY, Brown HN, Crowley DE, Szaniszlo PJ (1993) Evidence for direct utilization of siderophore, ferioxamine b, in axenically grown cucumber. Plant Cell Environ 16:579–585
Xie GH, Cai MY, Guang CT, Steinberger Y (2003) Cultivable heterotrophic N2-fixing bacterial diversity in rice fields in the Yangtze River Plain. Biol Fertil Soils 37:29–38
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the project “Application of Microorganisms in Agriculture and Allied Sectors” of the NBAIM-ICAR, UP, Mau, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, K., Amaresan, N., Bhagat, S. et al. Isolation and characterization of rhizobacteria associated with coastal agricultural ecosystem of rhizosphere soils of cultivated vegetable crops. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27, 1625–1632 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0616-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-010-0616-z