Abstract
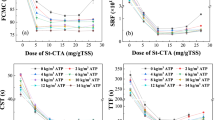
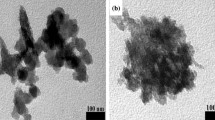
The supernatant fluid and sludge produced by traditional polyacrylamide flocculant (PAM) flocculation of municipal sewage emit a strong odor, and the dewatering performance of flocculant flocculating sludge based on acrylamide as the main synthetic raw material remains undesirable. In this study, we investigated a new green bioflocculant called SDF. This bioflocculant was made using 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl-modified starch as the raw material, acrylamide as the monomer, cerium nitrate as the initiator, and dextrin and bone gum as fillers. The results of the study indicated that the SDF-flocculated sludge exhibited a larger pore structure, superior dewatering performance, and a lower intensity of malodorous substances in the supernatant compared to PAM. Furthermore, it was found that the component with the strongest odor in the supernatant detected through purge and trap-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry was ethanethiol, and it was observed that the signal intensity released from the SDF supernatant was 30.62% lower on the first day and 7.91% lower cumulatively over the course of 7 days when compared to PAM. As a consequence, the SDF materials offer promising potential for treating odorous gas and reducing sludge in sewage treatment plants due to their easy fabrication, low cost, and superior dewatering performance.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available upon reasonable request.
References
Almonaityte, K., Bendoraitiene, J., Babelyte, M., Rosliuk, D., & Rutkaite, R. (2020). Structure and properties of cationic starches synthesized by using 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 164, 2010–2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.089
Amuda, O. S., Amoo, I. A., & Ajayi, O. O. (2006). Performance optimization of coagulant/flocculant in the treatment of wastewater from a beverage industry. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 129(1–3), 69–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.07.078
Barbusinski, K., Kalemba, K., Kasperczyk, D., Urbaniec, K., & Kozik, V. (2017). Biological methods for odor treatment – a review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 152, 223–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.093
Bharti, S., Mishra, S., & Sen, G. (2013). Ceric ion initiated synthesis of polyacrylamide grafted oatmeal: Its application as flocculant for wastewater treatment. Carbohydrate Polymers, 93(2), 528–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.11.072
Carpinteyro-Urban, S., & Torres, L. G. (2013). Use of response surface methodology in the optimization of coagulation-flocculation of wastewaters employing biopolymers. International Journal of Environmental Research, 7(3), 817–826. https://doi.org/10.22059/IJER.2013.651
Chang, Q., Hao, X., & Duan, L. (2008). Synthesis of crosslinked starch-graft-polyacrylamide-co-sodium xanthate and its performances in wastewater treatment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 159(2–3), 548–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.02.053
Chen, Z., Zhang, W., Wang, D., Ma, T., & Bai, R. (2015). Enhancement of activated sludge dewatering performance by combined composite enzymatic lysis and chemical re-flocculation with inorganic coagulants: Kinetics of enzymatic reaction and re-flocculation morphology. Water Research, 83, 367–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.06.026
Chen, Y., Tian, G., Zhai, B., Zhang, H., Liang, Y., & Liang, H. (2019). Cationic starch-grafted-cationic polyacrylamide based graphene oxide ternarycomposite flocculant for the enhanced flocculation of oil sludge suspension. Composites Part B: Engineering, 177, 107416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107416
Choi, Y.-Y., Baek, S.-R., Kim, J.-I., Choi, J.-W., Hur, J., Lee, T.-U., Park, C.-J., & Lee, B. J. (2017). Characteristics and biodegradability of wastewater organic matter in municipal wastewater treatment plants collecting domestic wastewater and industrial discharge. Water, 9(6), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9060409
Dkhissi, O., El Hakmaoui, A., Souabi, S., Chatoui, M., Jada, A., & Akssira, M. (2018). Treatment of vegetable oil refinery wastewater by coagulation-flocculation process using the cactus as a bio-flocculant. Journal of Materials and Environmental Sciences, 9(1), 18–25. https://doi.org/10.26872/jmes.2018.9.1.3
Fan, F., Xu, R., Wang, D., & Meng, F. (2020). Application of activated sludge for odor control in wastewater treatment plants: approaches, advances and outlooks. Water Research, 181, 115915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115915
Fowles, J., Boatman, R., Bootman, J., Lewis, C., Morgott, D., Rushton, E., van Rooij, J., & Banton, M. (2013). A review of the toxicological and environmental hazards and risks of tetrahydrofuran. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 43(10), 811–828. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408444.2013.836155
Gebicki, J., Byliński, H., & Namieśnik, J. (2016). Measurement techniques for assessing the olfactory impact of municipal sewage treatment plants. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5024-2
Gong, X., Yang, X., Zheng, H., & Wu, Z. (2017). Elimination of ethanethiol released from municipal wastes by absorption sequencing electrochemical oxidation. Environmental Technology, 38(13–14), 1708–1715. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1317836
Hu, P., Ren, J., Hu, X., & Yang, H. (2021). Comparison of two starch-based flocculants with polyacrylamide for the simultaneous removal of phosphorus and turbidity from simulated and actual wastewater samples in combination with FeCl3. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 167, 223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.176
Hu, P., Shen, S., Zhao, D., Wei, H., Ge, J., Jia, F., Zhang, X., & Yang, H. (2021). The influence of hydrophobicity on sludge dewatering associated with cationic starch-based flocculants. Journal of Environmental Management, 296, 113218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113218
Hyrycz, M., Ochowiak, M., Krupinska, A., Wlodarczak, S., & Matuszak, M. (2022). A review of flocculants as an efficient method for increasing theefficiency of municipal sludge dewatering: mechanisms, performances, influencing factors and perspectives. Science of The Total Environment, 820, 153328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153328
Jiang, G., Melder, D., Keller, J., & Yuan, Z. (2017). Odor emissions from domestic wastewater: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 47(17), 1581–1611. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2017.1386952
Kajitvichyanukul, P., & Suntronvipart, N. (2006). Evaluation of biodegradability and oxidation degree of hospital wastewater using photo-Fenton process as the pretreatment method. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 138(2), 384–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.064
Lee, J., Lee, S., Yu, S., & Rhew, D. (2016). Relationships between water quality parameters in rivers and lakes: BOD5, COD, NBOPs, and TOC. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5251-1
Lewkowska, P., Cieślik, B., Dymerski, T., Konieczka, P., & Namieśnik, J. (2016). Characteristics of odors emitted from municipal wastewater treatment plant and methods for their identification and deodorization techniques. Environmental Research, 151, 573–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.08.030
Li, H., Cai, T., Yuan, B., Li, R., Yang, H., & Li, A. (2014). Flocculation of both kaolin and hematite suspensions using the starch-based flocculants and their floc properties. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 54(1), 59–67. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie503606y
Li, Y., Xu, Q., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Wang, D., Yang, G., Yuan, X., Yang, F., Huang, J., & Wu, Z. (2020). Peroxide/zero-valent iron (Fe0) pretreatment for promoting dewaterability of anaerobically digested sludge: a mechanistic study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 400, 123112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123112
Li, L., Peng, C., Deng, L., Zhang, F., Wu, D., Ma, F., & Liu, Y. (2022). Understanding the synergistic mechanism of PAM-FeCl3 for improved sludge dewaterability. Journal of Environmental Management, 301, 113926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113926
Liang, S., Zhang, T., Fu, X., Zhu, C., & Mou, H. (2020). Partially degradedchitosan-based flocculation to achieve effective deodorization of oyster (Crassostrea gigas) hydrolysates. Carbohydrate Polymers, 234, 115948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115948
Liu, J., Wei, Y., Li, K., Tong, J., Wang, Y., & Jia, R. (2016). Microwave-acid pretreatment: a potential process for enhancing sludge dewaterability. Water Research, 90, 225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.12.012
Maćczak, P., Kaczmarek, H., & Ziegler-Borowska, M. (2020). Recent achievements in polymer bio-based flocculants for water treatment. Materials, 13(18), 3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13183951
Macczak, P., Kaczmarek, H, & Ziegler-Borowska, M. (2020). Recent achievements in polymer bio-based flocculants for water treatment. Materials (Basel) 13(18). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13183951
Mao, S., Xu, X., Zhang, L., Bai, B., Hu, N., & Wang, H. (2021). Methylated mud snail protein as a bio-flocculant for high turbidity wastewater treatment. Water Science and Technology, 84(3), 737–751. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.262
Mao, Y., Millett, R., Lee, C. S., Yakubov, G., Harding, S. E., & Binner, E. (2020). Investigating the influence of pectin content and structure on its functionality in bio-flocculant extracted from okra. Carbohydrate Polymers, 241, 116414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116414
Masekameni, M.D., Moolla, R., Gulumian, M., & Brouwer, D. (2019). Risk assessment of benzene, toluene, ethyl benzene, and xylene concentrationsfrom the combustion of coal in a controlled laboratory environment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16010095
Mishra, S., Mukul, A., Sen, G., & Jha, U. (2011). Microwave assisted synthesis of polyacrylamide grafted starch (St-g-PAM) and its applicability as flocculant for water treatment. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 48(1), 106–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.10.004
Mohammadzadeh, H., Mohammadi, H., Tavakoli, M. A., & Sadeghi, S. (2021). Sudden death due to acetone toxicity. Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Research, 7(3), 217–220. https://doi.org/10.18502/pbr.v7i3.7703
Mohd Nasir, N., Mohd Yunos, F.H., Wan Jusoh, H.H., Mohammad, A., Lam, S.S. and Jusoh, A. (2019). Subtopic: advances in water and wastewatertreatment harvesting of Chlorella sp. microalgae using Aspergillus niger as bio-flocculant for aquaculture wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Management 249, 109373. http://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109373
Nasrollahzadeh, M., Sajjadi, M., Iravani, S., & Varma, R. S. (2021). Starch, cellulose, pectin, gum, alginate, chitin and chitosan derived (nano)materials for sustainable water treatment: a review. Carbohydrate Polymers, 251, 116986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116986
Peng, H., Zhong, S., Xiang, J., Lin, Q., Yao, C., Dong, J., Yin, G., Yao, K., Zeng, S., & Zhong, J. (2017). Characterization and secondary sludge dewatering performance of a novel combined aluminum-ferrous-starch flocculant (CAFS). Chemical Engineering Science, 173, 335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2017.08.005
Ren, B., Zhao, Y., Lyczko, N., & Nzihou, A. (2019). Current status and outlook of odor removal technologies in wastewater treatment plant. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 10(6), 1443–1458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0384-9
Ren, B., Lyczko, N., Zhao, Y., & Nzihou, A. (2021). Simultaneous hydrogensulfide removal and wastewater purification in a novel alum sludge-based odor-gas aerated biofilter. Chemical Engineering Journal, 419, 129558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129558
Sha, L., Wu, Z., Ling, Z., Liu, X., Yu, X., & Zhang, S. (2022). Investigation on the improvement of activated sludge dewaterability using different iron forms (ZVI vs. Fe (II))/peroxydisulfate combined vertical electro-dewatering processes. Chemosphere, 292, 133416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133416
Srivastava, A., Mishra, D. K., & Behari, K. (2010). Graft copolymerization of N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone onto chitosan: Synthesis, characterization and studyof physicochemical properties. Carbohydrate Polymers, 80(3), 790–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.12.031
Suopajärvi, T., Liimatainen, H., Hormi, O., & Niinimäki, J. (2013). Coagulation–flocculation treatment of municipal wastewater based on anionized nanocelluloses. Chemical Engineering Journal, 231, 59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.07.010
Suopajärvi, T., Koivuranta, E., Liimatainen, H., & Niinimäki, J. (2014). Flocculation of municipal wastewaters with anionic nanocelluloses: Influence of nanocellulose characteristics on floc morphology and strength. Journalof Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2(4), 2005–2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.08.023
Teh, C. Y., & Wu, T. Y. (2014). The potential use of natural coagulants and flocculants in the treatment of urban waters. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 39, 1603–1608. https://doi.org/10.3303/cet1439268
Wan, S., Li, G., An, T., Guo, B., Sun, L., Zu, L., & Ren, A. (2010). Biodegradation of ethanethiol in aqueous medium by a new Lysinibacillus sphaericus strain RG-1 isolated from activated sludge. Biodegradation, 21(6), 1057–1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9366-8
Wang, Q., Wei, W., Gong, Y., Yu, Q., Li, Q., Sun, J., & Yuan, Z. (2017). Technologies for reducing sludge production in wastewater treatment plants: State of the art. Science of the Total Environment, 587, 510–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.203
Xun, J., Lou, T., Xing, J., Zhang, W., Xu, Q., Peng, J., & Wang, X. (2019). Synthesis of a starch–acrylic acid–chitosan copolymer as flocculant for dye removal. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 136(20), 47437. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47437
Zhang, D., Wang, Y., Gao, H., Fan, X., Guo, Y., Wang, H., & Zheng, H. (2019). Variations in macro and micro physicochemical properties of activated sludge under a moderate oxidation-in situ coagulation conditioning: Relationship between molecular structure and dewaterability. Water Research, 155, 245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.02.047
Zhang, H., Qi, H.-Y., Zhang, Y.-L., Ran, D.-D., Wu, L.-Q., Wang, H.-F., & Zeng, R. J. (2022). Effects of sewage sludge pretreatment methods on its use in agricultural applications. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 428, 128213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128213
Funding
The authors are grateful for the financial support for this work provided by the Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation (ZR2016DL01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jianbo Liu: conceptualization, funding acquisition, resources, supervision, and writing—review and editing. Gongcheng Lv: methodology, software, investigation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft. Shouhao Jia: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, software, and writing—review and editing. Xiaocong Liu: date curation and investigation. Junpeng Liu: software and investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Lv, G., Liu, X. et al. Preparation of a Novel Cationic Starch Bioflocculant and Its Application Performance in Municipal Sewage Odor Mitigation and Sludge Dewatering. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 630 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06631-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06631-y