Abstract
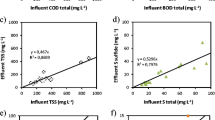
Water pollution caused by improper treatment of acid mine drainage (AMD) is one of the most common problems encountered in the mining process. However, the traditional physical and chemical methods are expensive, and the additional products are difficult to treat. Therefore, seeking a simple and efficient treatment method has become the main challenge in solving AMD. In this study, the efficiency of sulfate removal using sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) based on the upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor and the changes in the sludge microbial community structure before and after the reaction were studied. The properties of SRB, particularly their reducing effect, were studied. Results show that SRB had good reduction performance in the environment with pH 6.5 to 7.5. The best-reducing effect was achieved at 15% inoculum. Under different initial sulfate concentrations, the sulfate removal rate in the UASB reactor reached 80–90%. After the reaction, the species’ community abundance was increased, and the species diversity was enhanced. These investigations are conducive to providing new ideas and methods for treating AMD and solving the high sulfate concentrations in AMD.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Chai, G., Wang, D., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Li, J., Jing, X., & Lin, Y. (2023). Effects of organic substrates on sulfate-reducing microcosms treating acid mine drainage: Performance dynamics and microbial community comparison. Journal of Environmental Management, 330, 117148.
Chazan, A., Rozenberg, A., Mannen, K., Nagata, T., Tahan, R., Yaish, S., & Pushkarev, A. (2022). Diverse heliorhodopsins detected via functional metagenomics in freshwater Actinobacteria, Chloroflexi and Archaea. Environmental Microbiology, 24(1), 110–121.
Christensen, D. R., Gerick, J., & Eblen, J. (1984). Design and operation of an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation, 56, 1059–1062.
Colin, Y., Goñi-Urriza, M., Caumette, P., & Guyoneaud, R. (2015). Reprint of: Contribution of enrichments and resampling for sulfate reducing bacteria diversity assessment by high-throughput cultivation. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 138, 100–105.
Demir, E. K., Yaman, B. N., Çelik, P. A., & Sahinkaya, E. (2020). Iron oxidation in a ceramic membrane bioreactor using acidophilic bacteria isolated from an acid mine drainage. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 38, 101610.
Dev, S., Roy, S., & Bhattacharya, J. (2017). Optimization of the operation of packed bed bioreactor to improve the sulfate and metal removal from acid mine drainage. Journal of Environmental Management, 200, 135–144.
Fan, X. Y., Gao, J. F., Pan, K. L., Li, D. C., Dai, H. H., & Li, X. (2018). Functional genera, potential pathogens and predicted antibiotic resistance genes in 16 full-scale wastewater treatment plants treating different types of wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 268, 97–106.
Fatahi Nafchi, R., Yaghoobi, P., Reaisi Vanani, H., Ostad-Ali-Askari, K., Nouri, J., & Maghsoudlou, B. (2021). Eco-hydrologic stability zonation of dams and power plants using the combined models of SMCE and CEQUALW2. Applied Water Science, 11(7), 109.
Firsching, F. H. (1959). Precipitation of barium chromate from homogeneous solution using complexation and replacement: A separation of barium from relatively large amounts of strontium and lead. Talanta, 2(4), 326–331.
Ighalo, J. O., Kurniawan, S. B., Iwuozor, K. O., Aniagor, C. O., Ajala, O. J., Oba, S. N., & Igwegbe, C. A. (2022). A review of treatment technologies for the mitigation of the toxic environmental effects of acid mine drainage (AMD). Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 157, 37–58.
Isazadeh, S., Jauffur, S., & Frigon, D. (2016). Bacterial community assembly in activated sludge: mapping beta diversity across environmental variables. Microbiology Open, 5(6), 1050–1060.
Ji, M., Li, B., Majdi, A., Alkhalifah, T., Alturise, F., & Ali, H. E. (2023). Application of nano remediation of mine polluted in acid mine drainage water using machine learning model. Chemosphere, 311, 136926.
Kiiskila, J. D., Sarkar, D., Panja, S., Sahi, S. V., & Datta, R. (2019). Remediation of acid mine drainage-impacted water by vetiver grass (Chrysopogon zizanioides). A multiscale long-term study. Ecological Engineering, 129, 97–108.
Kikot, P., Viera, M., Mignone, C., & Donati, E. (2010). Study of the effect of pH and dissolved heavy metals on the growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria by a fractional factorial design. Hydrometallurgy, 104(3-4), 494–500.
Li, J., & Tabassum, S. (2022). Synergism of hydrolytic acidification and sulfate reducing bacteria for acid production and desulfurization in the anaerobic baffled reactor: High sulfate sewage wastewater treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 444, 136611.
Liu, H., Li, F., & Song, Y. (2004). Determination of sulfate content in water by barium sulfate photometric method. Journal of Pingdingshan Engineering College, 13(4), 46–47.
Liu, Y. H., Wand, H., & Hu, X. K. (2016). Recent advances in the biodegradation of hydrocarbons by acinetobacter species [J]. Microbiology China, 43(007), 1579–1589.
Ma, C., Yuan, L., Niu, Z., Zhao, J., & Huang, C. (2021a). Analysis of activated sludge microbial community structure and response relationship with environmental factors. Environmental Science, 42(8), 3890–3892.
Ma, Q. Q., Yuan, L. J., Niu, Z. D., Zhao, J., & Huang, C. (2021b). Microbial community structure of activated sludge and its response to environmental factors. Huan Jing ke Xue, 42(8), 3886–3893.
Nogueira, E. W., de Godoi, L. A. G., Yabuki, L. N. M., Brucha, G., & Damianovic, M. H. R. Z. (2021). Sulfate and metal removal from acid mine drainage using sugarcane vinasse as electron donor: Performance and microbial community of the down-flow structured-bed bioreactor. Bioresource Technology, 330, 124968.
Ostad-Ali-Askari, K. (2022). Management of risks substances and sustainable development. Applied Water Science, 12(4), 65.
Pei, L., Lu, Q., Hao, C., Du, Z., Lu, Y., & Zhang, F. (2016). Characterization of microbial community structure in summer and autumn in acidic mine wastewater from an iron ore mine in Anhui Province. Journal of Environmental Science, 36(7), 2397–2407.
Qian, T., Chen, X., Tao, Y., & Ou, T. (2014). Comparison of Ion Chromatography and Barium Sulfate Spectrophotometry for Sulfate Determination in Water. Journal of Environmental Hygiene, 4(06), 603–606.
Rambabu, K., Banat, F., Pham, Q. M., Ho, S. H., Ren, N. Q., & Show, P. L. (2020). Biological remediation of acid mine drainage: Review of past trends and current outlook. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, 2, 100024.
She, Z., Pan, X., Yue, Z., Shi, X., Gao, Y., Wang, S., & Wang, J. (2023). Contrasting prokaryotic and eukaryotic community assembly and species coexistence in acid mine drainage-polluted waters. Science of The Total Environment, 856, 158954.
Tang, T., Li, J., Yang, Z., Xiang, F., Wang, Y., & Li, Y. (2020). Research progress on the community structure of functional microorganisms for anaerobic digestion of sludge. Chemical Engineering, 39(1), 323–324.
Tyagi, V. K., & Lo, S. L. (2011). Application of physico-chemical pretreatment methods to enhance the sludge disintegration and subsequent anaerobic digestion: an up to date review. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 10(3), 215–242.
Xue, J., Yao, Y., Li, W., Shi, K., Ma, G., Qiao, Y., & Jiang, Q. (2023). Insights into the effects of operating parameters on sulfate reduction performance and microbial pathways in the anaerobic sequencing batch reactor. Chemosphere, 311, 137134.
Yuan, J., Bai, S., Bi, Y., Li, J., & Wen, S. (2022). Research progress in domestic and foreign mine acid wastewater treatment and comprehensive utilization. Nonferrous Metal Engineering, 12(4), 131–139.
Zampieri, B. D. B., Nogueira, E. W., de Oliveira, A. J. F. C., Sánchez-Andrea, I., & Brucha, G. (2022a). Effects of metals on activity and community of sulfate-reducing bacterial enrichments and the discovery of a new heavy metal-resistant SRB from Santos Port sediment (São Paulo, Brazil). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 922–935.
Zampieri, B. D. B., Nogueira, E. W., de Oliveira, A. J. F. C., Sánchez-Andrea, I., & Brucha, G. (2022b). Effects of metals on activity and community of sulfate-reducing bacterial enrichments and the discovery of a new heavy metal-resistant SRB from Santos Port sediment (São Paulo, Brazil). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 922–935.
Zhang, Y. (2022). IC reactor granular sludge culture domestication experiment. Petrochemical Safety and Environmental Protection Technology, 38(4), 48–50.
Zhang, Z., Zhang, C., Yang, Y., Zhang, Z., Tang, Y., Su, P., & Lin, Z. (2022). A review of sulfate-reducing bacteria: Metabolism, influencing factors and application in wastewater treatment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 376, 134109.
Zhao, Y., Zhu, Y., Guo, M., Xu, P., Qi, X., Wang, Y., & Jia, X. (2022). Sulfur valence variety and microbial community succession of desulphurization MEC [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 16(1), 264–271.
Zhiyi, H. U., Hongfei, L. I. N., Shuai, W. A. N. G., Qingting, W. A. N. G., Kun, D. A. I., Jianxiong, Z. E. N. G., & Fang, Z. H. A. N. G. (2022). Enhanced acidogenesis of waste activated sludge fermentation by an alginate-degrading consortium. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 16(1), 245–252.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from Major Science and Technology Innovation Projects in Shandong Province(2019JZZY020808). The findings achieved herein are solely the responsibility of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, L., Sun, S., Yu, F. et al. Performance of Sludge in the UASB Reactor for Treating Sulfate Wastewater: Sulfate Removal and Changes in the Community Structure Before and After Reaction. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 246 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06267-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06267-y