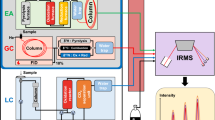
Abstract
Compound-Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA) is employed to investigate the biodegradation of metalaxyl in soil and plant. By studying the degradation of metalaxyl in unsterilized and sterilized soil with two initial concentrations of metalaxyl, microbial degradation has the most significant effect on the degradation of metalaxyl in soil. In addition, biodegradation and isotope fractionation of metalaxyl in water spinach with root application and leaf application are investigation by CSIA. It is shown that both absorption and degradation of metalaxyl in the roots and leaves of water spinach can cause the shift of δ13C values. Specifically, the δ13C values decreased during absorption while increased in degradation of metalaxyl in the roots and leaves of water spinach, indicating that the lighter isotope is absorbed in the absorption process at first and then degraded. Furthermore, the relationship between carbon isotope ratios and residual concentration of metalaxyl can be described by the Rayleigh equation, and the biodegradation rate of metalaxyl could be calculated by using CSIA without measuring the concentration of metalaxyl both in soil and plant. Therefore, the use of CSIA can quantitatively assess the degradation behavior of pesticide pollution in the environment and provide a certain scientific evidence and technical support in the process of environmental remediation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data sets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmed, S. M., Ismail, A. A., & Houusien, A. A. (2010). Dissipation and persistence of fungicides, carbendazim and metalaxyl in Egyptian soil under biotic and abiotic conditions. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 6(8), 1240–1246.
Bontempo, L., van Leeuwen, K. A., Paolini, M., Laursen, K. H., Micheloni, C., Prenzler, P. D., Ryan, D., & Camin, F. (2020). Bulk and compound-specific stable isotope ratio analysis for authenticity testing of organically grown tomatoes. Food Chemistry, 318, 11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126426
Coffey, A. (1986). Characterization of microorganisms involved in accelerated biodegradation of metalaxyl and metolachlor in soils. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 32(7), 562–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1139/m86-105
Constantinou, M., Louca-Christodoulou, D., & Agapiou, A. (2021). Method validation for the determination of 314 pesticide residues using tandem MS systems (GC-MS/MS and LC-MS/MS) in raisins: Focus on risk exposure assessment and respective processing factors in real samples (a pilot survey). Food Chemistry, 360, 129964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129964
Cui, J. L., Chen, C., Qin, Z. H., & Yu, C. N. (2012). Biodegradation of organic pollutants by thermophiles and their applications: A review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23(11), 3218–3226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-011-0280-z
Du, Y. J., Xu, X., Liu, Q. Z., Bai, L., Hang, K. X., & Wang, D. H. (2021). Identification of organic pollutants with potential ecological and health risks in aquatic environments: Progress and challenges. Science of the total environment, 806, 150691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150691
Elsner, M., Zwank, L., Hunkeler, D., & Schwarzenbach, R. P. (2005). A new concept linking observable stable isotope fractionation to transformation pathways of organic pollutants. Environmental science & technology, 39(18), 6896–6916. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0504587
Hayes, J. M., Freeman, K. H., Popp, B. N., & Hoham, C. H. (1990). Compound-specific isotopic analyses: a novel tool for reconstruction of ancient biogeochemical processes. Organic Geochemistry, 16(4-6), 1115–1128.
Herrmann, M., & Sur, R. (2021). Natural attenuation along subsurface flow paths based on modeling and monitoring of a pesticide metabolite from three case studies. Environmental Sciences Europe, 33, 36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-021-00490-2
Hirschorn, S. K., Grostern, A., Lacrampe-Couloume, G., Edwards, E. A., Mackinnon, L., Repta, C., Major, D. W., & Lollar, B. S. (2007). Quantification of biotransformation of chlorinated hydrocarbons in a biostimulation study: Added value via stable carbon isotope analysis. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 94(3-4), 249–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2007.07.001
Kopinke, F. D., Georgi, A., Voskamp, M., Richnow, H., & H. (2005). Carbon isotope fractionation of organic contaminants due to retardation on humic substances: implications for natural attenuation studies in aquifers. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(16), 6052–6062. https://doi.org/10.1021/es040096n
Liu, X., Wu, L. P., Kümmel, S., Merbach, I., Lal, R., & Richnow, H. H. (2020). Compound-specific Isotope Analysis and Enantiomer Fractionation to Characterize the Transformation of Hexachlorocyclohexane Isomers in a Soil-wheat Pot System. Environmental Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b07609
Liu, X., Wu, L., Kummel, S., & Richnow, H. H. (2021). Characterizing the biotransformation of hexachlorocyclohexanes in wheat using compound-specific stable isotope analysis and enantiomer fraction analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 406, 124301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124301
Mahmoud, A. H., Darwish, N. M., Kim, Y. O., Viayaraghavan, P., Kwon, J. T., Na, S. W., Lee, J. C., & Kim, H. J. (2020). Fenvalerate induced toxicity in Zebra fish, Danio rerio and analysis of biochemical changes and insights of digestive enzymes as important markers in risk assessment. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 32(2), 1569–1580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2019.12.013
Mancini, S. A., Lacrampe-Couloume, G., Jonker, H., van Breukelen, B. M., Groen, J., Volkering, F., & Lollar, B. S. (2002). Hydrogen isotopic enrichment: an indicator of biodegradation at a petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated field site. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(11), 2464–2470. https://doi.org/10.1021/es011253a
Masbou, J., Meite, F., Guyot, B., & Imfeld, G. (2018). Enantiomer-specific stable carbon isotope analysis (ESIA) to evaluate degradation of the chiral fungicide Metalaxyl in soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 353, 99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.03.047
Mehta, N., Saharan, G. S., & Kathpal, T. S. (1997). Absorption and degradation of metalaxyl in mustard plant (Brassica juncea). Ecotoxicol Environ Safety, 37(2), 119–124. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.1997.1533
Morasch, B., Richnow, H. H., Schink, B., Vieth, A., & Meckenstock, R. U. (2002). Carbon and hydrogen stable isotope fractionation during aerobic bacterial degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 68(10), 5191–5194. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.68.10.5191-5194.2002
Morasch, B., Hunkeler, D., Zopfi, J., Temime, B., & Hohener, P. (2011). Intrinsic biodegradation potential of aromatic hydrocarbons in an alluvial aquifer - Potentials and limits of signature metabolite analysis and two stable isotope-based techniques. Water Research, 45(15), 4459–4469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.05.040
Ohkawa, H., [Review of pH measurement (2): Practice of pH meter based on glass electrode method]. (1998). Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso Protein Nucleic Acid Enzyme, 43(3), 272.
Perez-Rodriguez, P., Schmitt, A. D., Gangloff, S., Masbou, J., & Imfeld, G. (2021). Plants affect the dissipation and leaching of anilide pesticides in soil mesocosms: Insights from compound-specific isotope analysis (CSIA). Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 308, 11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.107257
Qian, Y., Chen, K., Liu, Y., & Li, J. (2019). Assessment of hexachlorcyclohexane biodegradation in contaminated soil by compound-specific stable isotope analysis. Environmental Pollution, 254, 113008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113008
Sayed, A., Chys, M., Rop, J. D., Goeteyn, L., Spanoghe, P., & Sampers, I. (2021). Pesticide residues in (treated) wastewater and products of Belgian vegetable- and potato processing companies. Chemosphere, 280, 130619–130619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130619
Schmidt, T. C., & Jochmann, M. A. (2012). Origin and Fate of Organic Compounds in Water: Characterization by Compound-Specific Stable Isotope Analysis. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry, 5(1), 133–155. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-anchem-062011-143143
Sukul, P., Moza, P. N., Hustert, K., & Kettrup, A. (1992). Photochemistry of metalaxyl. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 40(12), 2488–2492. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00024a029
Suto, M., & Kawashima, H. (2021). Carbon isotope ratio of organic acids in sake and wine by solid-phase extraction combined with LC/IRMS. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 413(10), 355–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03003-x
Wang, F. H., Zhu, L. S., Wang, X. G., Wang, J., & Wang, J. H. (2015a). Impact of Repeated Applications of Metalaxyl on Its Dissipation and Microbial Community in Soil. Water, air and soil pollution, 226(12), 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2686-x
Wang, M. Y., Zhang, Q., Cong, L. J., Yin, W., & Wang, M. H. (2014). Enantioselective degradation of metalaxyl in cucumber, cabbage, spinach and pakchoi. Chemosphere, 95, 241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.08.084
Wang, M. Y., Hua, X. D., Zhang, Q., Yang, Y., Shi, H. Y., & Wang, M. H. (2015b). Enantioselective Degradation of Metalaxyl in Grape, Tomato, and Rice Plants. Chirality Chirality, 27(2), 109–114. https://doi.org/10.1002/chir.22397
Wu, L. P., Yao, J., Trebse, P., Zhang, N., & Richnow, H. H. (2014). Compound specific isotope analysis of organophosphorus pesticides. Chemosphere, 111, 458–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.037
Xu, Z. M., Shen, X. L., Zhang, X. C., Liu, W. P., & Yang, F. X. (2015). Microbial degradation of alpha-cypermethrin in soil by compound-specific stable isotope analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 295, 37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.062
Xu, Z. M., Liu, W. P., & Yang, F. X. (2018). A new approach to estimate bioavailability of pyrethroids in soil by compound-specific stable isotope analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 349, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.038
Zhang, H., Zhang, Y. M., Hou, Z. G., Wang, X. M., Wang, J., Lu, Z. B., Zhao, X. F., Sun, F. J., & Pan, H. Y. (2016). Biodegradation potential of deltamethrin by the Bacillus cereus strain Y1 in both culture and contaminated soil. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 106, 53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.10.005
Zheng, Z., Liu, S. Y., Freyer, A. J., & Bollag, J. M. (1989). Transformation of Metalaxyl by the Fungus Syncephalastrum racemosum. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 55(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.55.1.66-71.1989
Funding
This work was supported by Nantong Science and Technology Plan Project [JC2019156] and the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province [No. SJCX_1152].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design, Jian Shi; experiment execution, Zheng Zhang; writing-manuscript, Ruilu Yang. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, J., Zhang, Z. & Yang, R. Quantitative Assessment of Degradation Degree of Metalaxyl in Soil and Plant by Compound-Specific Isotope Analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 134 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05587-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05587-9