Abstract
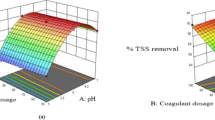
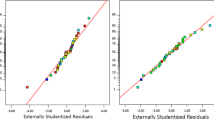
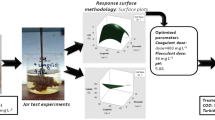
The objective of this work was to optimize the synthetic dairy effluent (SDE) treatment using the central composite rotatable design (CCRD) and the Doehlert matrix to evaluate the adjustment of the models to the data, besides verifying if it is possible to find the same optimum point to the turbidity removal, chemical oxygen demand (COD), and UV254 compounds using two experimental designs. The coagulation and flocculation assays were made in jar test and the flotation in a flotatest in bench scale. For each experimental design, the effect of two organic coagulants was evaluated in the removal of turbidity, COD, and UV254 compounds of the SDE: the polyacrylamide (PAM) and the Tanfloc. The generated mathematical models in both experimental designs adjusted well to the data, showing a high capacity of prediction. To the PAM coagulant, the optimal point found in the CCRD design was 46.49 mg L−1 of coagulant in a pH of 6.53; in the Doehlert design, the optimal point in the CCRD was 48.40 mg L−1 of coagulant in a pH of 6.50. When Tanfloc was used, in the CCRD, the optimal point found was 40.42 mg L−1 of coagulant in a pH of 5.00 and, in Doehlert design, the optimum found was 37.57 mg L−1 in a pH of 5.05. It is concluded that, using a smaller number of runs, through Doehlert design is possible to find the optimal point really close to the obtained through CCRD in which are observed efficiencies of similar pollutant removal.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M., & Whitcomb, P. (2007). DOE simplified: practical tools for effective experimentation (2nd ed.). New York: Productive Press.
APHA, AWWA, & WEF. (2017). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (23nd ed.). Washinegton: American Public Health Association, AmericanWaterWorks Association, Water Environment Federation.
Barros Neto, B., Scarminio, I. S., & Bruns, R. E. (2007). Como fazer experimentos (3nd ed.). Campinas: Editora Unicamp.
Bashir, M. J. K., Aziz, H. A., Aziz, S. Q., & Amr, S. A. (2012). An overview of wastewater treatment processes optimization using response surface metheodology (RSM). In: The 4th International Engieneering Conference-Towards Engineering of 21st century. 4. 2012, Malaysia, 1-11.
Beltrán-Heredia, J., Sánchez-Martín, J., & Rodríguez-Sánchez, M. T. (2011). Textile wastewater purification through natural coagulants. Applied Water Science, 1(1–2), 25–33.
Bezerra, M. A., Santelli, R. E., Oliveira, E. P., Villar, L. S., & Escaleira, L. A. (2008). Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta, 76(5), 965–977.
Brião, V. B., Tavares, C. R. G., Favaretto, D. P. C., & Hemkemeier, M. (2015). Ultrafiltração de efluente modelo e efluente industrial de laticínios. Rev. CIATEC-UPF, 7(1), 1–12.
Calado, V., & Montgomery, D. C. (2003). Planejamento de experimentos usando o Statistica. Rio de Janeiro: E-Papers.
Doehlert, D. H. (1970). Uniform shell designs. Applied Statistics, 19(3), 231–239.
Ferreira, S. L. C., Santos, W. N. L., Quintella, C. M., Neto, B. B., & Bosque-Sendra, J. M. (2004). Doehlert matrix: a chemometric tool for analytical chemistry – review. Talanta, 63, 1061–1067.
Grizotto, R. K., Bruns, R. E., Aguierre, J. M., & Batista, G. (2005). Otimização via metodologia de superfície de resposta dos parâmetros tecnológicos para produção de fruta estruturada e desidratada a partir de polpa concentrada de mamão. Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos, 25(1), 158–164.
Hammami, S., Ouejhani, A., Bellakhal, N., & Dachraoui, M. (2009). Application of Doehlert matrix to determine the optimal conditions of electrochemical treatment of tannery effluents. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 251–258.
Healy, M. G., Rodgers, M., & Mulqueen, J. (2007). Performance of a stratified sand filter in removal of chemical oxygen demand, total suspended solids and ammonia nitrogen from high-strength wastewaters. Journal of Environmental Management, 83, 409–415.
Kakoi, B., Kaluli, J. W., Ndiba, P., & Thion’g, G. (2017). Optimization of Maerua decumbent bio-coagulant in paint industry wastewater treatment with response surface methodology. Journal of Cleaner Production., 164, 1124–1134.
Ma, J., Fu, K., Jiang, L., Ding, L., Guan, Q., Zhang, S., Zhang, H., Shi, J., & Fu, X. (2017). Flocculation performance of cationic polyacrylamide with high cationic degree in humic acid synthetic water treatment and effect of kaolin particles. Separation and Purification Technology, 181, 201–212.
Mason, R. L., Gunst, R. F., & Hess, J. L. (2003). Statistical design and analysis of experiments: with applications to engineering and science (2nd ed.). New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Montgomery, D. C. (2010). Design and analysis of experiments (7nd ed.). New Delhi: Wiley India Pvt. Ltd.
Nair, A. T., Makwana, A. R., & Ahammed, M. M. (2014). The use of response surface methodology for modelling and analysis of water and wastewater treatment processes: a review. Water Science & Technology, 69(3), 464–478.
Najib, T., Solgi, M., Farazmand, A., Heydarian, S. M., & Nasernejad, B. (2017). Optimization of sulfate removal by sulfate reducing bacteria using response surface methodology and heavy metal removal is sulfidogenic UASB reactor. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5(4), 3256–3265.
Oladoja, N. A. (2015). Headway on natural polymeric coagulants in water and wastewater treatment operations. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 6, 174–192.
Olmez, T. (2009). The optimization of Cr(VI) reduction and removal by electrocoagulation using response surface methodology. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 162(2–3), 1371–1378.
Ouejhani, A., Hellal, F., Dachraoui, M., Lallevé, G., & Fauvarque, J. F. (2008). Application of Doehlert matrix to the study of electrochemical oxidation of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) in order to recover chromium from wastewater tanning baths. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 157, 423–431.
Pereira, E. L., Borges, A. C., Heleno, F. F., Costa, T. H. H. C., & Mounteer, A. H. (2017). Factors influencing anaerobic biodegradation of biodiesel industry wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollution, 228, 213–228.
Pereira, M. S., Borges, A. C., Heleno, F. F., Squillace, L. F. A., & Faroni, L. R. D. (2018). Treatment of synthetic milk industry wastewater using batch dissolved air flotation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 189, 729–737.
Semren, T. Z., Karaconji, I. B., Safner, T., Brajenovic, N., Lovakovic, B. T., & Pizent, A. (2018). Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of urinary volatile organic metabolites: optimization of the HS-SPME procedure and sample storage conditions. Talanta, 176, 537–543.
Teófilo, R. F., & Ferreira, M. C. (2006). Quimiometria II: Planilhas eletrônicas para cálculos de planejamentos experimentais. um tutorial. Química Nova, 29(2), 338–350.
Tyagi, M., Rana, A., Kumari, S., & Jagadevan, S. (2018). Adsorptive removal of cyanide from coke oven wastewater onto zero-valent iron: optimization through response surface methodology, isotherm and kinetic studies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 178, 398–407.
Van Gyseghem, E., Jimidar, M., Sneyers, R., Redlich, D., Verhoeven, E., Massart, D. L., & Vander Heyden., Y. (2004). Selection of reversed-phase liquid chromatographic columns with diverse selectivity towards the potential separation of impurities in drugs. Journal of Chromatography A, 1042 (1–2), 69–80.
Funding
This study received financial support from the following Brazilian Agencies: Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muniz, G.L., Borges, A.C., Souza, D.V. et al. Comparison of the Central Composite Rotatable Design with Doehlert Matrix on the Optimization of the Synthetic Dairy Effluent Treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 306 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3965-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3965-0