Abstract
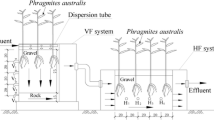
A multi-soil layer vertical flow constructed wetland (MSL-VFCW) was developed as an innovative soil-based system for wastewater treatment. The goal of this research was to employ the MSL-VFCW, as a novel technique for treating septic tank effluent. These experimental units were operated for 3 months by continuous feeding with the septic tank effluent at the hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 10 h (MSL-VFCW1), 20 h (MSL-VFCW2), and 36 h (MSL-VFCW3), while a control unit was operated at on HRT of 20 h (VFCW4). The experimental results revealed that the highest treatment performance the MSL-VFCW units was found when operated at the HRT of 36 h which could obtain total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD), 5-day biological oxygen demand (BOD5), and NH3–N removal efficiencies greater than 94% (p < 0.05). The multi-soil layers used in the MSL-VFCW unit were found to support microbial growth responsible for organic and NH3–N removals. The abundance and dominance of microbial clusters in the MSL-VFCW analyzed by using Miseq sequencing revealed that the percent abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in MSL layers were higher than the CW layer, resulting in higher in NH3–N removal efficiency. TCOD, BOD5, and NH3–N removals in the MSL-VFCW unit could be explained by first-order completely mixed model with k20 values of 1.42, 1.54, and 10.33 day−1, respectively, higher than the values reported for other constructed wetland system which suggested the applicability of the developed techniques for wastewater treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation (2005). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (21th edition). Washington: United States of America.
Chen, X., Luo, A. C., Sato, K., Wakatsuki, T., & Masunaga, T. (2009). An introduction of a multi soil layering system: a novel green technology for wastewater treatment in rural areas. Water and Environment Journal, 23(4), 255–262.
Cyplik, P., Marecik, M., Piotrowska-Cyplik, A., Olejnik, A., Drożdżyńska, A., & Chrzanowski, L. (2012). Biological denitrification of high nitrate processing wastewaters from explosives production plant. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223(4), 1791–1800.
Desta, A. F., Assefa, F., Leta, S., Stomeo, F., Wamalwa, M., Njahira, M., & Appolinaire, D. (2014). Microbial community structure and diversity in an integrated system of anaerobic-aerobic reactors and a constructed wetland for the treatment of tannery wastewater in Modjo, Ethiopia. PLoS One, 9(12), e115576.
Ding, K., Wen, X., Li, Y., Shen, B., & Zhang, B. (2015). Ammonia-oxidizing archaea versus bacteria in two soil aquifer treatment systems. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99, 1337–1347.
Dong, X., & Reddy, G. B. (2010). Soil bacterial communities in constructed wetlands treated with swine wastewater using PCR-DGGE technique. Bioresource Technology, 101(4), 1175–1182.
Guan, Y., Chen, X., Zhang, S., & Luo, A. C. (2012). Performance of multi-soil-layering system (MSL) treating leachate from rural unsanitary landfills. Science of the Total Environment, 420, 183–190.
Ho, C. C., & Wang, P. H. (2015). Efficiency of a multi-soil-layering system on wastewater treatment using environment-friendly filter materials. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(3), 3362–3380.
Iasur-Kruh, L., Hadar, Y., Milstein, D., Gasith, A., & Minz, D. (2010). Microbial population and activity in wetland microcosms constructed for improving treated municipal wastewater. Microbial Ecology, 59(4), 700–709.
Kadam, A., Oza, G., Nemade, P., Dutta, S., & Shankar, H. (2008). Municipal wastewater treatment using novel constructed soil filter system. Chemosphere, 71(5), 975–981.
Koottatep, T., Surinkul, N., Polprasert, C., Kamal, A. S. M., Koné, D., Montangero, A., Heinss, U., & Strauss, M. (2005). Treatment of septage in constructed wetland in tropical climate: lessons learnt from seven years of operation. Water Science & Technology, 51(9), 119–126.
Koottatep T., Pussayanavin T., Khamyai S., Sangchun W., & Polprasert C. (2018). “Performance evaluation pilot-scale novel soil based-system for treating septic tank effluent”, Asian Institute of Technology, Bangkok, Thailand, Progress report submitted to Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, U.S.A.
Masunaga, T., Sato, K., Mori, J., Shirahama, M., Kudo, H., & Wakatsuki, T. (2007). Characteristics of wastewater treatment using a multi-soil-layering system in relation to wastewater contamination levels and hydraulic loading rates. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 53(2), 215–223.
Matko, V. (2003). Porosity determination by using stochastic method. Journal of Automatika, 44(3–4), 155–162.
Metcalf & Eddy. (2014). Wastewater engineering: treatment and resource recovery (5th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment of Thailand: MNRE. (2010). Definition of standard of wastewater discharge from domestic wastewater treatment plant in Thailand. Thailand: Royal Thai Government.
Reddy, K. R., & Debusk, T. A. (1987). Utilization of aquatic plants in water pollution control. Water Science and Technology, 19(10), 61–79.
Reed, S.C., Crites, R.W., & Middlebrooks, E.J. (1995). Natural systems for waste management and treatment (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
Srithep, P., Khinthong, B., Chodanon, T., Powtongsook, S., Pungrasmi, W., & Limpiyakorn, T. (2015). Communities of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, ammonia-oxidizing archaea and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in shrimp ponds. Annals of Microbiology, 65(1), 267–278.
Steer, D., Fraser, L., Boddy, J., & Seibert, B. (2002). Efficiency of small constructed wetlands for subsurface treatment of single-family domestic effluent. Ecological Engineering, 18(4), 429–440.
Von Sperling, M., & de Lemos Chernicharo, C. A. (2005). Biological wastewater treatment in warm climate regions. London: IWA pubbshilng.
Vymazal, J. (2007). Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Science of the Total Environment, 380(1), 48–65.
Wakatsuki, T., Esumi, H., & Omura, S. (1993). High performance and N&P removal on-site municipal wastewater treatment system by multi-soil-layering method. Water Science & Technology, 27(1), 31–40.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Center of Excellence on Hazardous Substance Management, Chulalongkorn University, for molecular analysis supports.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Seattle, WA [grant number OPP1029022].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koottatep, T., Suksiri, P., Pussayanavin, T. et al. Development of a Novel Multi-soil Layer Constructed Wetland Treating Septic Tank Effluent with Emphasis on Organic and Ammonia Removals. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 258 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3907-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3907-x