Abstract
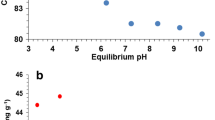
The zeta potential of hydrous manganese dioxide (HMO) may significantly influence its adsorption towards heavy metals. The effect of zeta potential of HMO on adsorption efficiency of three heavy metal ions, Pb(II), Cd(II), and Ni(II), was investigated. The zeta potential values decreased with decreasing Mn2+/MnO 4 − ratio in the HMO synthesis. The larger adsorption capacity was observed for HMO with more negative zeta potentials, and its zeta potential values increased after the adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Ni(II). The adsorption equilibrium of HMO at 303.15 K could be well described by Langmuir isotherm equation with qmax value of 502.85 mg/g for Pb(II), 155.11 mg/g for Cd(II), and 87.52 mg/g for Ni(II), respectively. Higher initial heavy metal concentration and solution pH both favored the enhancement of adsorption capacity. The pseudo-second-order equation could best fit the adsorption process. Furthermore, the Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis revealed that Pb(II), Cd(II), and Ni(II) may form inner-sphere complex on HMO surface. In addition, HMO adsorbent can be regenerated readily by treating with 50% KMnO4 solutions. After five rounds, the zeta potential value decreased to − 50.6 mV and the Pb(II) removal efficiency is 91% as compared to previous HMO removal efficiency of 93%. These findings revealed that the surface zeta potential of HMO adsorbent might be used as a parameter to determine its performance for the removal of heavy metals from contaminated water.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, S. J., Gan, Q., Matthews, R., & Johnson, P. A. (2005). Kinetic modeling of the adsorption of basic dyes by kudzu. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 286, 101–109.
Acharya, J., Sahu, J. N., Mohanty, C. R., & Meikap, B. C. (2009). Removal of lead(II) from wastewater by activated carbon developed from tamarind wood by zinc chloride activation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 149, 249–262.
Bao, W., Liu, L., Zou, H., Gan, S., Xu, X., Ji, G., Gao, G., & Zheng, K. (2013). Removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solutions using Na-A zeolite from oil shale ash Chin. Journal of Chemical Engineering, 21, 974–982.
Chen, Q., Luo, Z., Hills, C., Xue, G., & Tyrer, M. (2009). Precipitation of heavy metals from wastewater using simulated flue gas: sequent additions of fly ash, lime and carbon dioxide. Water Research, 43, 2605–2614.
Chen, R., Zhang, Y., Shen, L., Wang, X., Chen, J., Ma, A., & Jiang, W. (2015). Lead(II) and methylene blue removal using a fully biodegradable hydrogel based on starch immobilized humic acid. Chemical Engineering Journal, 268, 348–355.
Dinu, M. V., Perju, M. M., & Drăgan, E. S. (2011). Composite IPN ionic hydrogels based on polyacrylamide and dextran sulfate. Reactive & Functional Polymers, 71, 881–890.
Jiang, W., Wang, W., Pan, B., Zhang, Q., Zhang, W., & Lv, L. (2014). Facile fabrication of magnetic chitosan beads of fast kinetics and high capacity for copper removal. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 6, 3421–3426.
Li, X., Zhou, H., Wu, W., Wei, S., Xu, Y., & Kuang, Y. (2015). Studies of heavy metal ion adsorption on chitosan/sulfydryl-functionalized graphene oxide composites. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science., 448, 389–397.
Liu, Z., & Ooi, K. (2003). Preparation and Alkali-Metal Ion Extraction/Insertion Reactions with Nanofibrous Manganese Oxide Having 2 × 4 Tunnel Structure. Chemistry of Materials, 15, 3696–3703.
Liu, Z., Ooi, K., Kanoh, H., Tang, W., Yang, X., & Tomida, T. (2001). Synthesis of thermally stable silica-pillared layered manganese oxide by an intercalation/solvothermal reaction. Chemistry of Materials, 13, 473–478.
Liu, R., Liu, H., Qiang, Z., Qu, J., Li, G., & Wang, D. (2009). Effects of calcium ions on surface characteristics and adsorptive properties of hydrous manganese dioxide. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 331, 275–280.
Murray, J. W. (1974). The surface chemistry of hydrous manganese dioxide. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 46, 357–371.
Morfesis, A., Jacobson, A. M., Frollini, R., Helgeson, M., Billica, J., & Gertig, K. R. (2009). Role of zeta (ζ) potential in the optimization of water treatment facility operations. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 48, 2305–2308.
Mahamadi, C., & Nharingo, T. (2010). Competitive adsorption of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Zn2+ ions onto Eichhornia crassipes in binary and ternary systems. Bioresource Technology, 101, 859–864.
Meng, X., Wang, H. J., Lei, D., Qu, D., Zhai, Y. J., & Wang, Y. L. (2013). Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by hydrous manganese dioxide: adsorption behavior and mechanism. Journal of Environmental Science, 25, 479–486.
Maliyekkal, S. M., Lisha, K. P., & Pradeep, T. (2010). A novel cellulose–manganese oxide hybrid material by in situ soft chemical synthesis and its application for the removal of Pb(II) from water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181, 986–995.
Mejias Carpio, I. E., Mangadlao, J. D., Nguyen, H. N., Advincula, R. C., & Rodrigues, D. F. (2014). Graphene oxide functionalized with ethylenediamine triacetic acid for heavy metal adsorption and anti-microbial applications. Carbon, 77, 289–301.
Peng, G., & Tian, G. (2010). Using electrode electrolytes to enhance electrokinetic removal of heavy metals from electroplating sludge. Chemical Engineering Journal, 165, 388–394.
Peng, L., Zeng, Q., Tie, B., Lei, M., Yang, J., Luo, S., & Song, Z. (2015). Manganese dioxide nanosheet suspension: a novel absorbent for cadmium(II) contamination in waterbody. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 456, 108–115.
Ren, Y., Abbood, H. A., He, F., Peng, H., & Huang, K. (2013). Magnetic EDTA-modified chitosan/SiO2/Fe3O4 adsorbent: preparation, characterization, and application in heavy metal adsorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 226, 300–311.
Wan, S., Zhao, X., Lv, L., Su, Q., Gu, H., Pan, B., Zhang, W., Lin, Z., & Luan, J. (2010). Selective adsorption of Cd(II) and Zn(II) ions by nano-hydrous manganese dioxide (HMO)-encapsulated cation exchanger. Industiral & Engineering Chemistry Research, 49, 7574–7579.
Stumm, W., & Morgan, J. J. (1970). Aquatic chemistry. Wiley.
Savaji, K. V., Niitsoo, O., & Couzis, A. (2014). Influence of particle/solid surface zeta potential on particle adsorption kinetics. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 431, 165–175.
Sheha, R. R. (2007). Sorption behavior of Zn(II) ions on synthesized hydroxyapatites. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 310, 18–26.
Shen, C., Chen, C., Wen, T., Zhao, Z., Wang, X., & Xu, A. (2015). Superior adsorption capacity of g-C3N4 for heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 456, 7–14.
Su, Q., Pan, B., Wan, S., Zhang, W., & Lv, L. (2010). Use of hydrous manganese dioxide as a potential sorbent for selective removal of lead, cadmium, and zinc ions from water. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 349, 607–612.
Taty-Costodes, V. C., Fauduet, H., Porte, C., & Delacroix, A. (2003). Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions, from aqueous solutions, by adsorption onto sawdust of Pinus sylvestris. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 105, 121–142.
Thong, Z., Han, G., Cui, Y., Gao, J., Chung, T., Chan, S. Y., & Wei, S. (2014). Novel nanofiltration membranes consisting of a sulfonated pentablock copolymer rejection layer for heavy metal removal. Environmental Science and Technology, 48, 13880–13887.
Tripathy, S. S., Bersillon, J., & Gopal, K. (2006). Adsorption of Cd2+ on hydrous manganese dioxide from aqueous solutions. Desalination, 194, 11–21.
Uddin, M. K. (2017). A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chemical Engineering Journal, 308, 438–462.
Xiong, L., Chen, C., Chen, Q., & Ni, J. (2011). Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions using titanate nanotubes prepared via hydrothermal method. Journal of Hazardous Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.
Yang, X., Makita, Y., Liu, Z., Sakane, K., & Ooi, K. (2004). Structural characterization of self-assembled MnO2 nanosheets from birnessite manganese oxide single crystals. Chemistry of Materials, 16, 5581–5588.
Zhu, Q., & Li, Z. K. (2015). Hydrogel-supported nanosized hydrous manganese dioxide: synthesis, characterization, and adsorption behavior study for Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ removal from water. Chemical Engineering Journal, 281, 69–80.
Zhu, G., Zhu, J., Jiang, W., Zhang, Z., Wang, J., Zhu, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2017). Surface oxygen vacancy induced α-MnO2 nanofiber for highly efficient ozone elimination. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 209, 729–737.
Zaman, M. I., Mustafa, S., Khan, S., & Xing, B. (2009). Effect of phosphate complexation on Cd2+ sorption by manganese dioxide (β-MnO2). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 330, 9–19.
Zhang, L., Ma, J., & Yu, M. (2008). The microtopography of manganese dioxide formed in situ and its adsorptive properties for organic micropollutants. Solid State Sciences, 10, 148–153.
Zhang, Y., & Li, Z. (2017). Heavy metals removal using hydrogel-supported nanosized hydrous ferric oxide: synthesis, characterization, and mechanism. Science of The Total Environment, 580, 776–786.
Zou, W., Han, R., Chen, Z., Jinghua, Z., & Shi, J. (2006). Kinetic study of adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions using manganese oxide coated zeolite in batch mode. Colloids and Surfaces, 279, 238–246.
Zhai, Y., & Wang, H. (2016). Kinetics and mechanism study on adsorption of cadmium by freshly synthesized hydrous manganese dioxide. Desalination, 57, 6981–6990.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Department of Environmental Protection of Guangdong Province (B2152990) and the Guangdong Provincial Department of Science and Technology (B2130520, D9131430).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, C., Xie, F. Adsorption Behavior of Manganese Dioxide Towards Heavy Metal Ions: Surface Zeta Potential Effect. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 77 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3712-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3712-6