Abstract
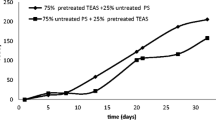
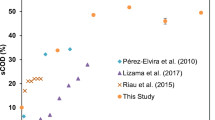
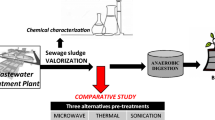
This study describes the effect of microwave and low-frequency ultrasonic pretreatment power intensity, time and density on thickened excess activated sludge (TEAS) characteristics and anaerobic digester performance. Key parameters affecting the efficiency of ultrasonic and microwave pretreatment were identified and optimised. The effect of change in ultrasonication and microwave pretreatment conditions on sludge degradation and other characteristics were analysed. Ultrasonication power, density and time were important factors in the sludge solubilisation process. Microwave density and pretreatment time also influenced solubilisation of TEAS, and the effects were investigated for treatment densities of 3.2, 4.6 and 6.4 W/ml and treatment duration of 1–7 min. Higher sludge degradability, higher volatile solid removal and better digester performance were achieved for anaerobic digestion with lower ultrasonication power of 80 W, ultrasonication time of 6 min, and ultrasonic density of 0.32 W/ml. The volume of biogas produced and kinetics, dewaterability of digested sludge, COD reduction and other sludge properties were optimised for the aforementioned ultrasonication and microwave pretreatment conditions for TEAS. It was observed that sludge dewaterability deteriorated with increasing sonication power density and sludge solubilisation. Hence, the balance between sludge dewaterability and solubilisation should be maintained for optimum performance. Thus, the selection of ultrasonic pretreatment time and power is a trade-off between sludge solubilisation and dewaterability.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA. (2000). American Water Works Association, Water Pollution Control Federation, and Water Environment Federation standard methods for the examination of water and waste water. Washington DC, USA: American Public Health Association.
Apul, O. G., & Sanin, F. D. (2010). Ultrasonic pretreatment and subsequent anaerobic digestion under different operational conditions. Bioresource Technology, 101(23), 8984–8992.
Bougrier, C., Carrère, H., & Delgenès, J. P. (2005). Solubilisation of waste-activated sludge by ultrasonic treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 106(2), 163–169.
Carrère, H., Dumas, C., Battimelli, A., Batstone, D. J., Delgenès, J. P., Steyer, J. P., & Ferrer, I. (2010). Pretreatment methods to improve sludge anaerobic degradability: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183(1–3), 1–15.
Chu, C. P., Chang, B.-V., Liao, G. S., Jean, D. S., & Lee, D. J. (2001). Observations on changes in ultrasonically treated waste-activated sludge. Water Research, 35(4), 1038–1046.
Coelho, N. M. G. (2012). Application of microwaves and thermophilic anaerobic digestion to wastewater sludge treatment, PhD thesis, The Ottawa-Carleton Institute for Environmental Engineering Department of Civil Engineering, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada.
Eskicioglu, C., Terzian, N., Kennedy, K. J., Droste, R. L., & Hamoda, M. (2007). Athermal microwave effects for enhancing digestibility of waste activated sludge. Water Research, 41(11), 2457–2466.
Eskicioglu, C., Kennedy, K., & Droste, R. (2008). Initial examination of microwave pretreatment on primary, secondary and mixed sludges before and after anaerobic digestion. Water Science and Technology, 57(3), 311–318.
Farooq, R., Rehman, F., Baig, S., Sadique, M., Khan, S., & Farooq, U. (2009). The effect of ultrasonic irradiation on the anaerobic digestion of activated sludge. World Applied Sciences Journal, 6(2), 234–237.
Federation, A. A. P. H. A. W. E. (2000). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water. Washington DC, USA.
Fernández-Cegrí, V., de la Rubia, M. A., Raposo, F., & Borja, R. (2012). Impact of ultrasonic pretreatment under different operational conditions on the mesophilic anaerobic digestion of sunflower oil cake in batch mode. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 19(5), 1003–1010.
Grady Jr, C., Daigger, G., & Lim, H. (1999). Biological wastewater treatment: revised and expanded. New York: Marcel Dekker. Inc 72, l.
Haug, R., Stuckey, D., Gossett, J., & McCarty, P. (1978). Effect of thermal pretreatment on digestibility and dewaterability of organic sludges. Journal Water Pollution Control Federation, 50(1), 73–85.
Hong, C., Si, Y., Xing, Y., Wang, Z., Qiao, Q., & Liu, M. (2015). Effect of surfactant on bound water content and extracellular polymers substances distribution in sludge. RSC Advances, 5(30), 23383–23390.
Jang, J.-H., & Ahn, J.-H. (2013). Evaluation of a microwave-heating anaerobic digester treating municipal secondary sludge. Environmental Technology, 34(7), 885–889.
Kuglarz, M., Karakashev, D., & Angelidaki, I. (2013). Microwave and thermal pretreatment as methods for increasing the biogas potential of secondary sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Bioresource Technology, 134, 290–297.
Lin, C.-Y., & Lee, Y.-S. (2002). Effect of thermal and chemical pretreatments on anaerobic ammonium removal in treating septage using the UASB system. Bioresource Technology, 83(3), 259–261.
Liu, C., Xiao, B., Dauta, A., Peng, G., Liu, S., & Hu, Z. (2009). Effect of low power ultrasonic radiation on anaerobic biodegradability of sewage sludge. Bioresource Technology, 100(24), 6217–6222.
Liu, J., Yu, D., Zhang, J., Yang, M., Wang, Y., Wei, Y., & Tong, J. (2016). Rheological properties of sewage sludge during enhanced anaerobic digestion with microwave-H2O2 pretreatment. Water Research, 98, 98–108.
Miron, Y., Zeeman, G., Van Lier, J. B., & Lettinga, G. (2000). The role of sludge retention time in the hydrolysis and acidification of lipids, carbohydrates and proteins during digestion of primary sludge in CSTR systems. Water Research, 34(5), 1705–1713.
Oh, S. E. (2006). Improvement of anaerobic digestion rate of biosolids in waste activated sludge (WAS) by ultrasonic pretreatment. Environmental Engineering Research Seoul, 11(3), 143.
Oliveira, I., Reed, J. P., Abu-Orf, M., Wilson, V., Jones, D., & Esteves, S. R. (2016). The potential use of shear viscosity to monitor polymer conditioning of sewage sludge digestates. Water Research, 105, 320–330.
Park, W. J. (2011). Effects of microwave pretreatment on mesophilic anaerobic digestion for mixture of primary and secondary sludges compared with thermal pretreatment. Environmental Engineering Research, 16(2), 103–109.
Park, S.-W., & Jang, C.-H. (2011). Effects of carbonization and solvent-extraction on change in fuel characteristics of sewage sludge. Bioresource Technology, 102(17), 8205–8210.
Park, B., Ahn, J., Kim, J., & Hwang, S. (2004). Use of microwave pretreatment for enhanced anaerobiosis of secondary sludge. Resources from Sludge: Forging New Frontiers, 50(9), 17–23.
Penaud, V., Delgenes, J., & Moletta, R. (2000). Influence of thermo-chemical pre-treatment conditions on solubilization and anaerobic biodegradability of a microbial biomass. Environmental Technology, 21, 87–96.
Pilli, S., Bhunia, P., Yan, S., LeBlanc, R. J., Tyagi, R. D., & Surampalli, R. Y. (2011). Ultrasonic pretreatment of sludge: a review. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 18(1), 1–18.
Portenlanger, G. (1999). Mechanical and radical effects of ultrasound. Ultrasound in Environmental Engineering. TU Hamburg-Harburg Reports on Sanitary Engineering 25, 139–151.
Quarmby, J., Scott, J., Mason, A., Davies, G., & Parsons, S. (1999). The application of ultrasound as a pre-treatment for anaerobic digestion. Environmental Technology, 20(11), 1155–1161.
Saha, M., Eskicioglu, C., & Marin, J. (2011). Microwave, ultrasonic and chemo-mechanical pretreatments for enhancing methane potential of pulp mill wastewater treatment sludge. Bioresource Technology, 102(17), 7815–7826.
Saifuddin, N., & Fazlili, S. (2009). Effect of microwave and ultrasonic pretreatments on biogas production from anaerobic digestion of palm oil mill effluent. American Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 2, 139–146.
Tanaka, S., & Kamiyama, K. (2002). Thermo-chemical pre-treatment in the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Water Science and Technology, 46, 173–179.
Tiehm, A., Nickel, K., Zellhorn, M., & Neis, U. (2001). Ultrasonic waste activated sludge disintegration for improving anaerobic stabilization. Water Research, 35(8), 2003–2009.
Toreci, I., Droste, R. L., & Kennedy, K. J. (2011). Mesophilic anaerobic digestion with high-temperature microwave pretreatment and importance of inoculum acclimation. Water Environment Research, 83(6), 549–559.
Tyagi, V. K., Lo, S.-L., Appels, L., & Dewil, R. (2013). Ultrasonic treatment of waste sludge: a review on mechanisms and applications. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, null-null.
Urbain, V. B., Block, J. C., & Manem, J. (1993). Bioflocculation in activated sludge: an analytic approach. Water Research, 27, 829–838.
Wang, F., Wang, Y., & Ji, M. (2005). Mechanisms and kinetics models for ultrasonic waste activated sludge disintegration. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 123(1–3), 145–150.
Yeneneh, A. M. (2014) Study on performance enhancement of anaerobic digestion of municipal sewage sludge. PhD thesis, Chemical Engineering Department, Curtin University.
Yeneneh, A. M., Hong, E., Sen, T. K., Kayaalp, A., & Ang, H. M. (2016). Effects of temperature, polymer dose, and solid concentration on the rheological characteristics and dewaterability of digested sludge of wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 227(4), 1–14.
Yeom, I. T., Lee, K. R., Lee, Y. H., Ahn, K. H., & Lee, S. H. (2002). Effects of ozone treatment on the biodegradability of sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Science and Technology, 46(4–5), 421–425.
Yu, Q., Lei, H., Yu, G., Feng, X., Li, Z., & Wu, Z. (2009). Influence of microwave irradiation on sludge dewaterability. Chemical Engineering Journal, 155(1–2), 88–93.
Zhao Xiang, H. K., Yan, L., & Yao, Y. (2009). A preliminary study on numerical simulation of microwave heating process for chemical reaction and discussion of hotspot and thermal runaway phenomenon. Science China—Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 52(4), 551–562.
Zheng, J., Kennedy, K. J., & Eskicioglu, C. (2009). Effect of low temperature microwave pretreatment on characteristics and mesophilic digestion of primary sludge. Environmental Technology, 30(4), 319–327.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Water Corporation of Western Australia and Curtin University for providing financial support and the required laboratory facility for this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeneneh, A.M., Sen, T.K., Ang, H.M. et al. Optimisation of Microwave, Ultrasonic and Combined Microwave-Ultrasonic Pretreatment Conditions for Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3197-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3197-0