Abstract
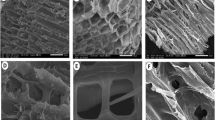
Thermally robust hydroxylated biochar (HBC) and sulphonated biochar (SBC) were synthesised from paper and pulp sludge (PPS) and used for the adsorption of Zn2+ from synthetic wastewater through batch experiments. FTIR analyses proved successful incorporation of the hydroxyl and sulphonic functional groups in HBC and SBC, respectively. The effects of initial solution pH, initial Zn2+ concentration, solution temperature and equilibrium contact time were investigated. The removal efficiency of Zn2+ increased with increase in both solution temperature and initial Zn2+ concentration. Adsorption of Zn2+ was greatest at pH 3. HBC and SBC removed 38–99% and 68–90% of Zn2+ from solution, respectively. Zn2+ adsorption on SBC followed both Langmuir (R 2 = 0.994) and Freundlich isotherm models (R 2 = 0.999), while adsorption on HBC followed the Freundlich model (R 2 = 0.989). Zn2+ adsorption on both biosorbents followed pseudo-second-order kinetics (R 2 = 0.994–0.999). The increase in enthalpy of adsorption indicated the adsorption process was endothermic and a decrease in Gibbs free energy signified the spontaneity of adsorption. Positive entropy change values imply that the adsorbed Zn2+ ions are randomly distributed over the adsorbent surface. The research demonstrated that although their adsorption mechanisms had salient differences, HBC and SBC can effectively remove Zn2+ from wastewater. Development of HBC and SBC from PPS provides potential low-cost biosorbents for water and wastewater, while simultaneously minimising the environmental and public health risks associated with current disposal practices of PPS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghani, N. T., & El-Chaghaby, G. A. (2014). Biosorption for metal ions removal from aqueous solutions: a review of recent studies. International Journal of Latest Research in Science and Technology, 3, 24–42.
Agrawal, A., Sahu, K. K., & Pandey, B. D. (2004). A comparative adsorption study of copper on various industrial solid wastes. AIChE Journal, 50, 2430–2438.
Ahmad, M., Ok, Y. S., Kim, B., Ahn, J., Lee, Y. H., Zhang, M., Moon, D. H., Al-Wabel, M. I., & Lee, S. S. (2016). Impact of soybean Stover- and pine needle-derived biochars on Pb and as mobility, microbial community, and carbon stability in a contaminated agricultural soil. Journal of Environmental Management, 166, 131–139.
Alslaibi, T. M., Abustan, I., Ahmad, M. A., & Foul, A. A. (2015). Comparative studies on the olive stone activated carbon adsorption of Zn2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+ from synthetic wastewater. Desalination and Water Treatment, 54, 166–177.
Aly, Z., & Luca, V. (2013). Uranium extraction from aqueous solution using dried and pyrolyzed tea and coffee wastes. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 295, 889–900.
Bhatt, A. S., Sakaria, P. L., Vasudevan, M., Pawar, R. R., Sudheesh, N., Bajaj, H. C., & Mody, H. M. (2012). Adsorption of an anionic dye from aqueous medium by organoclays: equilibrium modeling, kinetic and thermodynamic exploration. RSC Advances, 2, 8663–8671.
Bhattacharya, A. K., Naiya, T. K., Mandal, S. N., & Das, S. K. (2008). Adsorption, kinetics and equilibrium studies on removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using different low-cost adsorbents. Chemical Engineering Journal, 137, 529–541.
Bunhu, T., Lilian Tichagwa, L., & Chaukura, N. (2016). Competitive sorption of Cd2+ and Pb2+ from a binary aqueous solution by poly (methyl methacrylate)-grafted montmorillonite clay nanocomposite. Applied Water Science. doi:10.1007/s13201-016-0404-5.
Chaukura, N., Gwenzi, W., Tavengwa, N., & Manyuchi, M. M. (2016a). Biosorbents for the removal of synthetic organics and emerging pollutants: opportunities and challenges for developing countries. Environmental Development, 19, 84–89.
Chaukura N., Murimba E.C., Gwenzi W. (2016b). Synthesis, characterisation and methyl orange adsorption capacity of ferric oxide–biochar nano-composites derived from pulp and paper sludge. Applied Water Science 1–12. Doi: 10.1007/s13201-016-0392-5.
Desta, M. B. (2013). Batch sorption experiments: langmuir and freundlich isotherm studies for the adsorption of textile metal ions onto teff straw (Eragrostis tef) agricultural waste. Journal of Thermodynamics. doi:10.1155/2013/375830.
El-Said, A. G., Badawy, N. A., Abdel-Aal, A. Y., & Garamon, S. E. (2011). Optimization parameters for adsorption and desorption of Zn (II) and Se (IV) using rice husk ash: kinetics and equilibrium. Ionics, 17, 263–270.
Forján, R., Asensio, V., Rodríguez-Vila, A., & Covelo, E. F. (2016). Contribution of waste and biochar amendment to the sorption of metals in a copper mine tailing. Catena, 137, 120–125.
Gadd, G. M. (2009). Biosorption: critical review of scientific rationale, environmental importance and significance for pollution treatment. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 84, 13–28.
Gong, R., Ye, J., Dai, W., Yan, X., Hu, J., Hu, X., Li, S., & Huang, H. (2013). Adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution with finger-citron-residue-based activated carbon. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 52, 14297–14303.
Gwenzi, W., Musarurwa, T., Nyamugafata, P., Chaukura, N., Chaparadza, A., & Mbera, S. (2014). Adsorption of Zn2+ and Ni2+ in a binary aqueous solution by biosorbants derived from sawdust and water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). Water Science and Technology, 70, 1419–1427.
Gwenzi, W., Chaukura, N., Mukome, F. N. D., Machado, S., & Nyamasoka, B. (2015). Biochar production and applications in sub-Saharan Africa: opportunities, constraints, risks and uncertainties. Journal of Environmental Management, 150, 250–261.
Han, Y., Cao, X., Ouyang, X., Sohi, S. P., & Chen, J. (2016). Adsorption kinetics of magnetic biochar derived from peanut hull on removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution: effects of production conditions and particle size. Chemosphere, 145, 336–341.
Inyang, M., Gao, B., Pullammanappallil, P., Ding, W., & Zimmerman, A. R. (2010). Biochar from anaerobically digested sugarcane bagasse. Bioresource Technology, 101, 8868–8872.
Inyang, M., Gao, B., Yao, Y., Xue, Y., Zimmerman, A. R., Pullammanappallil, P., & Cao, X. (2012). Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by biochars derived from anaerobically digested biomass. Bioresource Technology, 110, 50–56.
Jiang, S., Huang, L., Nguyen, T. A. H., Ok, Y. S., Rudolph, V., Yang, H., & Zhang, D. (2016). Copper and zinc adsorption by softwood and hardwood biochars under elevated sulphate-induced salinity and acidic pH conditions. Chemosphere, 142, 64–71.
Jin, H., Hanif, M. U., Capareda, S., Chang, Z., Huang, H., & Ai, Y. (2016). Copper (II) removal potential from aqueous solution by pyrolysis biochar derived from anaerobically digested algae-dairy-manure and effect of KOH activation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 4, 365–372.
Kakavandi, B., Jafari, A. J., Kalantary, R. R., Nasseri, S., Ameri, A., & Esrafily, A. (2013). Synthesis and properties of Fe3O4-activated carbon magnetic nanoparticles for removal of aniline from aqueous solution: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Iranian Journal of Environmental Health Sciences & Engineering, 10, 19–28.
Kilic, M., Kirbiyik, C., Cepeliogullar, O., & Putun, A. E. (2013). Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by bio-char, a by-product of pyrolysis. Applied Surface Science, 283, 856–862.
Méndez, A., Barriga, S., Fidalgo, J. M., & Gascó, G. (2009). Adsorbent materials from paper industry waste materials and their use in Cu(II) removal from water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 15, 736–743.
Mohan, D., Singh, P., Sarswat, A., Steele, P. H., & Pittman, C. U., Jr. (2015). Lead sorptive removal using magnetic and nonmagnetic fast pyrolysis energy cane biochars. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 448, 238–250.
Mukome, F. N. D., Zhang, X., Silva, L. C. R., Six, J., & Parikh, S. J. (2013). Use of chemical and physical characteristics to investigate trends in biochar feedstocks. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61, 2196–2204.
Park, D., Yun, Y., & Park, J. M. (2010). The past, present, and future trends of biosorption. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 15, 86–102.
Park, J., Ok, Y. S., Kim, S., Cho, J., Heo, J., Delaune, R. D., & Seo, D. (2016). Competitive adsorption of heavy metals onto sesame straw biochar in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere, 142, 77–83.
Rahimi, S., Moattari, M., Rajabi, L., Derakhshan, A. A., & Keyhani, M. (2015). Iron oxide/hydroxide (a, c-FeOOH) nanoparticles as high potential adsorbents for lead removal from polluted aquatic media. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 23, 33–43.
Ruziwa, D. T., Chaukura, N., Gwenzi, W., & Pumure, I. (2015). Removal of Zn2+ and Pb2+ ions from aqueous solution using sulphonated waste polystyrene. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3, 2528–2537.
Setyono, D., & Valiyaveettil, S. (2016). Functionalized paper—a readily accessible adsorbent for removal of dissolved heavy metal salts and nanoparticles from water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 302, 120–128.
Tan, X., Liu, Y., Zeng, G., Wang, X., Hu, X., Gu, Y., & Yang, Z. (2015). Application of biochar for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere, 125, 70–85.
Trakal, L., Veselská, V., Šafarík, I., Vítková, M., Cíhalová, S., & Komárek, M. (2016). Lead and cadmium sorption mechanisms on magnetically modified biochars. Bioresource Technology, 203, 318–324.
Vilakati, G. D., Mishra, A. K., Mishra, S. B., Mamba, B. B., & Thwala, J. M. (2012). Metal ion adsorption behavior of lignocellulosic fiber–ethylene vinyl acetate composites. Polymer Engineering & Science, 52, 760–767.
Wang, F., Tan, L., Liu, Q., Li, R., Li, Z., Zhang, H., Hu, S., Liu, L., & Wang, J. (2015). Biosorption characteristics of Uranium (VI) from aqueous solution by pollen pini. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 150, 93–98.
Weng, C., & Huang, C. P. (2004). Adsorption characteristics of Zn (II) from dilute aqueous solution by fly ash. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 247, 137–143.
Xie, S., Yang, J., Chen, C., Zhang, X., Wang, Q., & Zhang, C. (2008). Study on biosorption kinetics and thermodynamics of uranium by Citrobacter freudii. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 99, 126–133.
Yasemin, B., & Zeki, T. (2007). Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by sawdust adsorption. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19, 160–166.
Yu, L., & Luo, Y. (2014). The adsorption mechanism of anionic and cationic dyes by Jerusalem artichoke stalk-based mesoporous activated carbon. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2, 220–229.
Yu, J., Wang, L., Chi, R., Zhang, Y., Xu, Z., & Guo, J. (2013). Competitive adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ on magnetic modified sugarcane bagasse prepared by two simple steps. Applied Surface Science, 268, 163–170.
Zhang, M., Gao, B., Varnoosfaderani, S., Hebard, A., Yao, Y., & Inyang, M. (2013). Preparation and characterization of a novel magnetic biochar for arsenic removal. Bioresource Technology, 130, 457–462.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaukura, N., Gwenzi, W., Mupatsi, N. et al. Comparative Adsorption of Zn2+ from Aqueous Solution Using Hydroxylated and Sulphonated Biochars Derived from Pulp and Paper Sludge. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3191-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3191-6