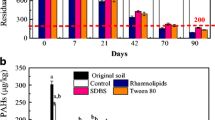
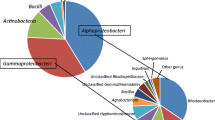
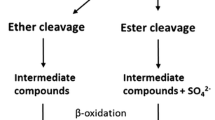
Abstract
Anionic surfactants, the earliest and the most common surfactants in detergent and cosmetic product formulations contribute significantly to the pollution profile of the ecosystem. Linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS), a major chemical constituent of detergents, forms an imperative group of anionic surfactants. Bioremediation of LAS by conventional processes such as activated sludge is ineffective due to the low kinetics of degradation by unsuitable organisms and foam production. Hence this study was focused on isolating and characterizing indigenous LAS-degrading bacteria from soil. Twenty different LAS-degrading bacteria were isolated from detergent-contaminated soil by enrichment culture technique and degradation efficiency was assessed by Methylene Blue Active Substances (MBAS) assay and by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis. The most efficient LAS-degrading isolates, L9 (81.33 ± 0.7) and L12 (81.81 ± 0.8), were selected and identified as Pseudomonas nitroreducens (MTCC 10463) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MTCC 10462). The 16S rDNA sequences of the isolates were deposited in NCBI GenBank under the accession numbers HQ 271083 (L9) and HQ 271084 (L12). The isolates were capable of degrading 0.05 g/l LAS at 25 °C and pH 7.0–7.5. Presence of a solid support caused biofilm formation which in turn enhanced LAS degradation. The isolates tend to display diauxic growth with alternate carbon source such as dextrose. These isolates also have the capability to degrade other xenobiotics like hydrocarbons and pesticides. Since xenobiotic pollutants in nature occur as a mixture of compounds rather than single pollutants, the potential of these two indigenous LAS-degrading isolates to degrade multiple xenobiotics gains relevance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew, E. J., Hales, S. G., Ur-Rehman, N. G. A., White, G. F., et al. (2002). Novel alkylsulphatases required for the biodegradation of the branched primary alkyl sulphate surfactant 2-butyloctyl sulphate. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 31–36.
Asok, A. K., & Jisha, M. S. (2012). Assessment of soil microbial toxicity on acute exposure of the anionic surfactant linear alkylbenzene sulphonate. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 1–10. doi:10.3923/jest.2012.
Asok, A. K., Ratheesh, K. K., Sherief, P. M., Jisha, M. S., et al. (2012). Oxydative stress and changes in gill morphology of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) exposed to sublethal concentrations of the anionic surfactant linear alkylbenzene sulphonate (LAS). Global Journal of Applied Environmental Sciences, 2(1), 1–11.
Berna, J. L., Ferrer, J., Moreno, A., Prats, D., Ruiz, F., et al. (1989). The fate of LAS in the environment. Tenside Surfactant Detergents, 23, 101–107.
Chaturvedi, V., & Kumar, Ashok. (2011). Diversity of culturable sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) degrading bacteria isolated from detergent contaminated ponds situated in Varanasi city, India. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 65, 961–971.
Cirelli, A. E., Ojeda, Carlos, Mariano, J. L., Castro, Miquel Salgot, et al. (2008). Surfactants in sludge-amended agricultural soils: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 6, 135–148. doi:10.1007/s10311-008-0146-1.
Claus, G. W., & Balkwill, D. (1989). Understanding microbes: A laboratory textbook for microbiology. NY: Freeman.
Deksissa, T., & Vanrolleghem, P. A. (2003). Effect of nutrient dynamics on organic contaminant fate in rivers: A microcosm study. Communications in Agricultural and Applied Biological Sciences, 68(3), 111–114.
DeWolf, W., & Feijitel, T. (1998). Terrestrial risk assessment for linear alkyl benzene sulfonate (LAS) in sludge-amended soils. Chemosphere, 36, 1319–1343.
Dhouib, A., Hamad, N., Hassairi, I., et al. (2003). Degradation of anionic surfactants by Citrobacter braakii. Process Biochemistry, 38, 1245–1250.
Eichhorn, P., Rodrigues, S. V., Baumann, W., Knepper, T. P., et al. (2002). Incomplete degradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate surfactants in Brazilian surface waters and pursuit of their polar metabolites in drinking waters. Science of the Total Environment, 284, 123–134.
Garcia, M. T., Campos, E., Ribosa, I., Latorre, A., Sanchez-Leal, J., et al. (2005). Anaerobic digestion of LAS: Biodegradation kinetics and metabolite analysis. Chemosphere, 60, 1636–1643.
Ghose, N. C., Saha, Dipankar, Gupta, Anjali, et al. (2009). Synthetic detergents (surfactants) and organochlorine pesticide signatures in surface water and groundwater of Greater Kolkata, India. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 4, 290–298. doi:10.4236/jwarp.2009.
Hayashi, K. (1975). A rapid determination of sodium dodecyl sulfate with methylene blue. Analytical Biochemistry, 67, 503–506.
Hofer, R., Jeney, Z., & Bucher, F. (1995). Chronic effects of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) and ammonia on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fry at water criteria limits. Water Research, 29, 2725–2729.
Holt, J. G., Krieg, N. R., Sneath, P. H. A., Staloj, J. T., Williams, S. T., et al. (1994). Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology (9th ed.). Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins.
Jensen, J., Lokke, H., Holmstrup, M., Krogh, P. H., Elsgaard, L., et al. (2001). Effects and risk assessment of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates in agricultural soil. 5. Probabilistic risk assessment of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates in sludge-amended soils. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 1690–1697.
Kertesz, M. A., Kolbener, P., Stockinger, H., Beil, S., Cook, A. M., et al. (1994). Desulfonation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonated surfactants and related compounds by bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60, 2296–2303.
Khleifat, K. M. (2006). Biodegradation of linear alkylbenzene sulphonate by a two member facultative anaerobic bacterial consortium. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 39, 1030–1035.
Khleifat, K. M., Tarawneh, Khaled A., Wedyan, Mohammad Ali, Al-Tarawneh, Amjad A., Khalid, Al Sharafa, et al. (2008). Growth kinetics and toxicity of Enterobacter cloacae grown on linear alkylbenzene sulfonate as sole carbon source. Current Microbiology, 57, 364–370. doi:10.1007/s00284-008-9203-z.
Knaebel, D. B., Federle, T. W., Vestal, J. R., et al. (1990). Mineralisation of linear alkylbenzene sulphonate (LAS) and linear alcohol ethoxylate (LAE) in 11 contrasting soils. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 9, 981–988.
Knaebel, D. B., Federle, T. W., McAvoy, D. C., Vestals, J. R., et al. (1994). Effect of mineral and organic soil constituents on microbial mineralization of organic compounds in a natural soil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60, 4500–4508.
Konopka, A., Zakharova, T., Oliver, L., Turco, R.F., et al. (2000). Microbial biodegradation of organic wastes containing surfactants in a continuous-flow reactor. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 18, 235-/40.
Mackay, D., Di Guardo, A., Paterson, S., Kicsi, G., Cowan, C. E., Kane, D. M., et al. (1996). Assessment of chemical fate of LAS in the environment using evaluative, regional and local scale models, illustrative application to chlorobenzene and linear alkylbenzene sulphonates. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 15(9), 1638–1648.
Nakae, A., Tsuji, Kazuro, Yamanka, Makoto, et al. (1981). Determination of alkylchain distribution of alkylbenzene sulphonate by liquid chromatography. Analytical Chemistry, 53, 1818–1821.
Prats, D., Lopez, Carmen, Vellinjo, Diana, Vavo, Pedro, Leon, Victor M., et al. (2006). Effect of temperature on biodegradation of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate and alcohol ethoxylate. Journal of Surfactants and Detergaens, 9, 69–75.
Schleheck, D. (2003). Biodegradation of synthetics surfactants: Linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS) and related compounds. PhD Thesis. Germany: University of Konstanz.
Singh, A., Van Hamme, J. D., Ward, O. P., et al. (2007). Surfactants in microbiology and biotechnology. Biotechnology Advances, 25, 99–122.
Swisher, R. D. (1987). Surfactant biodegradation (2nd ed., pp. 587–614). New York: Dekker.
Takamatsu, Y., Nishimura, O., Inamori, Y., Sudo, R., Matsumura, M., et al. (1996). Effect of temperature on biodegradability of surfactants in aquatic microcosm system. Water Science and Technology, 34(7–8), 61–68.
Trehy, M. L., Gledhill, W. E., Mieure, J. P., Adamove, J. E., Nielsen, A. M., Perkins, H. O., et al. (1996). Environmental monitoring for lauryl alkylbenzenes, dialkyltetralin sulfonates and their biodegradation intermediated. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 15, 233–240.
Van der Meeren, P., & Verstraete, W. (1996). Surfactants in relation to bioremediation and wastewater treatment. Current Opinion in Colloid and Interface Science, 1(5), 624–634.
Vives-Rego, J., Lopez-Amoros, R., Guindulain, T., Garcia, M. T., Comas, J., Sanchez-Leal, J., et al. (2000). Microbial aspect of linear alkylbenzene sulphonate degradation in coastal water. Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, 3(3), 303–307.
Yeldho, D., Rebello, Sharrel, Jisha, M. S., et al. (2011). Plasmid-mediated biodegradation of the anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulphate, by Pseudomonas aeruginosa S7. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 86, 110–113. doi:10.1007/s00128-010-0162-2.
Zhang, Z., Schwartz, Scott, Wagner, Lukas, Miller, Webb, et al. (2000). A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. Journal of Computational Biology, 7(1–2), 203–214.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Kerala State Council for Science, Technology, and Environment (KSCSTE), Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asok, A.K., Jisha, M.S. Biodegradation of the Anionic Surfactant Linear Alkylbenzene Sulfonate (LAS) by Autochthonous Pseudomonas sp.. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 5039–5048 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1256-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1256-8