Abstract
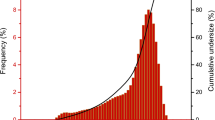
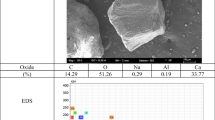
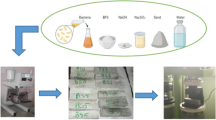
Urban rainfall–runoff residuals contain metals such as Cr, Zn, Cu, As, Pb and Cd and are thus reasonable candidates for treatment using Portland cement-based solidification–stabilization (S/S). This research is a study of S/S of urban storm water runoff solid residuals in Portland cement with quicklime and sodium bentonite additives. The solidified residuals were analyzed after 28 days of hydration time using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) and solid-state 29Si nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results indicate that the main cement hydration products are ettringite, calcium hydroxide and hydrated calcium silicates. Zinc hydroxide and lead and zinc silicates are also present due to the reactions of the waste compounds with the cement and its hydration products. 29Si NMR analysis shows that the coarse fraction of the waste apparently does not interfere with cement hydration, but the fine fraction retards silica polymerization.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter, H., Butler, L. G., Branz, S., Cartledge, F. K., & Tittlebaum, M. E. (1990). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 24, 145–155.
Alloway, B. J., & Ayres, D. C. (1993). Chemical principles of environmental pollution. London: Blackie.
Cartledge, F. K., Butler, L. G., Chalasani, D., Eaton, H. C., Frey, F. P., Herrera, E., et al. (1990). Immobilization mechanisms in solidification/stabilization of Cd and Pb salts using portland cement fixing agents. Environmental Science & Technology, 24, 847–873.
Conner, J. R., & Hoeffner, S. L. (1998). A critical review of stabilization/solidification technology. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 28, 325–396.
Dean, C. M., Sansalone, J. J., Cartledge, F. K., & Pardue, J. H. (2005). Influence of hydrology on rainfall–runoff metal element speciation. ASCE Journal of Environmental Engineering, 131, 632–642.
Drapper, D., Tomlinson, R., & Williams, P. (2000). Pollutant concentrations in road runoff: Southeast Queensland case study. ASCE Journal of Environmental Engineering, 126, 313–320.
Dweck, J., Büchler, P. M., & Cartledge, F. K. (2001). Study by thermogravimetry of the evolution of the ettringite phase during type II portland cement hydration. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 64, 1011–1016.
Fitch, J. R., & Cheeseman, C. R. (2003). Characteristics of environmentally exposed cement-based stabilised/solidified industrial waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 101, 239–255.
Fitzgerald, J. J. (1999). Solid-state NMR spectroscopy of inorganic materials. Washington: American Chemical Society.
Gilliam, T. M. & Wiles, C. C. (Eds.) (1992). Stabilization and solidification of hazardous, radioactive and mixed wastes. Philadelphia: ASTM.
Glasser, F. P. (1997). Fundamental aspects of cement solidification and stabilization. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 52, 151–170.
Glenn, D. W., Liu, D., & Sansalone, J. J. (2001). Influence of highway runoff chemistry, hydrology, and residence time on nonequilibrium partitioning of heavy metals. Implications for treatment at the highway shoulder. Transportation Research Record, 1755, 129–140.
Harris, R. K., & Mann, B. E. (1978). NMR and the periodic table. London: Academic.
Hewitt, C. N., & Rashed, M. B. (1992). Removal rates of selected pollutants in the runoff waters from a major rural highway. Water Research, 26, 311–319.
Iffland, N., Isensee, H. J., Wagner, G., Witte, H. (1978). Solidification and disposal of radioactive borate-containing liquids. US Patent 4,122,028.
Janusa, M. A., Wu, X., Cartledge, F. K., & Butler, L. G. (1993). Solid-state deuterium NMR spectroscopy of d5-phenol in white portland cement: A new method for assessing solidification/stabilization. Environmental Science & Technology, 27, 1426–1433.
Johnson, C. A. (2004). Cement stabilization of heavy-metal-containing wastes. Geological Society Special Publication, 236, 595–606.
Lin, S.-H., & Juang, R.-S. (2002). Heavy metal removal from water by sorption using surfactant-modified montmorillonite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 92, 315–326.
Mackenzie, K. J. D., & Smith, M. E. (2002). Multinuclear solid-state NMR of inorganic materials. London: Elsevier.
Mason, J. (1987). Multinuclear NMR. New York: Plenum.
Palomo, A., & Palacios, M. (2003). Alkali-activated cementitious materials: Alternative matrices for the immobilization of hazardous wastes: Part I. Stabilisation of boron. Cement and Concrete Research, 33, 289–295.
Park, C.-K. (2000). Hydration and solidification of hazardous wastes containing heavy metals using modified cementitious materials. Cement and Concrete Research, 30, 429–435.
Pinto, C. A., Dweck, J., Sansalone, J. J., Cartledge, F. K., Tittlebaum, M. E., & Büchler, P. M. (2005). Early stages of solidification/stabilization of storm water runoff solid residuals in cement. Journal of Thermal Analysis & Calorimetry, 80, 715–720.
Pordjosantoso, A. K., & Kennedy, B. J. (2003). Heavy metals in cement phases: On the solubility of Mg, Cd, Pb and Ba in Ca3Al2O6. Cement and Concrete Research, 33, 1077–1084.
Ortego, J. D., Barroeta, Y., Cartledge, F. K., & Akhter, H. (1991). Leaching effects on silicate polymerization. An FTIR and 29Si NMR study of lead and zinc in portland cement. Environmental Science & Technology, 25, 1171–1174.
Rebouças, A. C., Braga, B., & Tundisi, J. G. (1999). Sweet water of Brazil. São Paulo: Escrituras (in Portuguese).
Roy, A., Eaton, H. C., Cartledge, F. K., & Tittlebaum, M. E. (1992). Solidification/stabilization of hazardous waste: Evidence of physical encapsulation. Environmental Science & Technology, 26, 1349–1353.
Sansalone, J. J. (1999). In-situ performance of a passive treatment system for metal source control. Water Science & Technology, 39, 193–200.
Sansalone, J. J., Koran, J. M., Smithson, J. A., & Buchberger, S. G. (1998). Physical characteristics of urban roadway solids transported during rain events. ASCE Journal of Environmental Engineering, 124, 427–440.
Sansalone, J., & Zheng, T. (2004). In situ partial exfiltration of rainfall runoff. I: Quality and quantity attenuation. ASCS Journal of Environmental Engineering, 130, 990–1007.
Spence, R. D. (Ed.) (1992) Chemistry and microstructure of solidified waste forms. Boca Raton, FL: Lewis Publishers.
Turer, D., Maynard, J. B., & Sansalone, J. J. (2001). Heavy metal contamination in soils of urban highways comparison between runoff and soil concentrations at Cincinnati, Ohio. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 132, 293–314.
Thomson, N. R., McBean, E. A., Snodgrass, W., & Mostrenko, I. (1997). Sample size needs for characterizing pollutant concentrations in highway runoff. ASCS Journal of Environmental Engineering, 123, 1061–1065.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1986). Handbook for stabilization/solidification of hazardous wastes EPA/540/2-86/001. Cincinnati: USEPA.
Ziegler, F., Giere, R., & Johnson, C. A. (2001). Sorption mechanisms of zinc to calcium silicate hydrate: Sorption and microscopic investigations. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 4556–4561.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Geophysical Sciences Department, specially Dr. Ray Ferrell, Louisiana State University, USA for the use of X-ray Diffractometer, Dr. Dale Treleaven at Chemistry Department, Louisiana State University, USA for the use of the 29Si NMR, Samuel Boggan from Southern University and Willian G. Barlett from Louisiana State University for their assistance. This study was performed with the financial support of the Brazilian Research Council (CNPq), Brazilian Ministry of Education (CAPES), UWMRC/USEPA and Louisiana Water Resources Research Institute (LWRRI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinto, C.A., Sansalone, J.J., Cartledge, F.K. et al. Cement Stabilization of Runoff Residuals: A Study of Stabilization/Solidification of Urban Rainfall–Runoff Residuals in Type 1 Portland Cement by XRD and 29Si NMR Analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut 188, 261–270 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9542-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9542-6