Abstract
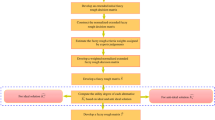
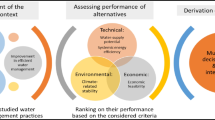
In this paper, a new fuzzy group decision-making methodology which determines and incorporates negotiation powers of decision makers is developed. The proposed method is based on a combination of interval type-2 fuzzy sets and a multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) model, namely TOPSIS. To examine the applicability of the proposed methodology, it is used for finding the best scenario of allocating water and reclaimed wastewater to domestic, agricultural, and industrial water sectors and restoring groundwater quantity and quality in the Varamin region located in Tehran metropolitan area in Iran. The results show that the selected scenario leads to an acceptable groundwater conservation level during a long-term planning horizon. Although the capital cost of this scenario is high, which leads to groundwater restoration during the 34-year planning horizon, it is determined as the best allocation scenario. This scenario also entails the second least pumping cost, due to less water allocation from the groundwater. To evaluate the results of the proposed methodology, they are compared with those obtained using some well-known interval type-2 decision-making approaches including arithmetic-based, TOPSIS-based, and likelihood-based comparison methods. The Spearman correlation coefficient shows that the obtained results generally concur with those of the other methods. It is also concluded that the proposed methodology gives more reasonable results by calculating and considering the negotiation powers of decision makers in an extended TOPSIS-based group decision-making model.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen S-M, Hong J-A (2014) Fuzzy multiple attributes group decision-making based on ranking interval type-2 fuzzy sets and the TOPSIS method. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems 44(12):1665–1673
Chen S-M, Lee L-W (2010a) Fuzzy multiple attributes group decision-making based on the ranking values and the arithmetic operations of interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Expert Syst Appl 37(1):824–833
Chen S-M, Lee L-W (2010b) Fuzzy multiple attributes group decision-making based on the interval type-2 TOPSIS method. Expert Syst Appl 37(4):2790–2798
Chen S-M, Yang M-W, Lee L-W, Yang S-W (2012) Fuzzy multiple attributes group decision-making based on ranking interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Expert Syst Appl 39(5):5295–5308
Chen T-Y (2015) An interval type-2 fuzzy technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solutions using a likelihood-based comparison approach for multiple criteria decision analysis. Comput Ind Eng 85:57–72
Darbandsari P, Kerachian R, Malakpour-Estalaki S, Khorasani H (2020) An agent-based conflict resolution model for urban water resources management. Sustain Cities Soc 57:102112
Estalaki SM, Kerachian R, Nikoo MR (2016) Developing water quality management policies for the Chitgar urban lake: application of fuzzy social choice and evidential reasoning methods. Environ Earth Sci 75:404
Ghorabaee MK (2016) Developing an MCDM method for robot selection with interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 37:221–232
Hosseini MB, Tarokh MJ (2011) Interval type-2 fuzzy set extension of DEMATEL method. In: International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Information Technology, Springer, pp. 157–165
Hosseini MB, Tarokh MJ (2013) Type-2 fuzzy set extension of DEMATEL method combined with perceptual computing for decision making. Journal of Industrial Engineering International 9(1):10
Hwang C-L, Yoon K. (1981). Methods for multiple attribute decision making. Multiple attribute decision making, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 58–191
Kahraman C, Öztayşi B, Sarı İU, Turanoğlu E (2014) Fuzzy analytic hierarchy process with interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Knowl-Based Syst 59:48–57
Kahraman C, Sarı İU. (2012) Multicriteria environmental risk evaluation using type II fuzzy sets. In: International Conference on Information Processing and Management of Uncertainty in Knowledge-Based Systems. Springer, pp. 449–457
Lee L-W, Chen S-M (2008) Fuzzy multiple attributes group decision-making based on the extension of TOPSIS method and interval type-2 fuzzy sets. In: 2008 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, IEEE, pp. 3260–3265
Liang Q, Mendel JM (2000) Interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems: theory and design. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 8(5):535–550
Mardani A, Jusoh A, Zavadskas EK (2015) Fuzzy multiple criteria decision-making techniques and applications–two decades review from 1994 to 2014. Expert Syst Appl 42(8):4126–4148
Mendel JM (2007) Advances in type-2 fuzzy sets and systems. Inf Sci 177(1):84–110
Mendel JM, John RI, Liu F (2006) Interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems made simple. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 14(6):808–821
Montazer G, Saremi HQ (2008) An application of type-2 fuzzy notions in website structures selection: utilizing extended TOPSIS method. WSEAS Trans Comput 7(1):8–15
Motlaghzadeh K, Kerachian R, Tavvafi A (2020) An evidential reasoning-based leader-follower game for hierarchical multi-agent decision making under uncertainty. J Hydrol 591:125294
Najafi A, Karimpour MH, Ghaderi M (2014) Application of fuzzy AHP method to IOCG prospectivity mapping: a case study in Taherabad prospecting area, eastern Iran. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 33:142–154
Pourmand E, Mahjouri N (2018) A fuzzy multi-stakeholder multi-criteria methodology for water allocation and reuse in metropolitan areas. Environ Monit Assess 190(7):444
Qin J, Liu X, Pedrycz W (2015a) An extended VIKOR method based on prospect theory for multiple attribute decision making under interval type-2 fuzzy environment. Knowl-Based Syst 86:116–130
Qin Y, Zhang Z, Liu X, Li M, Kou L (2015b) Dynamic risk assessment of metro station with interval type-2 fuzzy set and TOPSIS method. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 29(1):93–106
Ribeiro RA, Falcão A, Mora A, Fonseca JM (2014) FIF: a fuzzy information fusion algorithm based on multi-criteria decision making. Knowl-Based Syst 58:23–32
Wang J, Lin Y-I (2003) A fuzzy multicriteria group decision making approach to select configuration items for software development. Fuzzy Sets Syst 134(3):343–363
Wu Z, Chen Y (2007) The maximizing deviation method for group multiple attribute decision making under linguistic environment. Fuzzy Sets Syst 158(14):1608–1617
Yazici I, Kahraman C (2015) VIKOR method using interval type two fuzzy sets. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 29(1):411–421
Yao L, Xu Z, Lv C, Hashim M (2020) Incomplete interval type-2 fuzzy preference relations based on a multi-criteria group decision-making model for the evaluation of wastewater treatment technologies. Measurement 151:107137
Yekom-Consulting-Engineers. (2013). Quantity and quality modeling of Varamin plain's aquifer- Technical report
Yue Z (2011) A method for group decision-making based on determining weights of decision makers using TOPSIS. Appl Math Model 35(4):1926–1936
Yue Z (2012a) Approach to group decision making based on determining the weights of experts by using projection method. Appl Math Model 36(7):2900–2910
Yue Z (2012b) Extension of TOPSIS to determine weight of decision maker for group decision making problems with uncertain information. Expert Syst Appl 39(7):6343–6350
Yucesan M, Mete S, Serin F, Celik E, Gul M (2019) An integrated best-worst and interval type-2 fuzzy TOPSIS methodology for green supplier selection. Mathematics 7:182
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—I. Inf Sci 8(3):199–249
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourmand, E., Mahjouri, N., Hosseini, M. et al. A Multi-Criteria Group Decision Making Methodology Using Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets: Application to Water Resources Management. Water Resour Manage 34, 4067–4092 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02657-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02657-7