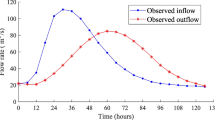
Abstract
Flood is one of the most destructive natural disasters that damages people’s lives dramatically. Thus, it is crucial for researchers and politicians to research flood routing. The non-linear Muskingum model has been significantly considered by engineers and researchers in flood routing. In this study, in order to increase the accuracy of outflow prediction, the new non-linear Muskingum model, with four variable parameters, is proposed for the first time. In the proposed model, the inflows are divided into three sub-regions, and each of the four hydrologic parameters has a various value in each sub-region. How to select the sub-regions, as well as the values of the hydrologic parameters, is determined by combining both the Particle Swarm Optimization and Genetic Algorithm. The proposed model is studied in four case studies. Compared to the non-linear Muskingum model with three parameters, the amount of sum squared deviation (SSQ) decreased 52 and 6.9% for the first and second case studies, respectively. Compared to the best variable parameter model, the SSQ for the third and fourth case studies reduced 76 and 62%, respectively. The results showed that the SSQ was considerably decreased significantly in all of the four case studies, and the proposed model has superiority over other non-linear Muskingum models, which have been used by other researchers so far.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzali SH (2016) Variable-parameter Muskingum model. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Civil Engineering 40(1):59–68
Ayvaz MT, Gurarslan G (2017) A new partitioning approach for nonlinear Muskingum flood routing models with lateral flow contribution. J Hydrol 553:142–159
Bagatur T, Onen F (2018) Development of predictive model for flood routing using genetic expression programming. Journal of Flood Risk Management 11:444–454
Banerjee A, Chattopadhyay S, Gheorghe G, Gavrilas M (2019) Minimization of reliability indices and cost of power distribution systems in urban areas using an efficient hybrid meta-heuristic algorithm. Soft Comput 23(4):1257–1281
Barati R (2011) Parameter estimation of nonlinear Muskingum models using Nelder-Mead simplex algorithm. J Hydrol Eng 16(11):946–954
Barati R (2013) Application if excel solver for parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum models. KSCE J Civ Eng 17(5):1139–1148
Chen W, Panahi M, Tsangaratos P, Shahabi H, Ilia I, Panahi S, Ahmad BB (2019) Applying population-based evolutionary algorithms and a neuro-fuzzy system for modeling landslide susceptibility. Catena 172:212–231
Das A (2004) Parameter estimation for Muskingum models. J Irrig Drain Eng 130(2):140–147
Easa SM (2013) Improved nonlinear Muskingum model with variable exponent parameter. J Hydrol Eng ASCE 18(22):1790–1794
Easa SM (2014) New and improved four-parameter non-linear Muskingum model. Proc Inst Civ Eng 167(5):288–298
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In MHS'95. Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, pp.39-43
Eberhart R, Shi Y (2001) Particle swarm optimization: developments, applications and resources. In Proceedings of the 2001 congress on evolutionary computation, IEEE Cat. No. 01TH8546, 1, pp.81-86
Ehteram M, Binti Othman F, Mundher Yaseen Z, Abdulmohsin Afan H, Falah Allawi M, Bt. Abdul Malek M, Najah Ahmed A, Shahid S, P. Singh V, el-Shafie A (2018) Improving the Muskingum flood routing method using a hybrid of particle swarm optimization and bat algorithm. Water 10(6):807
Farahani NN, Farzin S, Karami H (2018) Flood routing by kidney algorithm and Muskingum model. Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3482-x
Farahani N, Karami H, Farzin S, Ehteram M, Kisi O, El Shafie A (2019) A new method for flood routing utilizing four-parameter nonlinear Muskingum and shark algorithm. Water Resour Manag 33:4879–4893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02409-2
Garg H (2016) A hybrid PSO-GA algorithm for constrained optimization problems. Appl Math Comput 274:292–305
Geem ZW (2006) Parameter estimation for the nonlinear Muskingum model using the BFGS technique. J Irrig Drain Eng 132(5):474–478
Geem ZW (2011) Parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum model using parameter-setting-free harmony search. J Hydrol Eng 16(8):684–688
Gill MA (1978) Flood routing by the Muskingum method. J Hydrol 36(3–4):353–363
Hamedi F, Bozorg-Haddad O, Pazoki M, Asgari HR, Parsa M, Loaiciga HA (2016) Parameter estimation of extended nonlinear Muskingum models with the weed optimization algorithm. J Irrig Drain Eng 142(12):1–11
Kang L, Zhou L (2018) Parameter estimation of variable-parameter nonlinear Muskingum model using excel solver. In IOP Conference series: earth and environmental science, 121(5), pp.052047
Kang L, Zhou L, Zhang S (2017) Parameter estimation of two improved nonlinear Muskingum models considering the lateral flow using a hybrid algorithm. Water Resour Manag 31(14):4449–4467
Karahan H (2014) Discussion of “improved nonlinear Muskingum model with variable exponent parameter” by Said M. Easa. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering 19(10):07014007
Karahan H, Gurarslan G, Geem ZW (2013) Parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum flood-routing model using a hybrid harmony search algorithm. J Hydrol Eng 18(3):352–360
Kaveh A, Zolghadr A (2018) Meta-heuristic methods for optimization of truss structures with vibration frequency constraints. Acta Mech 229(10):3971–3992
Kim JH, Geem ZW, Kim ES (2001) Parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum model using harmony search. JAWRA Journal of the American Water Resources Association 37(5):1131–1138
Luo J, Xie J (2010) Parameter estimation for nonlinear Muskingum model based on immune clonal selection algorithm. J Hydrol Eng 15(10):844–851
Luo J, Yang X, Xie J (2016) Evaluation and improvement of routing procedure for nonlinear Muskingum models. International Journal of Civil Engineering 14(1):47–59
Moghaddam A, Behmanesh J, Farsijani A (2016) Parameters estimation for the new four-parameter nonlinear Muskingum model using the particle swarm optimization. Water Resour Manag 30(7):2143–2160
Mohan S (1997) Parameter estimation of nonlinear Muskingum models using genetic algorithm. J Hydraul Eng 123(2):137–142
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2016) Application of new hybrid optimization technique for parameter estimation of new improved version of Muskingum model. Water Resour Manag 30(13):4713–4730
Niazkar M, Afzali SH (2017) New nonlinear variable-parameter Muskingum models. KSCE J Civ Eng 21(7):2958–2967
Nikoo M, Ramezani F, Hadzima-Nyarko M, Nyarko EK (2016) Flood-routing modeling with neural network optimized by social-based algorithm. Nat Hazards 82(1):1–24
Orouji H, Bozorg-Haddad O, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Marino MA (2013) Estimation of Muskingum parameter by meta-heuristic algorithms. Proc Inst Civ Eng 166(6):315–324
Settles M (2005) An introduction to particle swarm optimization. University of Idaho, Department of Computer Science, pp 1–8
Tung YK (1985) River flood routing by nonlinear Muskingum method. J Hydraul Eng 111(12):1447–1460
Vatankhah AR (2014) Discussion of parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum flood-routing model using a hybrid harmony search algorithm by Halil Karahan, Gurhan Gurarslan, and Zong woo Geem. J Hydrol Eng 19(4):839–842
Vatankhah AR (2018) Discussion of “assessment of modified honey bee mating optimization for parameter estimation of nonlinear muskingum models” by Majid Niazkar and Seied Hosein Afzali. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering 23(4):07018002
Viessman W, Lewis GL (2003) Introduction to hydrology. Prentice Hall India (P) limited, New Jersey
Wilson EM (1974) Engineering hydrology. Macmillan Education LTD., Hampshire, United Kingdom
Wu J, Long J, Liu M (2015) Evolving RBF neural networks for rainfall prediction using hybrid particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm. Neurocomputing 148:136–142
Xu G, Cui Q, Shi X, Ge H, Zhan ZH, Lee HP, Wu C (2019) Particle swarm optimization based on dimensional learning strategy. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation 45:33–51
Yoon J, Padmanabhan G (1993) Parameter estimation of linear and nonlinear Muskingum models. J Water Resour Plan Manag 119(5):600–610
Yuan X, Wu X, Tian H, Yuan Y, Adnan RM (2016) Parameter identification of nonlinear Muskingum model with backtracking search algorithm. Water Resour Manag 30(8):2767–2783
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbari, R., Hessami-Kermani, MR. & Shojaee, S. Flood Routing: Improving Outflow Using a New Non-linear Muskingum Model with Four Variable Parameters Coupled with PSO-GA Algorithm. Water Resour Manage 34, 3291–3316 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02613-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02613-5