Abstract
Purpose
There is no clear information about the level of Apelin-13 in patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN). In this study, we investigated whether there is a relationship between Apelin-13 level and the severity of the disease in patients with DN.
Methods
In our case–control study, we included patients who applied to the endocrinology outpatient clinic in 2019. Patients without a history of diabetes were determined as the healthy group (group 1). The patients were divided into 4 groups according to their microalbumin and creatinine levels. Venous blood samples were obtained from all patients for routine laboratory parameters and Apelin-13 levels. Homeostatic Model Assessment-Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) for insulin resistance was calculated using the formula: plasma glucose X insulin level/405.
Results
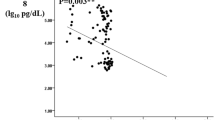
Albumin was found to be significantly lower in group 5 (p = 0.032), hemoglobin A1c, microalbumin/creatinine and HOMA-IR values were found to be significantly lower in group 1 (p < 0.001 for each). Apelin-13 level was found to be significantly higher in group 4 and group 5 (p < 0.001). A negative correlation was found between Apelin-13 and GFR (r = − 0.286, p = 0.003). A positive correlation was found between Apelin-13 and HOMA-IR (r = 0.309, p = 0.009) and microalbumin/creatinine (r = 0.296, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In patients with DN, Apelin-13 level increases with the severity of the disease and can be used as a biomarker for staging of DN.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett PH, Knowler WC (2006) Definition, diagnosis, and classification of diabetes mellitus and glucose homeostasis. In: Weir CR, King CL, Moses AC, Smith RC, Jacobson AM, Kahn CR (eds) Joslin’s diabetes mellitus. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, Malanda B (2018) IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 138:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.023
Davies MJ, D’Alessio DA, Fradkin J, Kernan WN, Mathieu C, Mingrone G, Rossing P, Tsapas A, Wexler DJ, Buse JB, Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018 (2018) A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 41(12):2669–2701. https://doi.org/10.2337/dci18-0033
Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, Chiang JL, de Boer IH, Goldstein-Fuchs J, Hirsch IB, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Narva AS, Navaneethan SD, Neumiller JJ, Patel UD, Ratner RE, Whaley-Connell AT, Molitch ME (2014) Diabetic kidney disease: a report from an ADA Consensus Conference. Diabetes Care 37(10):2864–2883. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc14-1296
Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y, Fujii R, Kakegawa T, Zou MX, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S, Hinuma S, Kitada C, Kurokawa T, Onda H, Fujino M (1998) Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251(2):471–476. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1998.9489
Buyuksimsek M, Gulumsek E, Aslan MZ, Ozturk HA, Bashir AM, Icen YK, Ay N, Acibucu F, Koc M, Sumbul HE, Saler T (2020) Serum elabela levels are elevated in patients with hyperthyroidism. Tohoku J Exp Med 251(4):255–261. https://doi.org/10.1620/tjem.251.255
Yasir M, Senthilkumar GP, Jayashree K, Ramesh Babu K, Vadivelan M, Palanivel C (2019) Association of serum omentin-1, apelin and chemerin concentrations with the presence and severity of diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Arch Physiol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2019.1680698
Chen H, Liu C, Cheng C, Zheng L, Huang K (2018) Effects of apelin peptides on diabetic complications. Curr Protein Pept Sci 19(2):179–189. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203718666170918154728
Alipour FG, Ashoori MR, Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y, Zarghami N (2017) An overview on biological functions and emerging therapeutic roles of apelin in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr 11(Suppl 2):S919–S923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2017.07.016
Hu H, He L, Li L, Chen L (2016) Apelin/APJ system as a therapeutic target in diabetes and its complications. Mol Genet Metab 119(1–2):20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.07.012
Read C, Nyimanu D, Williams TL, Huggins DJ, Sulentic P, Macrae R, Yang P, Glen RC, Maguire JJ, Davenport AP (2019) International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CVII. Structure and pharmacology of the apelin receptor with a recommendation that elabela/toddler is a second endogenous peptide ligand. Pharmacol Rev 71(4):467–502. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.119.017533
Day RT, Cavaglieri RC, Feliers D (2013) Apelin retards the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 304(6):F788–F800. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00306.2012
Chen H, Li J, Jiao L, Petersen RB, Li J, Peng A, Zheng L, Huang K (2014) Apelin inhibits the development of diabetic nephropathy by regulating histone acetylation in Akita mouse. J Physiol 592(3):505–521. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2013.266411
Guo C, Liu Y, Zhao W, Wei S, Zhang X, Wang W, Zeng X (2015) Apelin promotes diabetic nephropathy by inducing podocyte dysfunction via inhibiting proteasome activities. J Cell Mol Med 19(9):2273–2285. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12619
Liu Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Zeng X (2017) Apelin involved in progression of diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting autophagy in podocytes. Cell Death Dis 8(8):e3006. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.414
Hus-Citharel A, Bouby N, Frugière A, Bodineau L, Gasc JM, Llorens-Cortes C (2008) Effect of apelin on glomerular hemodynamic function in the rat kidney. Kidney Int 74(4):486–494. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2008.199
Erdem G, Dogru T, Tasci I, Sonmez A, Tapan S (2008) Low plasma apelin levels in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 116(5):289–292. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-1004564
Coskun Yavuz Y, Sevinc C, Deniz MS, Yavuz S, Altunoren O, Sayarlioglu H, Dogan E (2015) The role of Apelin 13 in progression of chronic kidney disease. Iran J Kidney Dis 9(5):369–373
Zhang H, Gong D, Ni L, Shi L, Xu W, Shi M, Chen J, Ai Y, Zhang X (2018) Serum elabela/toddler levels are associated with albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cell Physiol Biochem 48(3):1347–1354. https://doi.org/10.1159/000492093
Demirpence M, Yilmaz H, Colak A, Pamuk BO, Karakoyun I, Basok B (2018) Apelin: A potential novel serum biomarker for early detection of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. North Clin Istanb 6(2):151–155. https://doi.org/10.14744/nci.2018.6213421
Boucher J, Masri B, Daviaud D, Gesta S, Guigné C, Mazzucotelli A, Castan-Laurell I, Tack I, Knibiehler B, Carpéné C, Audigier Y, Saulnier-Blache JS, Valet P (2005) Apelin, a newly identified adipokine up-regulated by insulin and obesity. Endocrinology 146(4):1764–1771. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2004-1427
Castan-Laurell I, Dray C, Attané C, Duparc T, Knauf C, Valet P (2011) Apelin, diabetes, and obesity. Endocrine 40(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-011-9507-9
Gao Z, Zhong X, Tan YX, Liu D (2021) Apelin-13 alleviates diabetic nephropathy by enhancing nitric oxide production and suppressing kidney tissue fibrosis. Int J Mol Med 48(3):175. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2021.5008
Zheng Q, Tian G, Xu F, Ci X, Luan R, Wu L, Lu X (2021) The role of Elabela in kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol 53(9):1851–1857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-021-02790-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
İçen, G., Dağlıoğlu, G. & Evran, M. Evaluation of Apelin-13 levels in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Int Urol Nephrol 55, 345–353 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03323-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03323-0