Abstract
Background
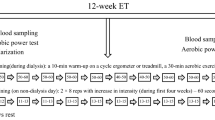
Chronic kidney disease patients on hemodialysis treatment are characterized by increased levels of inflammatory markers and oxidative stress, in addition to a significant deterioration in physical function. The benefits of physical exercise on the functional capacity of this patients are well known; however, it can also improve the endogenous antioxidant defense system and the inflammatory state, but still very few studies have been carried out. This is the first study to analyze the effect of a 4-month exercise program with combined aerobic and strength training in patients undergoing hemodialysis, under two modalities.
Methods
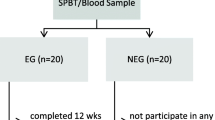
Seventy-one patients undergoing hemodialysis were enrolled and randomized in two groups, one of them performing an intra-dialysis exercise program (n = 36), and the other carrying out a home-based exercise program (n = 35). Serum levels of oxidative stress and inflammation biomarkers were determined before and after the intervention.
Results
IL-6 plasma levels showed a significant decrease in the intra-dialysis group after exercise (42.61 ± 9.21 to 26.40 ± 7.84, p = 0.03), while CRP levels decreased significantly in the home-based group (16.12 ± 24.18 to 8.50 ± 11.28, p = 0.03). MCP-1, TNF-α, ICAM-1 and the oxidative stress markers MDA, GSH and GSSG, did not undergo significant changes after the intervention.
Conclusion
Four months of combined strength and aerobic endurance exercise improve the inflammatory status of hemodialysis patients by significantly reducing IL-6 levels in those subjects who perform intra-dialysis exercise and CRP levels in those who do it at home.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dungey M, Hull KL, Smith AC, Burton JO, Bishop NC (2013) Inflammatory factors and exercise in chronic kidney disease. Int J Endocrinol 2013:569831. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/569831
Roubicek T, Bartlova M, Krajickova J, Haluzikova D, Mraz M, Lacinova Z, Kudla M, Teplan V, Haluzik M (2009) Increased production of proinflammatory cytokines in adipose tissue of patients with end-stage renal disease. Nutrition 25:762–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2008.12.012
Bergström J, Lindholm B, Lacson E, Owen W, Lowrie EG, Glassock RJ, Ikizler TA, Wessels FJ, Moldawer LL, Wanner C, Zimmermann J (2000) What are the causes and consequences of the chronic inflammatory state in chronic dialysis patients? Semin Dial 13:163–175
Heine GH, Ulrich C, Seibert E, Seiler S, Marell J, Reichart B, Krause M, Schlitt A, Köhler H, Girndt M (2008) CD14++CD16+ monocytes but not total monocyte numbers predict cardiovascular events in dialysis patients. Kidney Int 73:622–629. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5002744
Workeneh BT, Mitch WE (2010) Review of muscle wasting associated with chronic kidney disease. Am J Clin Nutr 91:1128S-1132S. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2010.28608B
Weiner DE, Tighiouart H, Amin MG, Stark PC, MacLeod B, Griffith JL, Salem DN, Levey AS, Sarnak MJ (2004) Chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality: a pooled analysis of community-based studies. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:1307–1315
Romeu M, Nogues R, Marcas L, Sánchez-Martos V, Mulero M, Martinez-Vea A, Mallol J, Giralt M (2010) Evaluation of oxidative stress biomarkers in patients with chronic renal failure: a case control study. BMC Res Notes 3:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-3-20
Dounousi E, Papavasiliou E, Makedou A, Ioannou K, Katopodis KP, Tselepis A, Siamopoulos KC, Tsakiris D (2006) Oxidative stress is progressively enhanced with advancing stages of CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 48:752–760. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.08.015
Quiroga B, Marin C, Goicoechea M, Luno J, Reque J (2012) Inflammatory biomarkers in chronic kidney disease: a review. Recent Patents Biomarkers 2:131–138
Haugen E, Nath KA (1999) The involvement of oxidative stress in the progression of renal injury. Blood Purif 17:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1159/000014377
Cibulka R, Racek J (2007) Metabolic disorders in patients with chronic kidney failure. Physiol Res 56:697–705
Cheema BSB, Singh MAF (2005) Exercise training in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis: a systematic review of clinical trials. Am J Nephrol 25:352–364. https://doi.org/10.1159/000087184
Blake C, Codd MB, Cassidy A, O’Meara YM (2000) Physical function, employment and quality of life in end-stage renal disease. J Nephrol 13:142–149
Painter P, Roshanravan B (2013) The association of physical activity and physical function with clinical outcomes in adults with chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 22:615–623. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNH.0b013e328365b43a
Kouidi EJ, Grekas DM, Deligiannis AP (2009) Effects of exercise training on noninvasive cardiac measures in patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Kidney Dis 54:511–521. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.03.009
Dungey M, Young HML, Churchward DR, Burton JO, Smith AC, Bishop NC (2017) Regular exercise during haemodialysis promotes an anti-inflammatory leucocyte profile. Clin Kidney J 10:813–821. https://doi.org/10.1093/ckj/sfx015
Lombardi G, Sanchis-Gomar F, Perego S, Sansoni V, Banfi G (2016) Implications of exercise-induced adipo-myokines in bone metabolism. Endocrine 54:284–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0834-0
Esgalhado M, Stockler-Pinto MB, de França Cardozo LFM, Costa C, Barboza JE, Mafra D (2015) Effect of acute intradialytic strength physical exercise on oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Res Clin Pract 34:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.krcp.2015.02.004
Groussard C, Rouchon-Isnard M, Coutard C, Romain F, Malardé L, Lemoine-Morel S, Martin B, Pereira B, Boisseau N (2015) Beneficial effects of an intradialytic cycling training program in patients with end-stage kidney disease. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 40:550–556. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2014-0357
Satiler W, Malle E, Kostner GM (1998) Methodological approaches for assessing lipid and protein oxidation and modification in plasma and isolated lipoproteins. Lipoprotein Protocols 110:167–192
Tsikas D (2017) Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: analytical and biological challenges. Anal Biochem 524:13–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.10.021
Gérard-Monnier D, Erdelmeier I, Régnard K, Moze-Henry N, Yadan JC, Chaudière J (1998) Reactions of 1-methyl-2-phenylindole with malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxyalkenals. Analytical applications to a colorimetric assay of lipid peroxidation. Chem Res Toxicol 11:1176–1183. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx9701790
Weber D, Davies MJ, Grune T (2015) Determination of protein carbonyls in plasma, cell extracts, tissue homogenates, isolated proteins: focus on sample preparation and derivatization conditions. Redox Biol 5:367–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.06.005
Reznick AZ, Packer L (1994) Oxidative damage to proteins: spectrophotometric method for carbonyl assay. Methods Enzymol 233:357–363
Hissin PJ, Hilf R (1976) A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal Biochem 74:214–226
Rauramaa R, Halonen P, Väisänen SB, Lakka TA, Schmidt-Trucksäss A, Berg A, Penttilä IM, Rankinen T, Bouchard C (2004) Effects of aerobic physical exercise on inflammation and atherosclerosis in men: the DNASCO Study: a 6-year randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 140:1007–1014
Castaneda C, Gordon PL, Parker RC, Uhlin KL, Roubenoff R, Levey AS (2004) Resistance training to reduce the malnutrition-inflammation complex syndrome of chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis 43:607–616
Viana JL et al (2014) Evidence for anti-inflammatory effects of exercise in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:2121–2130. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2013070702
Liao M-T et al (2016) Intradialytic aerobic cycling exercise alleviates inflammation and improves endothelial progenitor cell count and bone density in hemodialysis patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 95:e4134
Cheema B, Abas H, Smith B, O’Sullivan A, Chan M, Patwardhan A, Kelly J, Gillin A, Pang G, Lloyd B, Singh MF (2007) Progressive exercise for anabolism in kidney disease (peak): a randomized, controlled trial of resistance training during hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:1594–1601. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2006121329
Cheema BSB, Abas H, Smith BCF, O’Sullivan AJ, Chan M, Patwardhan A, Kelly J, Gillin A, Pang G, Lloyd B, Berger K, Baune BT, Fiatarone Singh MA (2011) Effect of resistance training during hemodialysis on circulating cytokines: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Appl Physiol 111:1437–1445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1763-5
Moraes C, Stockler-Pinto MB, Lobo JC, Barros AF, Wady MT, Seguins WS, Bessa B, Fouque D, Mafra D (2012) Resistance exercise program: intervention to reduce inflammation and improve nutritional status in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Res Clin Pract 31:A58. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.KRCP.2012.04.490
Wilund KR, Tomayko EJ, Wu P-T, Ryong Chung H, Vallurupalli S, Lakshminarayanan B, Fernhall B (2010) Intradialytic exercise training reduces oxidative stress and epicardial fat: a pilot study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:2695–2701. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq106
Afsar R, Shegarfy L, Shavandi N, Sanavi S (2010) Effects of aerobic exercise and resistance training on lipid profiles and inflammation status in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Indian J Nephorol 20(4):185–189
Ikizler T et al (2018) Metabolic effects of diet and exercise in patients with moderate to severe CKD: a randomized clinical trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 29(1):250–259
Moraes C et al (2014) Resistance exercise: a strategy to attenuate inflammation and protein-energy wasting in hemodialysis patients? Int Urol Nephrol 46(8):1655–1662
Barreto D et al (2010) Plasma interleukin-6 is independently associated with mortality in both hemodialysis and pre-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 77(6):550–556
Böhm J et al (2017) Acute effect of intradialytic aerobic exercise on solute removal, blood gases and oxidative stress in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Bras Nefrol 39(2):172–180
Luengo P et al (2009) Validation of alternative anthropometric indexes as cardiovascular risk markers. Endocrinol Nutr 56(9):439–446
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Susana Arahuetes Ruiz for her help.
Funding
This work has been financed by “Ayudas a Proyectos En Consolidación CEU—Banco Santander” (USPBS-PCON04-2015) Universidad CEU San Pablo. Madrid, Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RGM, ESO and JLL: conceived the project; AGT and RGM: performed patient enrollment, clinical review and monitoring; EMO and BPD: implemented and performed exercise program monitoring; IS-V and JLL: designed the biochemical experiments; EMO, IS-V and JLL: performed the biochemical experiments. AGT., RGM., IS-V, ESO and JLL: analyzed and interpreted data. IS-V, ESO: reviewed the article. EMO and JLL wrote the article. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The research proposal received approval from the Ethics Committee of Biomedical Research of University and Polytechnic Hospital La Fe of Valencia (register number 2016/0123) and all patients gave written informed consent to participate.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meléndez-Oliva, E., Sánchez-Vera Gómez-Trelles, I., Segura-Orti, E. et al. Effect of an aerobic and strength exercise combined program on oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers in patients undergoing hemodialysis: a single blind randomized controlled trial. Int Urol Nephrol 54, 2393–2405 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03146-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03146-z