Abstract
Background
Botulinum toxin type A (BTX-A) intravesical instillation and BTX-A intravesical injection are both effective treatments or overactive bladder (OAB) and interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS), but direct comparative studies of the two treatments are lacking.
Methods
We conducted a pairs-comparison meta-analysis and an adjusted indirect comparison meta-analysis extracting published data from randomized controlled trials in literature databases from the inception of each database to Aug. 31, 2021, evaluating efficacy and safety of BTX-A intravesical instillation and BTX-A intravesical injection. We also carried out a subgroup analysis.
Results
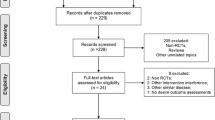
We identified 24 trials in 21 studies were included in our study, of which 18 trials in 17 studies were BTX-A intravesical injections, 6 trials in 4 studies were BTX-A intravesical instillation. Compared with the normal saline injection, BTX-A intravesical injections for patients with OAB and IC/ BPS can obviously improve the symptoms of urinary frequency, urgency episode, UI and UUI, but BTX-A significantly increased the rate of urinary retention and urinary tract infection and increased PVR (p < 0.05). Adjusted indirect comparison meta-analysis showed that BTX-A intravesical injections was more effective than BTX-A intravesical instillation (p > 0.05). Surprisingly, BTX-A intravesical instillation had fewer side effects than BTX-A intravesical injections (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Although BTX-A intravesical injections of OAB and IC/BPS has been significantly superior the BTX-A intravesical instillation, it has major side effects, but this needs to be confirmed by more large-scale, multicenter, direct comparison randomized controlled trials.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robinson D, Cardozo L (2019) Managing overactive bladder. Climacteric 22(3):250–256. https://doi.org/10.1080/13697137.2018.1552254
Marcu I, Campian EC, Tu FF (2018) Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Semin Reprod Med 36(2):123–135. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1676089
Chuang YC, Meng E, Chancellor M, Kuo HC (2020) Pain reduction realized with extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of symptoms associated with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome-A prospective, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurourol Urodyn 39(5):1505–1514. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.24382
Newman DK, Borello-France D, Sung VW (2018) Structured behavioral treatment research protocol for women with mixed urinary incontinence and overactive bladder symptoms. Neurourol Urodyn 37(1):14–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.23244
Lightner DJ, Gomelsky A, Souter L, Vasavada SP (2019) Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline amendment 2019. J Urol 202(3):558–563. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000000309
Hanno PM, Erickson D, Moldwin R, Faraday MM, American Urological Association (2015) Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: AUA guideline amendment. J Urol 193(5):1545–1553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2015.01.086
Peyronnet B, Mironska E, Chapple C et al (2019) A comprehensive review of overactive bladder pathophysiology: on the way to tailored treatment. Eur Urol 75(6):988–1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.038
Patnaik SS, Laganà AS, Vitale SG et al (2017) Etiology, pathophysiology and biomarkers of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Arch Gynecol Obstet 295(6):1341–1359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-017-4364-2
Ahlberg J, Edlund C, Wikkelsö C, Rosengren L, Fall M (2002) Neurological signs are common in patients with urodynamically verified “idiopathic” bladder overactivity. Neurourol Urodyn 21(1):65–70. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.2094
Ali RH, Gadallah NA, El Zohiery AK, Elwy M, Serag I (2019) Neurophysiologic study in idiopathic overactive bladder. Neurourol Urodyn 38(1):223–230. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.23834
Sacco E (2012) Fisiopatologia della vescica iperattiva [Physiopathology of overactive bladder syndrome]. Urologia 79(1):24–35. https://doi.org/10.5301/RU.2012.8972
Ballaro A (2008) The elusive electromyogram in the overactive bladder: a spark of understanding. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 90(5):362–367
Zhang L, Ihsan AU, Cao Y et al (2017) An immunogenic peptide, T2 induces interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome: an autoimmune mouse model for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Inflammation 40(6):2033–2041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0643-0
Kątnik-Prastowska I, Lis J, Matejuk A (2014) Glycosylation of uroplakins. Implications for bladder physiopathology. Glycoconj J 31(9):623–636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-014-9564-4
Aizawa N (2019) Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 154(5):255–258. https://doi.org/10.1254/fpj.154.255
Parsons CL, Bautista SL, Stein PC, Zupkas P (2000) Cyto-injury factors in urine: a possible mechanism for the development of interstitial cystitis. J Urol 164(4):1381–1384
Keay SK, Zhang CO (2016) Abnormal Akt signalling in bladder epithelial cell explants from patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome can be induced by antiproliferative factor treatment of normal bladder cells. BJU Int 118(1):161–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.13457
Grundy L, Caldwell A, Brierley SM (2018) Mechanisms underlying overactive bladder and interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Front Neurosci 12:931. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00931 (Published 2018 Dec 12)
Bschleipfer T, Doggweiler R, Schultz-Lampel D et al (2019) Diagnostik und therapie der interstitiellen zystitis (IC/BPS): S2k-Leitlinie der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Urologie [Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis (IC/PBS): S2k guideline of the German Society of Urology]. Urologe A. 58(11):1313–1323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00120-019-01054-2 (published correction appears in Urologe A. 2019 Dec; 58(12):1498)
Grzybowska ME, Rechberger T, Wrobel A et al (2021) The Urogynecology Section of the Polish Society of Gynecologists and Obstetricians guidelines on the management of non-neurogenic overactive bladder syndrome in women. Ginekol Pol 92(3):236–251. https://doi.org/10.5603/GP.2021.0046
Nitti VW, Patel A, Karram M (2021) Diagnosis and management of overactive bladder: a review. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/jog.14708 (published online ahead of print, 2021 Feb 16)
Chancellor MB, Smith CP (2021) Use of botulinum toxin in the genitourinary system. Handb Exp Pharmacol 263:171–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2019_308
Chen JL, Kuo HC (2020) Clinical application of intravesical botulinum toxin type A for overactive bladder and interstitial cystitis. Investig Clin Urol 61(Suppl 1):S33–S42. https://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2020.61.S1.S33
Chiu B, Tai HC, Chung SD, Birder LA (2016) Botulinum toxin A for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Toxins (Basel). 8(7):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8070201 (Published 2016 Jul 1)
Lin YH, Chiang BJ, Liao CH (2020) Mechanism of action of botulinum toxin A in treatment of functional urological disorders. Toxins (Basel). 12(2):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020129 (Published 2020 Feb 18)
Oh HM, Chung ME (2015) Botulinum toxin for neuropathic pain: a review of the literature. Toxins (Basel). 7(8):3127–3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7083127 (Published 2015 Aug 14)
Pellett S, Yaksh TL, Ramachandran R (2015) Current status and future directions of botulinum neurotoxins for targeting pain processing. Toxins (Basel). 7(11):4519–4563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7114519 (Published 2015 Nov 4)
Courseau M, Salle PV, Ranoux D, de Pouilly LA (2018) Efficacy of intra-articular botulinum toxin in osteoarticular joint pain: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin J Pain 34(4):383–389. https://doi.org/10.1097/AJP.0000000000000538
Luvisetto S, Gazerani P, Cianchetti C, Pavone F (2015) Botulinum toxin type a as a therapeutic agent against headache and related disorders. Toxins (Basel). 7(9):3818–3844. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7093818 (Published 2015 Sep 23)
Machado D, Kumar A, Jabbari B (2016) Abobotulinum toxin A in the treatment of chronic low back pain. Toxins (Basel). 8(12):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8120374 (Published 2016 Dec 15)
Safarpour Y, Jabbari B (2018) Botulinum toxin treatment of pain syndromes -an evidence based review. Toxicon 147:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2018.01.017
Sun Y, Luo D, Tang C, Yang L, Shen H (2015) The safety and efficiency of onabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of overactive bladder: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Int Urol Nephrol 47(1779):1788
Giannantoni A, Costantini E, Di Stasi SM, Tascini MC, Bini V, Porena M (2006) Botulinum A toxin intravesical injections in the treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a pilot study. Eur Urol 49(704):709
Kuo HC, Chancellor MB (2009) Comparison of intravesical botulinum toxin type A injections plus hydrodistention with hydrodistention alone for the treatment of refractory interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. BJU Int 104(5):657–661. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08495.x
Noninvasive intravesical instillation of OBTX-A. 35, Chen JL, Kuo HC (2020) Clinical application of intravesical botulinum toxin type A for overactive bladder and interstitial cystitis. Investig Clin Urol. 61(Suppl 1):S33–S42. https://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2020.61.S1.S33
Yeh TC, Chen PC, Su YR, Kuo HC (2020) Effect of botulinum toxin A on bladder pain-molecular evidence and animal studies. Toxins (Basel). 12(2):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020098 (Published 2020 Feb 3)
Chuang YC, Kaufmann JH, Chancellor DD, Chancellor MB, Kuo HC (2014) Bladder instillation of liposome encapsulated onabotulinumtoxina improves overactive bladder symptoms: a prospective, multicenter, double-blind, randomized trial. J Urol 192(6):1743–1749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2014.07.008
Kuo HC, Liu HT, Chuang YC, Birder LA, Chancellor MB (2014) Pilot study of liposome-encapsulated onabotulinumtoxina for patients with overactive bladder: a single-center study. Eur Urol 65(6):1117–1124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.01.036
Krhut J, Navratilova M, Sykora R et al (2016) Intravesical instillation of onabotulinum toxin A embedded in inert hydrogel in the treatment of idiopathic overactive bladder: a double-blind randomized pilot study. Scand J Urol 50(3):200–205. https://doi.org/10.3109/21681805.2015.1121406
Chuang YC, Kuo HC (2017) A prospective, multicenter, double-blind, randomized trial of bladder instillation of liposome formulation onabotulinumtoxinA for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J Urol 198(2):376–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2017.02.021
Fraser MO, Chuang YC, Tyagi P et al (2003) Intravesical liposome administration—a novel treatment for hyperactive bladder in the rat. Urology 61(3):656–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-4295(02)02281-1
Signorovitch JE, Sikirica V, Erder MH et al (2012) Matching-adjusted indirect comparisons: a new tool for timely comparative effectiveness research. Value Health 15(6):940–947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2012.05.004
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ et al (2019) RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 366:l4898. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4898 (Published 2019 Aug 28)
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a metaanalysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186 (PMID: 12111919)
Akiyama Y, Nomiya A, Niimi A et al (2015) Botulinum toxin type A injection for refractory interstitial cystitis: a randomized comparative study and predictors of treatment response. Int J Urol 22(9):835–841. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.12833
Kasyan G, Pushkar D (2012) Randomized controlled trial for efficacy of botulinum toxin type A in treatment of patients suffering bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis with Hunners Lesions: preliminary results. J Urol 187:e335–e336
Kuo HC, Jiang YH, Tsai YC, Kuo YC (2016) Intravesical botulinum toxin-A injections reduce bladder pain of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome refractory to conventional treatment—a prospective, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Neurourol Urodyn 35(5):609–614. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.22760
Manning J, Dwyer P, Rosamilia A, Colyvas K, Murray C, Fitzgerald E (2014) A multicentre, prospective, randomised, double-blind study to measure the treatment effectiveness of abobotulinum A (AboBTXA) among women with refractory interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Int Urogynecol J 25(5):593–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-013-2267-8
Chapple C, Sievert KD, MacDiarmid S et al (2013) OnabotulinumtoxinA 100 U significantly improves all idiopathic overactive bladder symptoms and quality of life in patients with overactive bladder and urinary incontinence: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Urol 64(2):249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2013.04.001
Denys P, Le Normand L, Ghout I et al (2012) Efficacy and safety of low doses of onabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of refractory idiopathic overactive bladder: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled dose-ranging study. Eur Urol 61(3):520–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2011.10.028
Dmochowski R, Chapple C, Nitti VW et al (2010) Efficacy and safety of onabotulinumtoxinA for idiopathic overactive bladder: a double-blind, placebo controlled, randomized, dose ranging trial. J Urol 184(6):2416–2422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2010.08.021
Dowson C, Sahai A, Watkins J, Dasgupta P, Khan MS (2011) The safety and efficacy of botulinum toxin-A in the management of bladder oversensitivity: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Int J Clin Pract 65(6):698–704. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2011.02663.x
Flynn MK, Amundsen CL, Perevich M, Liu F, Webster GD (2009) Outcome of a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial of botulinum A toxin for refractory overactive bladder. J Urol 181(6):2608–2615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.01.117
Nitti VW, Dmochowski R, Herschorn S et al (2017) OnabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of patients with overactive bladder and urinary incontinence: results of a phase 3, randomized, placebo controlled trial. J Urol 197(2S):S216–S223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2016.10.109
Rovner E, Kennelly M, Schulte-Baukloh H, Zhou J, Haag-Molkenteller C, Dasgupta P (2011) Urodynamic results and clinical outcomes with intradetrusor injections of onabotulinumtoxinA in a randomized, placebo-controlled dose-finding study in idiopathic overactive bladder. Neurourol Urodyn 30(4):556–562. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.21021
Cruz F, Herschorn S, Aliotta P et al (2011) Efficacy and safety of onabotulinumtoxinA in patients with urinary incontinence due to neurogenic detrusor overactivity: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Urol 60(4):742–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2011.07.002
Herschorn S, Gajewski J, Ethans K et al (2011) Efficacy of botulinum toxin A injection for neurogenic detrusor overactivity and urinary incontinence: a randomized, double-blind trial. J Urol 185(6):2229–2235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2011.02.004
Sahai A, Dowson C, Khan MS, Dasgupta P, GKT Botulinum Study Group (2010) Repeated injections of botulinum toxin-A for idiopathic detrusor overactivity. Urology 75(3):552–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2009.05.097
Tincello DG, Kenyon S, Abrams KR et al (2012) Botulinum toxin a versus placebo for refractory detrusor overactivity in women: a randomised blinded placebo-controlled trial of 240 women (the RELAX study). Eur Urol 62(3):507–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2011.12.056
Meng E, Hsu YC, Chuang YC (2018) Advances in intravesical therapy for bladder pain syndrome (BPS)/interstitial cystitis (IC). Low Urin Tract Symptoms 10(1):3–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/luts.12214
Yokoyama T, Chancellor MB, Oguma K et al (2012) Botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of lower urinary tract disorders. Int J Urol 19(3):202–215. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2042.2011.02946.x
Liu HT, Kuo HC (2007) Intravesical botulinum toxin A injections plus hydrodistension can reduce nerve growth factor production and control bladder pain in interstitial cystitis. Urology 70(3):463–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2007.04.038
Hanna-Mitchell AT, Wolf-Johnston AS, Barrick SR et al (2015) Effect of botulinum toxin A on urothelial-release of ATP and expression of SNARE targets within the urothelium. Neurourol Urodyn 34(1):79–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.22508
Lew MF (2002) Review of the FDA-approved uses of botulinum toxins, including data suggesting efficacy in pain reduction. Clin J Pain 18(6 Suppl):S142–S146. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002508-200211001-00005
Lovati C, Giani L (2017) Action mechanisms of Onabotulinum toxin-A: hints for selection of eligible patients. Neurol Sci 38(Suppl 1):131–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-2884-y
Jhang JF (2019) Using botulinum toxin A for treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome-possible pathomechanisms and practical issues. Toxins (Basel). 11(11):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110641 (Published 2019 Nov 4)
Patil S, Willett O, Thompkins T et al (2016) Botulinum toxin: pharmacology and therapeutic roles in pain states. Curr Pain Headache Rep 20(3):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-016-0545-0
Antonucci F, Rossi C, Gianfranceschi L, Rossetto O, Caleo M (2008) Long-distance retrograde effects of botulinum neurotoxin A. J Neurosci 28(14):3689–3696. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0375-08.2008
Bomba-Warczak E, Vevea JD, Brittain JM et al (2016) Interneuronal transfer and distal action of tetanus toxin and botulinum neurotoxins A and D in central neurons. Cell Rep 16(7):1974–1987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.06.104
Caleo M, Restani L (2018) Direct central nervous system effects of botulinum neurotoxin. Toxicon 147:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2017.10.027
Marinelli S, Vacca V, Ricordy R et al (2012) The analgesic effect on neuropathic pain of retrogradely transported botulinum neurotoxin A involves Schwann cells and astrocytes. PLoS ONE 7(10):e47977. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047977
Zhang W, Deng X, Liu C, Wang X (2017) Intravesical treatment for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome: a network meta-analysis. Int Urogynecol J 28(4):515–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-016-3079
Wang J, Wang Q, Wu Q, Chen Y, Wu P (2016) Intravesical botulinum toxin A injections for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled studies. Med Sci Monit 22:3257–3267. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.897350
Andrade C (2020) Mean difference, standardized mean difference (SMD), and their use in meta-analysis: as simple as it gets. J Clin Psychiatry 81(5):20f13681. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.20f13681 (Published 2020 Sep 22)
Shim SR, Cho YJ, Shin IS, Kim JH (2016) Efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin injection for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 48(8):1215–1227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1295-y
Giannantoni A, Gubbiotti M, Bini V (2019) Botulinum neurotoxin A intravesical injections in interstitial cystitis/bladder painful syndrome: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Toxins (Basel). 11(9):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090510 (Published 2019 Aug 30)
Arruda RM, Takano CC, Girão MJBC, Haddad JM, Aleixo GF, Castro RA (2018) Treatment of non-neurogenic overactive bladder with OnabotulinumtoxinA: systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Tratamento da bexiga hiperativa não neurogênica com toxina botulínica A: revisão sistemática e metanálise de ensaios clínicos prospectivos, randomizados e placebo-controlados. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 40(4):225–231. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1642631
López Ramos H, Torres Castellanos L, Ponce Esparza I, Jaramillo A, Rodríguez A, Moreno BC (2017) Management of overactive bladder with onabotulinumtoxinA: systematic review and meta-analysis. Urology 100:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2016.10.026
Lee HY, Doo SW, Yang WJ et al (2019) Efficacy and safety of noninvasive intravesical instillation of onabotulinum toxin-A for overactive bladder and interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. Urology 125:50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2018.11.037
Kaufman J, Tyagi V, Anthony M, Chancellor MB, Tyagi P (2010) State of the art in intravesical therapy for lower urinary tract symptoms. Rev Urol 12(4):e181–e189
Funding
There is no funding for the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yunfeng, G., Fei, L., Junbo, L. et al. An indirect comparison meta-analysis of noninvasive intravesical instillation and intravesical injection of botulinum toxin-A in bladder disorders. Int Urol Nephrol 54, 479–491 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03107-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03107-6