Abstract
Purpose
Late onset hypogonadism (LOH) is an age-dependent reduction of testosterone associated with alterations of metabolic profile, including glucose control, insulin sensitivity, and lipid profile. The purpose of this study was to investigate the efficacy of testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) for treating metabolic disturbances through a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs).
Methods
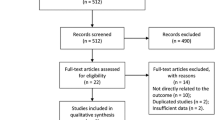
A systematic review of literature published from 1964 to November, 2019 was performed using the PubMed/Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases. Among the 1562 articles screened, 17 articles were selected for qualitative analysis and 16 articles (n = 1373) were included for data synthesis following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis (PRISMA). Criteria for final inclusion were RCTs.
Results
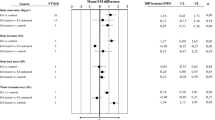
Sixteen studies were finally included (TRT group, n = 709; placebo group, n = 664). Among the metabolic markers, HbA1C [Mean difference (MD) = − 0.172, 95% CI − 0.329, − 0.015], HOMA IR (MD = − 0.514, 95% CI − 0.863, − 0.165), serum insulin (MD = − 12.622, 95% CI − 19.660, − 5.585), and leptin (MD = − 2.381, 95% CI − 2.952, − 1.810) showed significant improvement after TRT versus placebo. Among the lipid profiles, total cholesterol showed significant improvement (MD = − 0.433, 95% CI − 0.761, − 0.105) after TRT. However, HDL showed a decrease (MD = − 0.069, 95% CI − 0.121, − 0.018) after TRT. Among anthropometric markers, waist circumference showed significant improvement (MD = − 0.1640, 95% CI − 2.857, − 0.423).
Conclusion
This study demonstrated greater improvement in metabolic profiles for patients given TRT versus placebo. Further well-designed trials are needed to verify our findings and further elucidate effects of TRT on lipid profiles. This systematic review demonstrates that TRT can exert a net beneficial effect on metabolic profiles.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu FC, Tajar A, Beynon JM, Pye SR, Silman AJ, Finn JD, O’Neill TW, Bartfai G, Casanueva FF, Forti G, Giwercman A, Han TS, Kula K, Lean ME, Pendleton N, Punab M, Boonen S, Vanderschueren D, Labrie F, Huhtaniemi IT, EMAS Group (2010) Identification of late-onset hypogonadism in middle-aged and elderly men. N Engl J Med 363(2):123–135. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0911101
Corona G, Sforza A, Maggi M (2017) Testosterone replacement therapy: long-term safety and efficacy. World J Mens Health 35(2):65–76. https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2017.35.2.65
Corona G, Goulis DG, Huhtaniemi I, Zitzmann M, Toppari J, Forti G, Vanderschueren D, Wu FC (2020) European Academy of Andrology (EAA) guidelines on investigation, treatment and monitoring of functional hypogonadism in males: endorsing organization: European Society of Endocrinology. Andrology 8(5):970–987. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.12770
Ponce OJ, Spencer-Bonilla G, Alvarez-Villalobos N, Serrano V, Singh-Ospina N, Rodriguez-Gutierrez R, Salcido-Montenegro A, Benkhadra R, Prokop LJ, Bhasin S, Brito JP (2018) The efficacy and adverse events of testosterone replacement therapy in hypogonadal men: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 103(5):1745–1754
Corona GG, Rastrelli G, Maseroli E, Sforza A, Maggi M (2015) Testosterone replacement therapy and cardiovascular risk: a review. World J Mens Health 33(3):130–142. https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2015.33.3.130
Goodman N, Guay A, Dandona P, Dhindsa S, Faiman C, Cunningham GR, ARES Committee (2015) American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology position statement on the association of testosterone and cardiovascular risk. Endocr Pract 21(9):1066–1073. https://doi.org/10.4158/EP14434.PS
Chang Y, Kim JH, Noh JW, Cho YS, Park HJ, Joo KJ, Ryu S (2019) Prostate-specific antigen within the reference range, subclinical coronary atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular mortality. Circ Res 124(10):1492–1504. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.118.313413
Corona G, Isidori AM, Buvat J, Aversa A, Rastrelli G, Hackett G, Rochira V, Sforza A, Lenzi A, Mannucci E, Maggi M (2014) Testosterone supplementation and sexual function: a meta-analysis study. J Sex Med 11(6):1577–1592. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsm.12536
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7(3):177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2
Shim SR, Kim S-J (2019) Intervention meta-analysis: application and practice using R software. Epidemiol Health 41:e2019008
Basu R, Dalla Man C, Campioni M, Basu A, Nair KS, Jensen MD, Khosla S, Klee G, Toffolo G, Cobelli C, Rizza RA (2007) Effect of 2 years of testosterone replacement on insulin secretion, insulin action, glucose effectiveness, hepatic insulin clearance, and postprandial glucose turnover in elderly men. Diabetes Care 30(8):1972–1978. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc07-0359
Magnussen LV, Hvid LG, Hermann AP, Hougaard DM, Gram B, Caserotti P, Andersen MS (2017) Testosterone therapy preserves muscle strength and power in aging men with type 2 diabetes-a randomized controlled trial. Andrology 5(5):946–953. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.12396
Hackett G, Cole N, Saghir A, Jones P, Strange RC, Ramachandran S (2017) Testosterone replacement therapy: improved sexual desire and erectile function in men with type 2 diabetes following a 30-week randomized placebo-controlled study. Andrology 5(5):905–913. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.12399
Hackett G, Cole N, Bhartia M, Kennedy D, Raju J, Wilkinson P, Saghir A (2014) The response to testosterone undecanoate in men with type 2 diabetes is dependent on achieving threshold serum levels (the BLAST study). Int J Clin Pract 68(2):203–215. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.12235
Magnussen LV, Glintborg D, Hermann P, Hougaard DM, Hojlund K, Andersen M (2016) Effect of testosterone on insulin sensitivity, oxidative metabolism and body composition in aging men with type 2 diabetes on metformin monotherapy. Diabetes Obes Metab 18(10):980–989. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12701
Aversa A, Bruzziches R, Francomano D, Spera G, Lenzi A (2010) Efficacy and safety of two different testosterone undecanoate formulations in hypogonadal men with metabolic syndrome. J Endocrinol Invest 33(11):776–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03350341
Fui MNT, Prendergast LA, Dupuis P, Raval M, Strauss BJ, Zajac JD, Grossmann M (2016) Effects of testosterone treatment on body fat and lean mass in obese men on a hypocaloric diet: a randomised controlled trial. BMC Med. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-016-0700-9
Groti K, Zuran I, Antonic B, Forsnaric L, Pfeifer M (2018) The impact of testosterone replacement therapy on glycemic control, vascular function, and components of the metabolic syndrome in obese hypogonadal men with type 2 diabetes. Aging Male 21(3):158–169. https://doi.org/10.1080/13685538.2018.1468429
Shigehara K, Konaka H, Nohara T, Izumi K, Kitagawa Y, Kadono Y, Iwamoto T, Koh E, Mizokami A, Namiki M (2018) Effects of testosterone replacement therapy on metabolic syndrome among Japanese hypogonadal men: a subanalysis of a prospective randomised controlled trial (EARTH study). Andrologia. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12815
Jones TH, Arver S, Behre HM, Buvat J, Meuleman E, Moncada I, Morales AM, Volterrani M, Yellowlees A, Howell JD, Channer KS (2011) Testosterone replacement in hypogonadal men with type 2 diabetes and/or metabolic syndrome (the TIMES2 study). Diabetes Care 34(4):828–837. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-1233
Simon D, Charles MA, Lahlou N, Nahoul K, Oppert JM, Gouault-Heilmann M, Lemort N, Thibult N, Joubert E, Balkau B, Eschwege E (2001) Androgen therapy improves insulin sensitivity and decreases leptin level in healthy adult men with low plasma total testosterone: a 3-month randomized placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care 24(12):2149–2151
Heufelder AE, Saad F, Bunck MC, Gooren L (2009) Fifty-two-week treatment with diet and exercise plus transdermal testosterone reverses the metabolic syndrome and improves glycemic control in men with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes and subnormal plasma testosterone. J Androl 30(6):726–733. https://doi.org/10.2164/jandrol.108.007005
Fui MNT, Hoermann R, Grossmann M (2017) Effect of testosterone treatment on adipokines and gut hormones in obese men on a hypocaloric diet. J Endocr Soc 1(4):302–312. https://doi.org/10.1210/js.2017-00062
Hackett G, Cole N, Bhartia M, Kennedy D, Raju J, Wilkinson P (2014) Testosterone replacement therapy improves metabolic parameters in hypogonadal men with type 2 diabetes but not in men with coexisting depression: the BLAST study. J Sex Med 11(3):840–856. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsm.12404
Jensen RC, Christensen LL, Nielsen J, Schrøder HD, Kvorning T, Gejl K, Højlund K, Glintborg D, Andersen M (2018) Mitochondria, glycogen, and lipid droplets in skeletal muscle during testosterone treatment and strength training: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Andrology 6(4):547–555. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.12492
Janjgava S, Zerekidze T, Uchava L, Giorgadze E, Asatiani K (2014) Influence of testosterone replacement therapy on metabolic disorders in male patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and androgen deficiency. Eur J Med Res 19:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-014-0056-6
Wittert G, Bracken K, Robledo KP, Grossmann M, Yeap BB, Handelsman DJ, Stuckey B, Conway A, Inder W, McLachlan R, Allan C, Jesudason D, Fui MNT, Hague W, Jenkins A, Daniel M, Gebski V, Keech A (2021) Testosterone treatment to prevent or revert type 2 diabetes in men enrolled in a lifestyle programme (T4DM): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2-year, phase 3b trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 9(1):32–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30367-3
Rydén L, Grant PJ, Anker SD, Berne C, Cosentino F, Danchin N, Deaton C, Escaned J, Hammes HP, Huikuri H, Marre M, Marx N, Mellbin L, Ostergren J, Patrono C, Seferovic P, Uva MS, Taskinen MR, Tendera M, Tuomilehto J, Valensi P, Zamorano JL, Zamorano JL, Achenbach S, Baumgartner H, Bax JJ, Bueno H, Dean V, Deaton C, Erol C, Fagard R, Ferrari R, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Kirchhof P, Knuuti J, Kolh P, Lancellotti P, Linhart A, Nihoyannopoulos P, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Sirnes PA, Tamargo JL, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Wijns W, Windecker S, De Backer G, Sirnes PA, Ezquerra EA, Avogaro A, Badimon L, Baranova E, Baumgartner H, Betteridge J, Ceriello A, Fagard R, Funck-Brentano C, Gulba DC, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Kjekshus JK, Knuuti J, Kolh P, Lev E, Mueller C, Neyses L, Nilsson PM, Perk J, Ponikowski P, Reiner Z, Sattar N, Schächinger V, Scheen A, Schirmer H, Strömberg A, Sudzhaeva S, Tamargo JL, Viigimaa M, Vlachopoulos C, Xuereb RG (2013) ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD: the task force on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and developed in collaboration with the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J 34(39):3035–3087. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/eht108
Corona G, Giagulli VA, Maseroli E, Vignozzi L, Aversa A, Zitzmann M, Saad F, Mannucci E, Maggi M (2016) THERAPY OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: testosterone supplementation and body composition: results from a meta-analysis study. Eur J Endocrinol 174(3):R99-116. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-15-0262
Corona G, Maseroli E, Maggi M (2014) Injectable testosterone undecanoate for the treatment of hypogonadism. Expert Opin Pharmacother 15(13):1903–1926. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656566.2014.944896
Keating NL, O’Malley AJ, Smith MR (2006) Diabetes and cardiovascular disease during androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(27):4448–4456. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.06.2497
Harada N (2018) Role of androgens in energy metabolism affecting on body composition, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and longevity: lessons from a meta-analysis and rodent studies. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 82(10):1667–1682. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2018.1490172
Hackett G, Cole N, Mulay A, Strange RC, Ramachandran S (2019) Long-term testosterone therapy in type 2 diabetes is associated with reduced mortality without improvement in conventional cardiovascular risk factors. BJU Int 123(3):519–529
Magnussen LV, Andersen PE, Diaz A, Ostojic J, Hojlund K, Hougaard DM, Christensen AN, Nielsen TL, Andersen M (2017) MR spectroscopy of hepatic fat and adiponectin and leptin levels during testosterone therapy in type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Endocrinol 177(2):157–168. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-17-0071
Feingold KR, Brinton EA, Grunfeld C (2000) The effect of endocrine disorders on lipids and lipoproteins. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A et al (eds) Endotext. MDText.com, Inc, South Dartmouth
Finkle WD, Greenland S, Ridgeway GK, Adams JL, Frasco MA, Cook MB, Fraumeni JF Jr, Hoover RN (2014) Increased risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction following testosterone therapy prescription in men. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85805. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085805
Lunenfeld B, Mskhalaya G, Zitzmann M, Arver S, Kalinchenko S, Tishova Y, Morgentaler A (2015) Recommendations on the diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of hypogonadism in men. Aging Male 18(1):5–15. https://doi.org/10.3109/13685538.2015.1004049
Morgentaler A, Miner MM, Caliber M, Guay AT, Khera M, Traish AM (2015) Testosterone therapy and cardiovascular risk: advances and controversies. Mayo Clin Proc 90(2):224–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.10.011
Kim DK, Noh JW, Chang Y, Lee HY, Park JJ, Ryu S, Kim JHJA (2020) Association between prostate-specific antigen and serum testosterone: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Andrology 8:1194–1213
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by “Soonchunhyang University Research Fund”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.


11255_2021_2876_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file2 Changes of metabolic markers after testosterone replacement therapy: A, Adiponectin; B, hsCRP (JPG 273 KB)

11255_2021_2876_MOESM3_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file3 Changes of anthropometric markers after testosterone replacement therapy: A, Total lean body mass; B, Total fat mass (JPG 130 KB)

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S., Park, J., Kim, . et al. Efficacy of testosterone replacement therapy for treating metabolic disturbances in late-onset hypogonadism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 53, 1733–1746 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-021-02876-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-021-02876-w