Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to develop and validate nomograms to predict overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) in patients with prostate cancer.
Methods
Clinical data of patients with mPCa between 2010 and 2014 were retrieved retrospectively, and randomized into training (2/3) and validation sets (1/3). Nomograms were built with potential risk factors based on COX regression analysis. Accuracy was validated using the discrimination and calibration curve for the training and validation groups, respectively.
Results
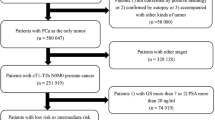
6659 mPCa patients were collected and enrolled, including 4440 in the training set and 2219 in the validation set. Multivariate analysis showed that age, marital status, PSA, biopsy Gleason score, T stage, and bone metastasis were independent risk factors for both OS and CSS. The concordance index (C-index) of OS was 0.735 (95% CI 0.722–0.748) for the internal validation and 0.735 (95% CI 0.717–0.753) for the external validation. For CSS, it was 0.734 (95% CI 0.721–0.747) and 0.742 (95% CI 0.723–0.761), respectively. The nomograms for predicting OS and CSS displayed better discrimination power in both training and validation sets. Moreover, a favorable consistency between the predicted and actual survival probabilities was demonstrated using calibration curves.
Conclusions
The nomograms showed good performances for predicting OS and CSS in patients with prostate cancer. It might be a convenient individualized predictive tool for prognosis in clinical practice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 68(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442
Gandaglia G, Abdollah F, Schiffmann J, Trudeau V, Shariat SF, Kim SP, Perrotte P, Montorsi F, Briganti A, Trinh QD, Karakiewicz PI, Sun M (2014) Distribution of metastatic sites in patients with prostate cancer: a population-based analysis. Prostate 74(2):210–216. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.22742
Huggins C, Hodges CV (1941) Studies on prostatic cancer I: the effect of castration, of estrogen and of androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. Cancer Res 168(1):293–297
Gillessen S, Attard G, Beer TM, Beltran H, Bossi A, Bristow R, Carver B, Castellano D, Chung BH, Clarke N, Daugaard G, Davis ID, de Bono J, Borges Dos Reis R, Drake CG, Eeles R, Efstathiou E, Evans CP, Fanti S, Feng F, Fizazi K, Frydenberg M, Gleave M, Halabi S, Heidenreich A, Higano CS, James N, Kantoff P, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen PL, Khauli RB, Kramer G, Logothetis C, Maluf F, Morgans AK, Morris MJ, Mottet N, Murthy V, Oh W, Ost P, Padhani AR, Parker C, Pritchard CC, Roach M, Rubin MA, Ryan C, Saad F, Sartor O, Scher H, Sella A, Shore N, Smith M, Soule H, Sternberg CN, Suzuki H, Sweeney C, Sydes MR, Tannock I, Tombal B, Valdagni R, Wiegel T, Omlin A (2018) Management of patients with advanced prostate cancer: the report of the advanced prostate cancer consensus conference APCCC 2017. Eur Urol 73(2):178–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2017.06.002
Cornford P, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E, De Santis M, Gross T, Henry AM, Joniau S, Lam TB, Mason MD, van der Poel HG, van der Kwast TH, Rouviere O, Wiegel T, Mottet N (2017) EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: treatment of relapsing, metastatic, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol 71(4):630–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.002
Wu JN, Fish KM, Evans CP, Devere White RW, Dall’Era MA (2014) No improvement noted in overall or cause-specific survival for men presenting with metastatic prostate cancer over a 20-year period. Cancer 120(6):818–823. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.28485
Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC, Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, Meyer L, Gress DM, Byrd DR, Winchester DP (2017) The eighth edition AJCC cancer staging manual: continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin 67(2):93–99. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21388
Liu Y, Xia Q, Xia J, Zhu H, Jiang H, Chen X, Zheng Y, Zhang F, Li S (2018) The impact of marriage on the overall survival of prostate cancer patients: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) analysis. Can Urol Assoc J. https://doi.org/10.5489/cuaj.5413
Guo Y, Mao S, Zhang A, Wang R, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Wang L, Zhang W, Wu Y, Ye L, Yang B, Yao X (2019) Prognostic significance of young age and non-bone metastasis at diagnosis in patients with metastatic prostate cancer: a SEER population-based data analysis. J Cancer 10(3):556–567. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.29481
Preisser F, Mazzone E, Knipper S, Nazzani S, Bandini M, Shariat SF, Tian Z, Saad F, Montorsi F, Zorn KC, Graefen M, Tilki D, Karakiewicz PI (2019) Rates of positive surgical margins and their effect on cancer-specific mortality at radical prostatectomy for patients with clinically localized prostate cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer 17(1):e130–e139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2018.09.024
Gu X, Gao X, Cui M, Xie M, Ma M, Qin S, Li X, Qi X, Bai Y, Wang D (2018) Survival outcomes of radical prostatectomy and external beam radiotherapy in clinically localized high-risk prostate cancer: a population-based, propensity score matched study. Cancer Manag Res 10:1061–1067. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S157442
Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ, DeMatteo RP (2015) Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol 16(4):e173–e180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71116-7
Song W, Lv CG, Miao DL, Zhu ZG, Wu Q, Wang YG, Chen L (2018) Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting survival in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Eur J Surg Oncol 44(10):1657–1665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2018.07.004
Iasonos A, Schrag D, Raj GV, Panageas KS (2008) How to build and interpret a nomogram for cancer prognosis. J Clin Oncol 26(8):1364–1370. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2007.12.9791
Attiyeh MA, Fernandez-Del Castillo C, Al Efishat M, Eaton AA, Gonen M, Batts R, Pergolini I, Rezaee N, Lillemoe KD, Ferrone CR, Mino-Kenudson M, Weiss MJ, Cameron JL, Hruban RH, D’Angelica MI, DeMatteo RP, Kingham TP, Jarnagin WR, Wolfgang CL, Allen PJ (2018) Development and validation of a multi-institutional preoperative nomogram for predicting grade of dysplasia in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) of the pancreas: a report from the pancreatic surgery consortium. Ann Surg 267(1):157–163. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000002015
Huang Z, Sun B, Wu S, Meng X, Cong Y, Shen G, Song S (2018) A nomogram for predicting survival in patients with breast cancer brain metastasis. Oncol Lett. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8259
Sonpavde G, Pond GR, Rosenberg JE, Choueiri TK, Bellmunt J, Regazzi AM, Mullane SA, Necchi A, Raggi D, Lee JL, Lee S, Simpson J, Derleth CL, Lin SW, Bajorin DF (2018) Nomogram to assess the survival benefit of new salvage agents for metastatic urothelial carcinoma in the era of immunotherapy. Clin Genitourin Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2018.03.016
Song W, Zhu ZG, Wu Q, Lv CG, Wang YG, Chen L, Miao DL (2018) A nomogram to predict overall survival for biliary tract cancer. Cancer Manag Res 10:1535–1541. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s163291
Zhao J, Sun G, Liao B, Zhang X, Armstrong CM, Yin X, Liu J, Chen J, Yang Y, Zhao P, Tang Q, Wang Z, Chen Z, Li X, Wei Q, Li X, Chen N, Gao AC, Shen P, Zeng H (2018) Novel nomograms for castration-resistant prostate cancer and survival outcome in patients with de novo bone metastatic prostate cancer. 122(6):994–1002. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.14398
Yang YJ, Lin GW, Li GX, Dai B, Ye DW, Wu JL, Xie HY, Zhu Y (2018) External validation and newly development of a nomogram to predict overall survival of abiraterone-treated, castration-resistant patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Asian J Androl 20(2):184–188. https://doi.org/10.4103/aja.aja_39_17
Cronin KA, Ries LA, Edwards BK (2014) The surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) program of the national cancer institute. Cancer 120(Suppl 23):3755–3757. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29049
Edge SB, Compton CC (2010) The American joint committee on cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol 17(6):1471–1474. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-0985-4
Harrell FE Jr, Lee KL, Mark DB (1996) Multivariable prognostic models: issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat Med 15(4):361–387. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0258(19960229)15:4%3c361:aid-sim168%3e3.0.co;2-4
Chen S, Lai Y, He Z, Li J, He X, Shen R, Ding Q, Chen H, Peng S, Liu W (2018) Establishment and validation of a predictive nomogram model for non-small cell lung cancer patients with chronic hepatitis B viral infection. J Transl Med 16(1):116. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-018-1496-5
Wolbers M, Koller MT, Witteman JC, Steyerberg EW (2009) Prognostic models with competing risks: methods and application to coronary risk prediction. Epidemiology 20(4):555–561. https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181a39056
Fang C, Wang W, Feng X, Sun J, Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Wang J, Chen H, Cai M, Lin J, Chen M, Chen Y, Li Y, Li S, Chen J, Zhou Z (2017) Nomogram individually predicts the overall survival of patients with gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Br J Cancer 117(10):1544–1550. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.315
Roberto M, Botticelli A, Strigari L, Ghidini M, Onesti CE, Ratti M, Benzoni I, Pizzo C, Falcone R, Lomiento D, Donida BM, Totaro L, Mazzuca F, Marchetti P (2018) Prognosis of elderly gastric cancer patients after surgery: a nomogram to predict survival. Med Oncol 35(7):111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-018-1166-8
Cao J, Yuan P, Wang L, Wang Y, Ma H, Yuan X, Lv W, Hu J (2016) Clinical nomogram for predicting survival of esophageal cancer patients after esophagectomy. Sci Rep 6:26684. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26684
Rudloff U, Jacks LM, Goldberg JI, Wynveen CA, Brogi E, Patil S, Van Zee KJ (2010) Nomogram for predicting the risk of local recurrence after breast-conserving surgery for ductal carcinoma in situ. J Clin Oncol 28(23):3762–3769. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.26.8847
Weiser MR, Landmann RG, Kattan MW, Gonen M, Shia J, Chou J, Paty PB, Guillem JG, Temple LK, Schrag D, Saltz LB, Wong WD (2008) Individualized prediction of colon cancer recurrence using a nomogram. J Clin Oncol 26(3):380–385. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2007.14.1291
Pierorazio PM, Walsh PC, Partin AW, Epstein JI (2013) Prognostic Gleason grade grouping: data based on the modified Gleason scoring system. BJU Int 111(5):753–760. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11611.x
Kim TH, Jeon HG, Jeong BC, Seo SI, Jeon SS, Choi HY, Lee HM (2017) Development of a new nomogram to predict insignificant prostate cancer in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. Scand J Urol 51(1):27–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681805.2016.1266384
Halabi S, Small EJ, Kantoff PW, Kattan MW, Kaplan EB, Dawson NA, Levine EG, Blumenstein BA, Vogelzang NJ (2003) Prognostic model for predicting survival in men with hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 21(7):1232–1237. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2003.06.100
Rusthoven CG, Carlson JA, Waxweiler TV, Yeh N, Raben D, Flaig TW, Kavanagh BD (2014) The prognostic significance of Gleason scores in metastatic prostate cancer. Urol Oncol 32(5):707–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2014.01.004
Shah S, Boucai L (2018) Effect of Age on Response to Therapy and Mortality in Patients With Thyroid Cancer at High Risk of Recurrence. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 103(2):689–697. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2017-02255
Chen CH, Chang TT, Cheng KS, Su WW, Yang SS, Lin HH, Wu SS, Lee CM, Changchien CS, Chen CJ, Sheu JC, Chen DS, Lu SN (2006) Do young hepatocellular carcinoma patients have worse prognosis? The paradox of age as a prognostic factor in the survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Liver Int 26(7):766–773. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01309.x
Pettersson A, Robinson D, Garmo H, Holmberg L, Stattin P (2018) Age at diagnosis and prostate cancer treatment and prognosis: a population-based cohort study. Ann Oncol 29(2):377–385. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx742
Guo X, Zhang C, Guo Q, Xu Y, Feng G, Li L, Han X, Lu F, Ma Y, Wang X, Wang G (2018) The homogeneous and heterogeneous risk factors for the morbidity and prognosis of bone metastasis in patients with prostate cancer. Cancer Manag Res 10:1639–1646. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S168579
Bai DS, Chen P, Qian JJ, Jin SJ, Jiang GQ (2017) Effect of marital status on the survival of patients with gallbladder cancer treated with surgical resection: a population-based study. Oncotarget 8(16):26404–26413. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15476
Zhou H, Zhang Y, Song Y, Tan W, Qiu Z, Li S, Chen Q, Gao S (2017) Marital status is an independent prognostic factor for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors patients: an analysis of the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) database. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinre.2017.02.008
Aizer AA, Chen MH, McCarthy EP, Mendu ML, Koo S, Wilhite TJ, Graham PL, Choueiri TK, Hoffman KE, Martin NE, Hu JC, Nguyen PL (2013) Marital status and survival in patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol 31(31):3869–3876. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2013.49.6489
Zhou R, Yan S, Li J (2016) Influence of marital status on the survival of patients with gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 31(4):768–775. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.13217
Kundu SD, Roehl KA, Yu X, Antenor JA, Suarez BK, Catalona WJ (2007) Prostate specific antigen density correlates with features of prostate cancer aggressiveness. J Urol 177(2):505–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2006.09.039
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WDJ and PCY collected, analyzed, interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Wd., Yuan, Pc. Development and validation of prognostic nomograms for patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Int Urol Nephrol 51, 1743–1753 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02224-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02224-z