Abstract
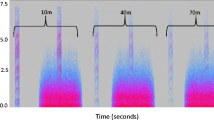
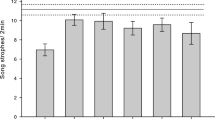
The urban environment can act as an ecological filter and impose several negative impacts on bird behaviour. Although some species are well adapted to anthropic habitats, others are sensitive to the effects of human disturbance. Here, we addressed whether noise pollution affects the territorial behaviour of the Great Kiskadee, Pitangus sulphuratus. Here we conducted a field experiment on territorial individuals in urban and rural areas. We presented a model decoy along with the playback of the species’ song at 10 m from the focal individual to simulate a territory invasion. We used simulated territory intrusions as a method to stimulate bird territorial behaviour and notedthe time birds took to respond to the stimuli in urban and non-urban areas with different noise levels. The results show that response latency had a positive correlation with noise pollution. We conclude that noise pollution can interfere with intraspecific communication, affecting territorial behaviour.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann J (1974) Observational study of behavior: sampling methods. Behavior 49:227–267
Dowling JL, Luther DA, Marra PP (2012) Comparative effects of urban development and anthropogenic noise on bird songs. Behav Ecol 23:201–209
Kunc HP (2014) The effects of anthropogenic noise on fish: a comment on Radford et al. Behav Ecol 25:1032–1032
Llambías PE, Ferretti V (2003) Parental care in the Great Kiskadee. Wilson Bull 115:214–216
Mendoza AM, Arce-plata MI (2012) Aproximación al impacto de la perturbación urbana en las vocalizaciones de. Revista de Ciencias 16:19–29
Mockford EJ, Marshall RC (2009) Effects of urban noise on song and response behaviour in great tits. Proc R Soc B 276:2979–2985
Munin RL, Fischer E, Longo JM (2012) Foraging of Great Kiskadees (Pitangus sulphuratus) and food items offered to nestlings in the Pantanal. Braz J Biol 72:459–462
Newman AE, Soma KK (2011) Aggressive interactions differentially modulate local and systemic levels of corticosterone and DHEA in a wild songbird. Horm Behav 60:389–396
Ortega C (2012) Effects of noise pollution on birds: a brief review of our knowledge. Ornithol Monogr 74:6–22
Schroeder J, Nakagawa S, Cleasby IR, Burke T (2012) Passerine birds breeding under chronic noise experience reduced fitness. PLoS One 7:e39200–e39200
Shannon G, Angeloni LM, Wittemyer G, Fristrup KM, Crooks KR (2014) Road traffic noise modifies behaviour of a keystone species. Anim Behav 94:135–141
Swaddle JP, Page LC (2007) High levels of environmental noise erode pair preferences in zebra finches: implications for noise pollution. Anim Behav 74:363–368
Tennessen JB, Parks SE, Langkilde T (2014) Traffic noise causes physiological stress and impairs breeding migration behaviour in frogs. Conserv Physiol 2:cou032
Veselý P, Buršíková M, Fuchs R (2016) Birds at the winter feeder do not recognize an artificially coloured predator. Ethology 122(12):937–944
Wacker DW, Coverdill AJ, Bauer CM, Wingfield JC (2010) Male territorial aggression and androgen modulation in high latitude populations of the Sooty, Passerella iliaca sinuosa, and Red Fox Sparrow, Passerella iliaca zaboria. J Ornithol 151:79–86
Wingfield JC (1994) Regulation of territorial behavior in the sedentary song sparrow, Melospiza melodia morphna. Horm Behav 28:1–15
Wingfield JC, Hahn TP (1994) Testosterone and territorial behaviour in sedentary and migratory sparrows. Anim Behav 47(1):77–89
Zwart MC, Dunn JC, McGowan PJ, Whittingham MJ (2015) Wind farm noise suppresses territorial defense behavior in a songbird. Behav Ecol 27(1):101–108
Acknowledgments
We thank CNPq and CAPES for financial support. We thank Fernando Igor De Godoy for song recording. We also thank Thais Regina de Almeida and two anonymous reviewers for valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lenis, P.R., Guillermo-Ferreira, R. Effect of noise on behavioural response to simulated territorial intrusion in the Great Kiskadee (Pitangus sulphuratus) (Aves: Tyrannidae). Urban Ecosyst 23, 93–96 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11252-019-00906-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11252-019-00906-1