Abstract
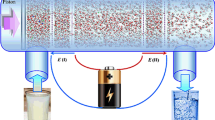
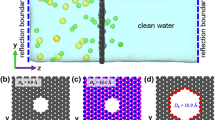
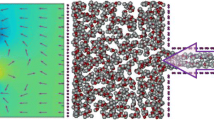
Through extensive MD simulations, desalination of water contaminated with various ions including \({\mathrm{Na}}^{+}\), \({\mathrm{K}}^{+}\), \({\mathrm{Mg}}^{2+}\), \({\mathrm{Ca}}^{2+}\), and \({\mathrm{Cl}}^{-}\) through monolayer graphene is explored, and the influences of nanopore diameter, applied pressure, contaminant concentration, and functional groups on the number of permeated water through the membrane and ion rejection are quantified. Obtained results reveal that there exists an optimum pore diameter in which maximum ion rejection by the membrane occurs. Also, it is demonstrated that the hydration energy of ions is potentially effective in ion rejection, so ions with lower hydration energy are more likely to pass through the membrane. This conclusion applies to all contaminant concentrations. Moreover, it is found that the effect of increasing the external pressure on the water permeability is more for the membranes with smaller diameters. This observation may be crucial in designing such membranes. Finally, it is shown that the hydroxylated pore has higher water permeability than the carboxylated pores. In contrast, the carboxylated pore is better at ion rejection than the hydroxylated and pristine pores.
Article Highlights
-
The desalination of water contaminated with various ions by graphene is evaluated.
-
The effects of pore size, ion concentration, and functional groups are explored.
-
The rejection of different ions for nanopores smaller than 9 Å is 100%.
-
As ion concentration increases, water permeation through the membrane decreases.
-
Water permeation for hydroxylated pore is greater than for carboxylated pore.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Azamat, J., Khataee, A., Joo, S.W.: Functionalized graphene as a nanostructured membrane for removal of copper and mercury from aqueous solution: a molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 53, 112–117 (2014)
Azamat, J., Khataee, A., Joo, S.W.: Molecular dynamics simulation of trihalomethanes separation from water by functionalized nanoporous graphene under induced pressure. Chem. Eng. Sci. 127, 285–292 (2015)
Bae, S., Kim, H., Lee, Y., Xu, X., Park, J.-S., Yi, Z., Balakrishnan, J., Lei, T., Kim, H.R., Song, Y.I., Kim, Y.-J., Kim, K.S., Özyilmaz, B., Ahn, J.-H., Hong, B.H., Iijima, S.: Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 574–578 (2010)
Bo, C., Haifeng, J., Xiang, L., Xuejiao, H.: Molecular insight of water desalination across multilayer graphene oxide membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(27), 22826–22836 (2017)
Bounds, D.: A molecular dynamics study of the structure of water around the ions Li+, Na+, K+, Ca++, Ni++ and Cl-. Mol. Phys. 54(6), 1335–1355 (1985)
Campione, A., Cipollina, A., Toet, E., Gurreri, L., Bogle, I.D.L., Micale, G.: Water desalination by capacitive electrodialysis: experiments and modelling. Desalination 473, 114150 (2020)
Cao, H., Yu, Q., Colby, R., Pandey, D., Park, C.S., Lian, J., Zemlyanov, D., Childres, I., Drachev, V., Stach, E.A., Hussain, M., Li, H., Pei, S.S., Chen, Y.P.: Large-scale graphitic thin films synthesized on Ni and transferred to insulators: Structural and electronic properties. J. Appl. Phys. 107(4), 044310 (2010)
Chen, S., Liu, W., Li, S.: Effect of long-range electrostatic repulsion on pore clogging during microfiltration. Phys. Rev. E 94, 063108 (2016)
Chen, E., Jia, L., Chen, C., Huang, F., Zhang, L.: Understanding the transport mechanism of seawater through FMOF-1 and its derivative via molecular dynamics simulation. J. Mol. Liq. 325, 115209 (2021)
Chen, Q., Yang, X.: Pyridinic nitrogen doped nanoporous graphene as desalination membrane: molecular simulation study. J. Membr. Sci. 496, 108–117 (2015)
Chogani, A., Moosavi, A., Bagher Sarvestani, A., Shariat, M.: The effect of chemical functional groups and salt concentration on performance of single-layer graphene membrane in water desalination process: a molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Mol. Liq. 301, 112–478 (2020)
Cohen-Tanugi, D., Grossman, J.C.: Water desalination across nanoporous graphene. Nano Lett. 12(7), 3602–3608 (2012)
Cohen-Tanugi, D., Grossman, J.C.: Water permeability of nanoporous graphene at realistic pressures for reverse osmosis. J. Chem. Phys. 141(7), 074704 (2014)
Cotton, F.A., Wilkinson, G., Murillo, C.A., Boch, M.: Advanced Inorganic Chemistry. Wiley, Chichester (1999)
Dang, L.X.: Mechanism and thermodynamics of ion selectivity in aqueous solutions of 18-Crown-6 Ether: a molecular dynamics study. J. Am. Chem. SOC. 26(117), 6954–6960 (1995)
Degrève, L., Vechi, S.M., Junior, C.Q.: The hydration structure of the Na+ and K+ ions and the selectivity of their ionic channels. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 1274(3), 149–156 (1996)
Dove, P.M., Nix, C.J.: The influence of the alkaline earth cations, magnesium, calcium, and barium on the dissolution kinetics of quartz. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61(16), 3329–3340 (1997)
Kumari, P., Alam, M., Siddiqi, W.A.: Usage of nanoparticles as adsorbents for waste water treatment: an emerging trend. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 22, e00128 (2019)
Gao, C., Zhang, M., Jiang, Z., Liao, J., Xie, X., Huang, T., Zhao, J., Bai, J., Pan, F.: Preparation of a highly water-selective membrane for dehydration of acetone by incorporating potassium montmorillonite to construct ionized water channel. Chem. Eng. Sci. 135, 461–471 (2015)
Geim, A., Novoselov, K.: The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 6, 183–191 (2007)
Havel, J., Högfeldt, E.: Evaluation of water sorption equilibrium data on Dowex ion exchanger using WSLET-MINUIT program. Scr. Fac. Sci. Nat. Univ. Masaryk. Brun. Chem. 25, 73–84 (1995)
Heerema, S.J., Dekker, C.: Graphene nanodevices for DNA sequencing. Nat. Nanotech 11, 127–136 (2016)
Hockney, R.W., Eastwood, J.W.: Computer Simulation Using Particles. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1988)
Hou, D., Qiao, G., Wang, P.: Molecular dynamics study on water and ions transport mechanism in nanometer channel of 13X zeolite. Chem. Eng. J. 420, 129975 (2021)
Huang, L., Zhang, M., Li, C., Shi, G.: Graphene-based membranes for molecular separation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6(14), 2806–2815 (2015)
Impey, R.W., Madden, P.A., McDonald, I.R.: Hydration and mobility of ions in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 87(25), 5071–5083 (1983)
Jorgensen, W.L., Chandrasekhar, J., Madura, J.D.: Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 79(2), 926 (1983)
Jorgensen, W.L., Maxwell, D.S., Tirado-Rives, J.: Development and testing of the OPLS All-atom force field on conformational energetics and properties of organic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 45(118), 11225–11236 (1996)
Joung, I.S., Cheatham, T.E.: Determination of Alkali and Halide monovalent ion parameters for use in explicitly solvated biomolecular simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 112(30), 9020–9041 (2008)
Jun, S., Tashi, T., Park, H.S.: Size dependence of the nonlinear elastic softening of nanoscale graphene monolayers under plane-strain bulge tests: a molecular dynamics study. J. Nanomater. 2011, 380286 (2011)
Kamal Kandezi, M., Shadman Lakmehsari, M., Matta, C.F.: Electric field assisted desalination of water using B- and N-doped-graphene sheets: a non-equilibrium molecular dynamics study. J. Mol. Liq. 302, 112574 (2020)
Kim, K.S., Zhao, Y., Jang, H., Lee, S.Y., Kim, K.S., Ahn, J.-H., Kim, P., Choi, J.-Y., Hong, B.H.: Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes. Nature 457, 706–710 (2009)
Köhler, M. H., Bordin, J. R., Barbosa, M. C.: 2D nanoporous membrane for cation removal from water: effects of ionic valence, membrane hydrophobicity, and pore size. J. Chem. Phys. 148(22) (2018)
Konatham, D., Yu, J., Ho, T.A., Striolo, A.: Simulation insights for graphene-based water desalination membranes. Langmuir 29(38), 11884–11897 (2013)
Kong, C.L.: Combining rules for intermolecular potential parameters. II. Rules for the Lennard-Jones (12–6) potential and the Morse potential. J. Chem. Phys. 59(5), 2464–2467 (1973)
Lee, S.H., Rasaiah, J.C.: Molecular dynamics simulation of ion mobility. 2. Alkali metal and halide ions using the SPC/E model for water at 25 °C. J. Phys. Chem. 100, 1420–1425 (1996)
Liu, H., Jameson, C.J., Murad, S.: Molecular dynamics simulation of ion selectivity process in nanopores. Mol. Simul. 34(2), 169–175 (2008)
Liu, B., Wu, R., Baimova, J.A., Wu, H., Law, A.W.-K., Dmitriev, S.V., Zhou, K.: Molecular dynamics study of pressure-driven water transport through graphene bilayers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18(3), 1886–1896 (2016)
Liu, Y., Xie, D., Song, M., Jiang, L., Fu, G., Liu, L., Li, J.: Water desalination across multilayer graphitic carbon nitride membrane: Insights from non-equilibrium molecular dynamics simulations. Carbon 140, 131–138 (2018b)
Liu, Y., Chen, X.: Mechanical properties of nanoporous graphene membrane. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 034303-034303–8 (2014)
Liu, B., Law, A.W.-K., Zhou, K.: Strained single-layer C2N membrane for efficient seawater desalination via forward osmosis: a molecular dynamics study. J. Membr. Sci. 550, 554–562 (2018a)
Loh, G.C.: Fast water desalination by carbon-doped boron nitride monolayer: transport assisted by water clustering at pores. Nanotechnology 30(5), 055401 (2019)
Lv, F., Fang, C., Su, J.: Enhanced water transport through a carbon nanotube controlled by the lateral pressure. Nanotechnology 30(24), 245707 (2019)
Madima, N., Mishra, S.B., Inamuddin, I., Mish, A.K.: Carbon-based nanomaterials for remediation of organic and inorganic pollutants from wastewater. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 18, 1169–1191 (2020)
Marañón Di Leo, J., Marañón, J.: Confined ions and water in nanotube. J. Mol. Struct. (thoechem.) 709(1–3), 163–166 (2004)
Meidani, K., Cao, Z., BaratiFarimani, A.: Titanium carbide MXene for water desalination: a molecular dynamics study. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4(6), 6145–6151 (2021)
Mortazavi, V., Moosavi, A., Nouri-Borujerdi, A.: Enhancing water desalination in graphene-based membranes via an oscillating electric field. Desalination 495, 114672 (2020)
Mudhoo, A., Sillanpää, M.: Magnetic nanoadsorbents for micropollutant removal in real water treatment: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 19(6), 4393–4413 (2021)
Nguyen, C. T., Beskok, A.: Water desalination performance of h-BN and optimized charged graphene membranes. Microfluid Nanofluid, 24(5), (2020)
Nguyen, C.T., Beskok, A.: Charged nanoporous graphene membranes for water desalination. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 9483–9494 (2019)
O’Hern, S.C., Boutilier, M.S.H., Idrobo, J.-C., Song, Y., Kong, J., Laoui, T., Atieh, M., Karnik, R.: Selective ionic transport through tunable subnanometer pores in single-layer graphene membranes. Nano Lett. 14(3), 1234–1241 (2014)
Plimpton, S.: Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 117(1), 1–19 (1995)
Qin, Q., Liu, X., Wang, H., Sun, T., Chu, F., Xie, L., Brault, P., Peng, Q.: Highly efficient desalination performance of carbon honeycomb based reverse osmosis membranes unveiled by molecular dynamics simulations. Nanotechnology 32, 375705 (2021)
Qureshi, K., Ahmad, M.Z., Bhatti, I.A., Zahid, M., Nisar, J., Iqbal, M.: Graphene oxide decorated ZnWO4 architecture synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity evaluation. J. Mol. Liq. 285, 778–789 (2019)
Reina, A., Jia, X., Ho, J., Nezich, D., Son, H., Bulovic, V., Dresselhaus, M.S., Kong, J.: Large area, few-layer graphene films on arbitrary substrates by chemical vapor deposition. Nano Lett. 9(1), 30–35 (2009)
Rikhtehgaran, S., Lohrasebi, A.: Water desalination by a designed nanofilter of graphene-charged carbon nanotube: a molecular dynamics study. Desalination 365, 176–181 (2015)
Robertson, A.W., Lee, G.-D., He, K., Gong, C., Chen, Q., Yoon, E., Kirkland, A.I., Warner, J.H.: Atomic structure of graphene subnanometer pores. ACS Nano 9(12), 11599–11607 (2015)
Russo, P., Hu, A., Compagnini, G.: Synthesis, properties and potential applications of porous graphene: a review. Nano-Micro Lett. 5(4), 260–273 (2013)
Sint, K., Wang, B., Král, P.: Selective ion passage through functionalized graphene nanopores. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(49), 16448–16449 (2008)
Suk, M.E., Aluru, N.R.: Water transport through ultrathin graphene. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1(10), 1590–1594 (2010)
Tansel, B.: Significance of thermodynamic and physical characteristics on permeation of ions during membrane separation: Hydrated radius, hydration free energy and viscous effects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 86, 119–126 (2012)
Tansel, B., Sager, J., Rector, T., Garland, J., Strayer, R.F., Levine, L., Roberts, M., Hummerick, M., Bauer, J.: Significance of hydrated radius and hydration shells on ionic permeability during nanofiltration in dead end and cross flow modes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 51(1), 40–47 (2006)
Tansel, B., Sager, J., Garland, J., Xu, S.: Effect of transmembrane pressure on overall membrane resistance during cross-flow filtration of solutions with high-ionic content. J. Memb. Sci. 325(1–2), 205–210 (2009)
Teow, Y.H., Mohammad, A.W.: New generation nanomaterials for water desalination: a review. Desalination 451, 2–17 (2019)
Wang, S., Sun, H., Ang, H., Tadé, M.: Adsorptive remediation of environmental pollutants using novel graphene-based nanomaterials. Chem. Eng. J. 226, 336–347 (2013)
Wang, Y., He, Z., Gupta, K.M., Shi, Q., Lu, R.: Molecular dynamics study on water desalination through functionalized nanoporous graphene. Carbon 116, 120–127 (2017)
Wells, A.F.: Structural inorganic chemistry. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1984)
Xue, M., Qiu, H., Guo, W.: Exceptionally fast water desalination at complete salt rejection by pristine graphyne monolayers. Nanotechnology 24, 505720 (2013)
Yang, J., Luo, S., Zhou, X., Li, J., Fu, J., Yang, W., Wei, D.: Flexible, tunable, and ultrasensitive capacitive pressure sensor with microconformal graphene electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11(16), 14997–15006 (2019)
Zhang, Z., Zhang, F., Liu, Z., Cheng, G., Wang, X., Ding, J.: Molecular dynamics study on the reverse osmosis using multilayer porous graphene membranes. Nanomaterials 8(10), 805 (2018)
Zhao, W.-J., Liang, L., Kong, Z., Shen, J.-W.: A review on desalination by graphene-based biomimetic nanopore: From the computational modelling perspective. J. Mol. Liq. 342, 117582 (2021)
Zielkiewicz, J.: Structural properties of water: comparison of the SPC, SPCE, TIP4P, and TIP5P models of water. J. Chem. Phys. 123(10), 104501 (2005)
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 6497 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rahiminejad, M., Mortazavi, V., Moosavi, A. et al. Transport of Water Contaminated with Various Ions Through Nanoporous Graphene: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Transp Porous Med 146, 537–557 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-022-01870-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-022-01870-9