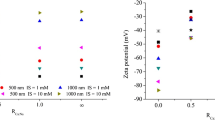
Abstract
Knowledge of colloid straining mechanism in porous media is of importance for protecting groundwater from being contaminated by biocolloids (e.g., bacteria and protozoa) and by contaminants whose transport can be facilitated by mobile particles. This study examined effects of flow velocity on colloid straining in porous media under unfavorable chemical conditions. Saturated column experiments were conducted using glass beads as collector and a \(3\,\mu \text{ m}\) carboxylate-modified polystyrene latex microsphere as model colloid. To unambiguously examine colloid straining mechanisms, attachment was minimized by extensively cleaning the collectors and adopting deionized water as solution. Results show that increasing flow velocity decreases colloid straining under unfavorable chemical conditions, in agreement with to theoretical finding in literature. This study additionally examined effects of nonionic surfactant (Triton X-100) on colloid straining in porous media under unfavorable chemical conditions. Results show that the addition of Triton X-100 decreases colloid straining and the decrease is enhanced by increasing the concentration of Triton X-100.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auset, M., Keller, A.A.: Pore-scale processes that control dispersion of colloids in saturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 40(3), W03503 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003WR002800
Auset, M., Keller, A.A.: Pore-scale visualization of colloid straining and filtration in saturated porous media using micromodels. Water Resour. Res. 42, W12S02 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005WR004639
Bendersky, M., Davis, J.M.: DLVO interaction of colloidal particles with topo-graphically and chemically heterogeneous surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 353, 87–97 (2011)
Bhattacharjee, S., Elimelech, M.: Surface element integration: a novel technique for evaluation of DLVO interaction between a particle and a flat plat. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 193, 273–285 (1997)
Bhattacharjee, S., Ko, C.-H., Elimelech, M.: DLVO interaction between rough surfaces. Langmuir 14, 3365–3375 (1998)
Bradford, S.A., Yates, S.R., Bettahar, M., Simunek, J.: Physical factors affecting the transport and fate of colloids in saturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 38(12), 1327 (2002). doi:10.2029/2002WR001340
Bradford, S.A., Simunek, J., Bettahar, M., van Genuchten, M.T., Yates, S.R.: Modeling colloid attachment, straining, and exclusion in saturated porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 37, 2242–2250 (2003)
Bradford, S.A., Simunek, J., Bettahar, M., Tadassa, Y.F., van Genuchten, M.T., Yates, S.R.: Straining of colloids at textural interfaces. Water Resour. Res. 41, W10404 (2005). doi:10.1029/2004WR003675
Bradford, S.A., Simunek, J., Bettahar, M., van Genuchten, M.T., Yates, S.R.: Significance of straining in colloid deposition: Evidence and implications. Water Resour. Res. 42, W12S15 (2006a). doi:10.1029/2005WR004791
Bradford, S.A., Simunek, J., Walker, S.L.: Transport and straining of E. coli O157: H7 in saturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 42, W12S12 (2006b). doi:10.1029/2005WR004805
Bradford, S.A., Torkzaban, S., Walker, S.L.: Coupling of physical and chemical mechanisms of colloid straining in saturated porous media. Water Res. 41, 3012–3024 (2007)
Bradford, S.A., Kim, H.N., Haznedaroglu, B.Z., Torkzaban, S., Walker, S.L.: Coupled factors influencing concentration-dependent colloid transport and retention in saturated porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 6996–7002 (2009)
Bradford, S.A., Torkzaban, S.T., Simunek, J.: Modeling colloid transport and retention in saturated porous media under unfavorable attachment conditions. Water Resour. Res. 47, W10503 (2011). doi:10.1029/2011WR010812
Brown, D.G., Jaffe, P.R.: Effects of nonionic surfactants on bacterial transport through porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 3877–3883 (2001)
Duffadar, R.D., Davis, J.M.: Interaction of micrometer-scale particles with nanotextured surfaces in shear flow. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 308, 20–29 (2007)
Duffadar, R.D., Davis, J.M.: Dynamic adhesion behavior of micrometer-scale particles flowing over patchy surfaces with nanoscale electrostatic heterogeneity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 326, 18–27 (2008)
Duffadar, R., Kalasin, S., Davis, J.M., Santore, M.M.: The impact of nanoscale chemical features on micron-scale adhesion: crossover from heterogeneity-dominated to mean-field behavior. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 327, 396–407 (2009)
Elimelech, M., O’Melia, C.R.: Kinetics of deposition of colloidal particles in porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 24, 1528–1536 (1990a)
Elimelech, M., O’Melia, C.R.: Effect of particle size on collision efficiency in the deposition of Brownian particles with electrostatic energy barriers. Langmuir 6, 1153–1163 (1990b)
Elimelech, M., Song, L.: Theoretical investigation of colloid separation from dilute aqueous suspensions by oppositely charged granular media. Sep. Technol. 2, 2–12 (1992)
Gonzalez, G., Travalloni-Louvisse, A.M.: The effect of Triton X-100 and ethanol on the wettability of quartz. Langmuir 5, 26–29 (1989)
Geffroy, C., Cohen Stuart, M.A., Wong, K., Cabane, B., Bergeron, V.: Adsorption of nonionic surfactants onto polystyrene Kinetics and reversibility. Langmuir 16, 6422–6433 (2000)
Gregory, J.: Approximate expressions for retarded van der waals interaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 83, 138–145 (1981)
Hait, S.K., Moulik, S.P.: Determination of critical micelle concentration (CMC) of nonionic surfactants by donor-acceptor interaction with iodine and correlation of CMC with hydrophile-lipophile balance and other parameters of the surfactants. J. Surfactants Deterg. 4(3), 303–309 (2001)
Herzig, J.P., Leclerc, D.M., LeGoff, P.: Flow of suspension through porous media-Application to deep filtration. Ind. Eng. Chem. 62, 8–35 (1970)
Hoek, E.M.V., Agarwal, G.K.: Extended DLVO interactions between spherical particles and rough surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 298, 50–58 (2006)
Hoek, E.M.V., Bhattacharjee, S., Elimelech, M.: Effect of membrane surface roughness on colloid-membrane DLVO interactions. Langmuir 19, 4836–4847 (2003)
Hogg, R., Healy, T.W., Fuerstenau, D.W.: Mutual coagulation of colloidal dispersions. Trans. Faraday Soc. 62, 1638–1651 (1966)
Jin, Y., Chu, Y., Li, Y.: Virus removal and transport in saturated and unsaturated sand columns. J. Contam. Hydrol. 43(2), 111–128 (2000)
Johnson, W.P., Li, X.: Comment on breakdown of colloid filtration theory: Role of the secondary energy minimum and surface charge heterogeneities. Langmuir 21, 10895–10895 (2005)
Johnson, W.P., Li, X., Yal, G.: Colloid retention in porous media: mechanistic confirmation of wedging and retention in zones of flow stagnation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41, 1279–1287 (2007)
Johnson, W.P., Ma, H., Pazmino, E.: Straining credibility: a general comment regarding common arguments used to infer straining as the mechanism of colloid retention in porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45(9), 3831–3832 (2011)
Kozlova, N., Santore, M.M.: Manipulation of micrometer-scale adhesion by tuning nanometer-scale surface features. Langmuir 22, 1135–1142 (2006)
Keller, A.A., Auset, M.: A review of visualization techniques of biocolloid transport processes at the pore scale under saturated and unsaturated conditions. Adv. Water Resour. 30, 1392–1407 (2007)
Kuznar, Z.A., Elimelech, M.: Direct microscopic observation of particle deposition in porous media: Role of the secondary energy minimum. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 294, 156–162 (2007)
Lazouskaya, V., Jin, Y., Or, D.: Interfacial interactions and colloid retention under steady flows in a capillary channel. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 303(1), 171–184 (2006)
Lazouskaya, V., Jin, Y.: Colloid retention at air-water interface in a capillary channel. Colloid. Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 325(3), 141–151 (2008)
Li, X., Johnson, W.P.: Nonmonotonic variations in deposition rate coefficients of microspheres in porous media under unfavorable deposition conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 1658–1665 (2005)
Li, X., Lin, C.L., Miller, J.D., Johnson, W.P.: Role of grain-to-grain contacts on profiles of retained colloids in porous media in the presence of an energy barrier to deposition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 3769–3774 (2006a)
Li, X., Lin, C.L., Miller, J.D., Johnson, W.P.: Pore-scale observation of microsphere deposition at grain-to-grain contacts over assemblage-scale porous media domains using x-ray microtomography. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 3762–3768 (2006b)
McDowell-Boyer, L.M.: Chemical mobilization of micron-sized particles in saturated porous media under steady flow conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 26, 586–593 (1992)
Nayeri, M., Karlsson, R., Bergenholtz, J.: Surfactant effects on colloidal interactions: concentrated micellar solutions of nonionic surfactant. Colloid. Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 368, 84–90 (2010)
Romero-Cano, M.S., Martin-Rodriguez, A., de las Nieves, F.J.: Electrokinetic behaviour of polymer colloids with adsorbed Triton X-100. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 280, 526–532 (2002)
Ryan, J.N., Elimelech, M.: Colloid mobilization and transport in groundwater. Colloid. Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 107, 1–56 (1996)
Ryan, J.N., Gschwend, P.M.: Effects of ionic strength and flow rate on colloid release: Relating kinetics to intersurface potential energy. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 164, 21–34 (1994)
Saiers, J.E., Ryan, J.N.: Introduction to special section on colloid transport in subsurface environments. Water Resour. Res. 42, W12S01 (2006). doi:10.1029/2006WR005620
Saleh, N., Sirk, K., Liu, Y., Phenrat, T., Dufour, B., Matyjaszewski, K., Tilton, R.D., Lowry, G.V.: Surface modifications enhance nanoiron transport and NAPL targeting in saturated porous media. Environ. Eng. Sci. 24(1), 45–57 (2007)
Santore, M.M., Kozlova, N.: Micrometer scale adhesion on nanometer-scale patchy surfaces: Adhesion rates, adhesion thresholds, and curvature-based selectivity. Langmuir 23, 4782–4791 (2007)
Shen, C., Li, B., Huang, Y., Jin, Y.: Kinetics of coupled primary- and secondary- minimum deposition of colloids under unfavorable chemical conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41, 6976–6982 (2007)
Shen, C., Huang, Y., Li, B., Jin, Y.: Effects of solution chemistry on straining of colloids in porous media under unfavorable conditions. Water Resour. Res. 44, W05419 (2008). doi:10.1029/2007WR006580
Shen, C., Huang, Y., Li, B., Jin, Y.: Predicting attachment efficiency of colloid deposition under unfavorable attachment conditions. Water Resour. Res. 46, W11526 (2010). doi:10.1029/2010WR00928
Shen, C., Li, B., Wang, C., Huang, Y., Jin, Y.: Surface roughness effect on deposition of nano- and micro-sized colloids in saturated columns at different solution ionic strengths. Vadose Zone J. 10, 1071–1081 (2011)
Shen, C., Wang, L.-P., Li, B., Huang, Y., Jin, Y.: Role of surface roughness in chemical detachment of colloids deposited at primary energy minima. Vadose Zone J. (2012a). doi:10.2136/vzj2011.0057
Shen, C., Lazouskaya, V., Jin, Y., Li, B., Ma, Z., Zheng, W., Huang, Y.: Coupled factors influencing detachment of nano- and micro-sized particles from primary minima. J. Contam. Hydrol. 134–135, 1–11 (2012b)
Shen, C., Lazouskaya, V., Zhang, H., Wang, F., Li, B., Jin, Y., Huang, Y.: Theoretical and experimental investigation of detachment of colloids from rough collector surfaces. Colloid. Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 410, 98–110 (2012c)
Shen, C., Wang, F., Li, B., Jin, Y., Wang, L.-P., Huang, Y.: Application of DLVO energy map to evaluate interactions between spherical colloids and rough surfaces. Langmuir 28, 14681–14692 (2012d)
Sirivithayapakorn, S., Keller, A.: Transport of colloids in saturated porous media: A pore scale observation of the size exclusion effect and colloid acceleration. Water Resour. Res. 39(4), 1109 (2003). doi:10.1029/2002WR001583
Tong, M., Johnson, W.P.: Excess colloid retention in porous media as a function of colloid size, fluid velocity, and grain angularity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 7725–7731 (2006)
Tong, M., Johnson, W.: Colloid population heterogeneity drives hyperexponential deviation from classic filtration theory. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41, 493–499 (2007)
Tong, M., Li, X., Brow, C.N., Johnson, W.P.: Detachment-influenced transport of an adhesion-deficient bacterial strain within water-reactive porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 2500–2508 (2005)
Tong, M., Ma, H., Johnson, W.P.: Funneling of flow into grain-to-grain contacts drives colloid-colloid aggregation in the presence of an energy barrier. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 2826–2832 (2008)
Torkzaban, S., Bradford, S.A., van Genuchten, MTh, Walker, S.L.: Colloid transport in unsaturated porous media: The role of water content and ionic strength on particle straining. J. Contam. Hydrol. 96, 113–127 (2008)
Torkzaban, S., Kim, H.N., Simunek, J., Bradford, S.A.: Hystersis of colloid retention and release in saturated porous media during transients in solution chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 1662–1669 (2010)
Tufenkji, N., Elimelech, M.: Correlation equation for predicting single-collector efficiency in physicochemical filtration in saturated porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 529–536 (2004)
Tufenkji, N., Elimelech, M.: Breakdown of colloid filtration theory: Role of the secondary energy minimum and surface charge heterogeneities. Langmuir 21, 841–852 (2005)
Xu, S., Saiers, J.E.: Colloid straining within water-saturated porous media: effects of colloid-size nonuniformity. Water Resour. Res. 45, W08414 (2009). doi:10.1019/2008WR007494
Xu, S., Gao, B., Saiers, J.E.: Straining of colloidal particles in saturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 42, W12S16 (2006). doi:10.1029/2006WR004948
Xu, S., Liao, Q., Saiers, J.E.: Straining of non-spherical colloids in saturated porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 771–778 (2008)
Yuan, H., Shapiro, A.A.: A mathematical model for non-monotonic deposition profiles in deep bed filtration systems. Chem. Eng. J. 166, 105–115 (2011)
Zhuang, J., Qi, J., Jin, Y.: Retention and transport of amphiphilic colloids under unsaturated flow conditions: effect of particle size and surface property. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(20), 7853–7859 (2005)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41271009, 40901109), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 6123034), National Key Technology R&D Program (No. 2012BAD05B02), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 20090008120041), and Special Fund for National Land Resource-scientific Research from National Ministry of Land and Resources, China (201011006-3). The authors wish to thank two anonymous reviewers for their very helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
C. Shen and Y. Huang are contributed equally to this manuscript and share the corresponding authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Shen, C., Zhang, H. et al. Effects of Flow Velocity and Nonionic Surfactant on Colloid Straining in Saturated Porous Media Under Unfavorable Conditions. Transp Porous Med 98, 193–208 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-013-0140-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-013-0140-3