Abstract
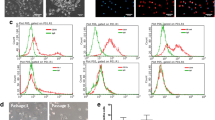
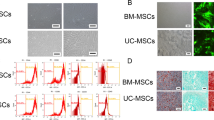
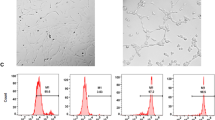
Exosomes (exos) exert biological functions to maintain the dynamic balance of cells and tissues by transferring biological cargo to recipient cells. Thus, this study explored human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hucMSCs)-derived exo transfer of microRNA (miR)-342-3p in deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT rat models were established via inferior vena cava (IVC) ligation. HucMSCs-exos were extracted and injected into rats with DVT to observe whether they could influences thrombus formation in vivo. HucMSCs-exos were co-cultured with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in vitro to observe angiogenesis. miR-342-3p and endothelin A receptor (EDNRA) expression in rats with DVT, as well as their interaction was analyzed. miR-342-3p was downregulated and EDNRA was upregulated in rats with DVT. HucMSCs-exos inhibited the formation of thrombus in rats with DVT, as well as promoted angiogenesis of HUVECs. Upregulated miR-342-3p delivery by hucMSCs-exos alleviated DVT in rats and improved angiogenesis of HUVECs. miR-342-3p targeted EDNRA, and the effect of hucMSCs-exos transfer of upregulated miR-342-3p was rescued by overexpressing EDNRA. Briefly, miR-342-3p loaded by hucMSCs-exos attenuates DVT by downregulating EDNRA, offering a novel direction to treat DVT.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Nisio M, van Es N, Buller HR (2016) Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Lancet 388(10063):3060–3073
Thachil J (2014) Deep vein thrombosis. Hematology 19(5):309–310
Bernardi E, Camporese G (2018) Diagnosis of deep-vein thrombosis. Thromb Res 163:201–206
Goldhaber SZ, Bounameaux H (2012) Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. Lancet 379(9828):1835–1846
Maufus M et al (2018) Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis recurrence: ultrasound criteria. Thromb Res 161:78–83
Ding DC et al (2015) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: a new era for stem cell therapy. Cell Transpl 24(3):339–347
Li T et al (2015) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: an overview of their potential in cell-based therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 15(9):1293–1306
Yaghoubi Y et al (2019) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived-exosomes in diseases treatment. Life Sci 233:116733
Yang W et al (2021) Mesenchymal stem-cell-derived exosomal miR-145 inhibits atherosclerosis by targeting JAM-A. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 23:119–131
Mao HY, Liu LN, Hu YM (2020) Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal miRNA-28-3p promotes apoptosis of pulmonary endothelial cells in pulmonary embolism. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(20):10619–10631
Wang L et al (2019) Blockade of NEAT1 represses inflammation response and lipid uptake via modulating miR-342-3p in human macrophages THP-1 cells. J Cell Physiol 234(4):5319–5326
Cheng S et al (2018) T2DM inhibition of endothelial miR-342-3p facilitates angiogenic dysfunction via repression of FGF11 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(1):71–78
Mercier O et al (2010) Endothelin A receptor blockade improves regression of flow-induced pulmonary vasculopathy in piglets. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 140(3):677–683
Zhou W et al (2021) MicroRNA19293p participates in murine cytomegalovirusinduced hypertensive vascular remodeling through Ednra/NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Int J Mol Med 47(2):719–731
Patel C et al (2014) Activation of the endothelin system mediates pathological angiogenesis during ischemic retinopathy. Am J Pathol 184(11):3040–3051
Wu P et al (2021) HucMSC exosome-delivered 14-3-3zeta alleviates ultraviolet radiation-induced photodamage via SIRT1 pathway modulation. Aging (Albany NY) 13(8):11542–11563
Dong B et al (2021) Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuate the inflammation of severe steroid-resistant asthma by reshaping macrophage polarization. Stem Cell Res Ther 12(1):204
Du X et al (2019) miR-21 induces endothelial progenitor cells proliferation and angiogenesis via targeting FASLG and is a potential prognostic marker in deep venous thrombosis. J Transl Med 17(1):270
Cao JY et al (2021) Exosomal miR-125b-5p deriving from mesenchymal stem cells promotes tubular repair by suppression of p53 in ischemic acute kidney injury. Theranostics 11(11):5248–5266
Ai P et al (2018) MiR-411 suppressed vein wall fibrosis by downregulating MMP-2 via targeting HIF-1alpha. J Thromb Thrombolysis 45(2):264–273
Sun J et al (2018) Endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosomes, loaded with miR-126, promoted deep vein thrombosis resolution and recanalization. Stem Cell Res Ther 9(1):223
Teng X et al (2015) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes improve the microenvironment of infarcted myocardium contributing to angiogenesis and anti-inflammation. Cell Physiol Biochem 37(6):2415–2424
Song BW et al (2015) 1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione-based small molecule-induced generation of mesenchymal stem cell-derived functional endothelial cells that facilitate rapid endothelialization after vascular injury. Stem Cell Res Ther 6:174
Ou M et al (2019) Upregulated MiR-9-5p protects against inflammatory response in rats with deep vein thrombosis via inhibition of NF-kappaB p50. Inflammation 42(6):1925–1938
Tang KC et al (2018) Effect of miR-495 on lower extremity deep vein thrombosis through the TLR4 signaling pathway by regulation of IL1R1. Biosci Rep 38(6)
Sun S et al (2020) Overexpressed microRNA-103a-3p inhibits acute lower-extremity deep venous thrombosis via inhibition of CXCL12. IUBMB Life 72(3):492–504
Du X et al (2020) miR-150 regulates endothelial progenitor cell differentiation via Akt and promotes thrombus resolution. Stem Cell Res Ther 11(1):354
Zhang Y et al (2020) IL (Interleukin)-6 contributes to deep vein thrombosis and is negatively regulated by miR-338-5p. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 40(2):323–334
Zhang Y et al (2015) Effect of exosomes derived from multipluripotent mesenchymal stromal cells on functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity in rats after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 122(4):856–867
Zhang Y et al (2019) Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through HIF-1alpha-mediated promotion of angiogenesis in a rat model of stabilized fracture. Cell Prolif 52(2):e12570
Huang JH et al (2020) Exosomes derived from miR-126-modified MSCs promote angiogenesis and neurogenesis and attenuate apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Neuroscience 424:133–145
Kong LY et al (2020) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes rescue oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury in endothelial cells. Curr Neurovasc Res 17(2):155–163
Liu J et al (2021) Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells accelerate cutaneous wound healing by enhancing angiogenesis through delivering angiopoietin-2. Stem Cell Rev Rep 17(2):305–317
Jung YY et al (2018) Atherosclerosis is exacerbated by chitinase-3-like-1 in amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Theranostics 8(3):749–766
Ray SL et al (2020) The role of miR-342 in vascular health. Study in subclinical cardiovascular disease in mononuclear cells, plasma, inflammatory cytokines and PANX2. Int J Mol Sci 21(19)
Sek AC et al (2015) Endothelial expression of endothelin receptor A in the systemic capillary leak syndrome. PLoS ONE 10(7):e0133266
Zhang W et al (2019) Enhanced endothelin A and B receptor expression and receptor-mediated vasoconstriction in rat mesenteric arteries after lipopolysaccharide challenge. Mediat Inflamm 2019:6248197
Darrah R et al (2010) EDNRA variants associate with smooth muscle mRNA levels, cell proliferation rates, and cystic fibrosis pulmonary disease severity. Physiol Genomics 41(1):71–77
Ozen G et al (2020) Interaction between PGI2 and ET-1 pathways in vascular smooth muscle from Group-III pulmonary hypertension patients. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 146:106388
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The Authors declare no conflicts of interest directly related to the contents of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Z., Chen, Q., Ding, H. et al. MicroRNA-342-3p loaded by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes attenuates deep vein thrombosis by downregulating EDNRA. J Thromb Thrombolysis 54, 411–419 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-022-02694-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-022-02694-6