Abstract
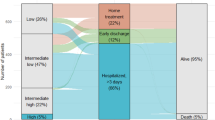
Most patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE) are still treated as inpatients. This is a retrospective cohort study of patients with acute PE, diagnosed using V/P SPECT between 2007 and 2011. Patients were treated at home if they were hemodynamically stable, did not require oxygen or parenteral analgetics, had no contraindications to anticoagulant treatment and V/P SPECT showed an extension of the PE of less than 40 %. The aim of the study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of home treatment with our algorithm. During the study period 416 outpatients were diagnosed with acute symptomatic PE of whom in total 260 (62.5 %) were discharged home from the emergency unit and another 47 (11 %) within 24 h from admission. During 3 months follow-up one (0.3 %) patient had a recurrent thrombotic event. Eleven (3.6 %) patients had a major or clinically relevant bleed and the overall mortality was 2 % (n = 6). There were no PE-related mortality. Home treatment should be considered and is safe in the majority of hemodynamically stable outpatients with small to medium size PE, quantified using V/P SPECT.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- INR:
-
International normalised ratio
- LMHW:
-
Low molecular weight heparin
- PE:
-
Pulmonary embolism
- V/P SPECT:
-
Ventilation/perfusion single photon emission tomography
- sPESI:
-
Simplified pulmonary embolism severity index
- VTE:
-
Venous thromboembolism
References
Wan S, Quinlan DJ, Agnelli G, Eikelboom JW (2004) Thrombolysis compared with heparin for the initial treatment of pulmonary embolism: a meta-analysis of the randomized controlled trials. Circulation 110:744–749
Torbicki A, Perrier A, Konstantinides S, Agnelli G, Galie N, Pruszczyk P, Bengel F, Brady AJ, Ferreira D, Janssens U, Kleptetko W, Mayer E, Remy-Jardin M, Bassande JP, Vahanian A, Camm J, de Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Filippatos G et al (2008) Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J 29:2276–2315
Jimenez D, Aujesky D, Yusen RD (2010) Risk stratification of normotensive patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Br J Haematol 151:415–424
Barra SN, Paiva L, Providencia R, Fernandes A, Marques AL (2013) A review on the state-of-the-art data regarding safe early discharge following admission for pulmonary embolism: what do we know? Clin Cardiol 36:507–515
Kearon C, Akl EA, Comerota AJ, Prandoni P, Bounameaux H, Goldhaber SZ, Nelson ME, Wells PS, Gould MK, Dentali F, Crowther M, Kahn SR (2012) Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American college of chest physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 141:e419S–e494S
Agterof MJ, Schutgens RE, Snijder RJ, Epping G, Peltenburg HG, Posthuma EF, Hardemann JA, van der Griend R, Koster T, Prins MH, Biesma DH (2010) Out of hospital treatment of acute pulmonary embolism in patients with a low NT-proBNP level. J Thromb Haemost 8:1235–1241
Zondag W, Mos IC, Creemers-Schild D, Hoogerbrugge AD, Dekkers OM, Dolsma J, Eijsvogel M, Faber LM, Hofstee HM, Hovens MM, Jonkers GJ, van Kralingen KW, Kruip MJ, Vlasfeld T, de Vreede MJ, Huismann MV (2011) Outpatient treatment in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: the Hestia Study. J Thromb Haemost 9:1500–1507
Aujesky D, Roy PM, Verschuren F, Righini M, Osterwalder J, Egloff M, Renaud B, Verhamme P, Stone RA, Legell C, Sanchez O, Pugh NA, N`gako A, Cornuz J, Hugli O, Beer HJ, Perrier A, Fine MJ, Yealy DM (2011) Outpatient versus inpatient treatment for patients with acute pulmonary embolism: an international, open-label, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 378:41–48
Otero R, Uresandi F, Jimenez D, Cabezudo MA, Oribe M, Nauffal D, Conget F, Rodriguez C, Cayuela A (2010) Home treatment in pulmonary embolism. Thromb Res 126:e1–e5
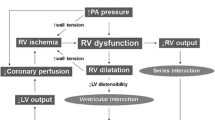
McIntyre KM, Sasahara AA (1974) Hemodynamic and ventricular responses to pulmonary embolism. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 17:175–190
Ghanima W, Abdelnoor M, Holmen LO, Nielssen BE, Sandset PM (2007) The association between the proximal extension of the clot and the severity of pulmonary embolism (PE): a proposal for a new radiological score for PE. J Intern Med 261:74–81
van der Meer RW, Pattynama PM, van Strijen MJ, van der Berg-Huijsmans, Hartmann IJ, Putter H, de Roos A, Huisman MV (2005) Right ventricular dysfunction and pulmonary obstruction index at helical CT. Radiology 235:798–803
Bazeed MF, Saad A, Sultan A, Ghanem MA, Khalil DM (2010) Prediction of pulmonary embolism outcome and severity by computed tomography. Acta Radiol 51:271–276
Ghysen A, Ghaye B, Willems V, Lambermont B, Gerard P, Dondelinger RF, D’orio V (2005) Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography and prognostic significance in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Thorax 60:956–961
Soares TH, de Bastos M, de Carvalho BV, Moreira W, Cabral CP, de Paula LF, Caram C, Rezende SM (2012) Prognostic value of computed tomographic pulmonary angiography and pulmonary embolism severity index in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 24:64–70
Clark AR, Milne D, Wilsher M, Burrowes KS, Bajaj M, Tawhai MH (2014) Lack of functional information explains the poor outcome of clot load scores at prediction outcome in acute pulmonary embolism. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 190:1–13
Bajc M, Neilly JB, Miniati M, Schuemichen C, Meignan M, Jonson B (2009) EANM guidelines for ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy: part 2. Algorithms and clinical considerations for diagnosis of pulmonary emboli with V/P(SPECT) and MDCT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36:1528–1538
Olsson CG, Bitzen U, Olsson B, Magnusson P, Carlsson, Jonson B, Bajc M (2006) Outpatient tinzaparin therapy in pulmonary embolism quantified with ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy. Med Sci Monit 12:9–13
Schulman S, Kearon C (2005) Definition of major bleeding in clinical investigations of antihemostatic medicinal products in non-surgical patients. J Thromb Haemost 3:692–694
Jimenez D, Aujesky D, Moores L, Gomez V, Lobo JL, Uresandi F, Otero R, Monreal M, Muriel A, Yusen RD (2010) Simplification of the pulmonary embolism severity index for prognostication in patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Arch Intern Med 170:1383–1389
Bajc M, Neilly JB, Miniati M, Schuemichen C, Meignan M, Jonson B (2009) EANM guidelines for ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy: part 1. Pulmonary imaging with ventilation/perfusion single photon emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36:1356–1370
Bajc M, Olsson C-G, Palmer J, Jonson B (2004) Quantitative ventilation/perfusion SPECT (QV/PSPECT): a primary method for diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. In: Freeman LM (ed) Nuclear medicine annual. Lippincott Williams&Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 173–186
Palmer J, Bitzen U, Jonson B, Bajc M (2001) Comprehensive ventilation/perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med 42:1288–1294
Alhadad A, Miniati M, Alhadad H, Gottsater A, Bajc M (2012) The value of tomographic ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy (V/PSPECT) for follow-up and prediction of recurrence in pulmonary embolism. Thromb Res 130:877–881
Begic A, Jogi J, Hadziredzepovic A, Kucukalic-Selimovic E, Begovic-Hadzimuratovic S, Bajc M (2011) Tomographic ventilation/perfusion lung scintigraphy in the monitoring of the effect of treatment in pulmonary embolism: serial follow-up over a 6-month period. Nucl Med Commun 32:508–514
Zondag W, Kooiman J, Klok F, Dekkers O, Huisman M (2013) Outpatient versus inpatient treatment in patients with pulmonary embolism: a meta-analysis. Eur Respir J 42:134–144
Kovacs MJ, Hawel JD, Rekman JF, Lazo-Langner A (2010) Ambulatory management of pulmonary embolism: a pragmatic evaluation. J Thromb Haemost 8:2406–2411
Erkens PM, Gandara E, Wells P, Shen AY, Bose G, Le Gal G, Rodger M, Prins MH, Carrier M (2010) Safety of outpatient treatment in acute pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Haemost 8:2412–2417
Lankeit M, Konstantinides S (2012) Is it time for home treatment of pulmonary embolism? Eur Respir J 40:742–749
Zwierzina D, Limacher A, Mean M, Righini M, Jaeger K, Beer HJ, Frauchiger B, Ostenwalder J, Kucher N, Matter CM, Banyai M, Angelillo-Scherrer A, Lämmle B, Egloff M, Aschwanden M, Mazzolai L, Hugli O, Huismann M, Bounameaux H, Cornuz J, Rodondi N, Aujesky D (2012) Prospective comparison of clinical prognostic scores in elderly patients with pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Haemost 10:2270–2276
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Berit Olsson and Alaa al Hadad for helping in the collection of data. Carl-Gustav Olsson for taking care of patients and implementing the algorithm. This study was supported by grants from the Research Funds at Skåne University Hospital and the Swedish state under the LUA/ALF agreement.
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elf, J.E., Jögi, J. & Bajc, M. Home treatment of patients with small to medium sized acute pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Thrombolysis 39, 166–172 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-014-1097-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-014-1097-y