Abstract
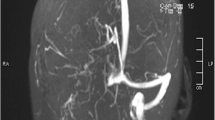
Cerebral veno-sinus thrombosis (CVT) during puerperium may have fatal consequences. A nonspecific clinical picture must be complete with computed tomography of the brain and digital substract angiography of the brain blood vessels, and, once the clinical diagnosis is confirmed, coagulation tests and genetic analysis of the coagulation factor are to be made as well. Genetic polymorphisms associated with thrombophilia such as factor V Leiden, prothrombin G20210A, MTHFR C677T, ACE and PIA1/A2 may be the cause of the hypercoagulability that results in CVT.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dindagur N, Kruthika-Vinod TP, Christopher R (2007) Factor V gene A4070G mutation and the risk of cerebral veno-sinus thrombosis occuring during puerperium. Thromb Res 119(4):497–500
Dindagur N, Kruthika-Vinod TP, Christopher R (2006) Thrombophilic gene polymorphisms in puerperal cerebral veno-sinus thrombosis. J Neurol Sci 249(1):25–30
Kochhar R, Khandelwal N, Singh P, Suri S (2006) Arterial contamination: a useful indirect sign of cerebral sino-venous thrombosis. Acta Neurol Scand 114(2):139–142
Ehtisham A, Stern BJ (2006) Cerebral venous thrombosis: a review. Neurologist 12(1):32–38
Rothrock JF (2006) Fatal puerperal transverse sinus thrombosis. Headache 46(8):1296–1297
Zhang Z, Long J, Li W (2000) Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: a clinical study of 23 cases. Clin Med J 113(11):1043–1045
Rafique MZ, Bari V, Ashraf K, Ahmad MN (2005) Cerebral deep venous thrombosis: a case report and literature review. J Pak Med Assoc 55(9):399–400
Lichy C, Dong-Si T, Reuner K, Genius J, Rickmann H, Hampe T, Dolan T, Stoll F, Grau A (2006) Risk of cerebral venous thrombosis and novel gene polymorphisms of the coagulation and fibrinolytic systems. J Neurol 253(3):316–320
PIA1/A2 polymorphism of the platelet glycoprotein receptor IIb/IIIIa and its correlation with myocardial infarction: an appraisal. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost (2006); 12(1):93–95
Kalita J, Srivastava R, Bansal V, Agarwal S, Misra UK (2006) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism in Indian stroke patients. Neurol India 54(3):260–263
Fernandez-Cadenas I, Molina CA, Alvarez-Sabin J, Ribo M, Penalba A, Ortega-Torres L, Delgado P, Quintana M, Rosell A, Montaner J (2006) ACE gene polymorphisms influence t-PA-induced brain vessel reopening following ischemic stroke. Neurosci Lett 398(3):167–171
Nagi S, Kaddour C, Soukri I, Ben Ghorbal I, Sevai R, Beighith L, Skandrani L, Touibi S (2006) Deep cerebral venous system thrombosis: report of two cases. J Radiol 87(9):1084–1088
Biousse V, Ameri A, Bousser MG (1999) Isolated intracranial hypertension as the olny sign of cerebral venous thrombosis. Neurology 53(7):1537–1542
Dikmen M, Ozbabalik D, Gunes HV, Degirmenci I, Bal C, Ozdemir G, Basaran A (2006) Acute stroke in relation to homocysteine and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphisms. Acta Neurol Scand 113(5):307–314
Gao X, Yang H, ZhiPing T (2006) Association studies of genetic polymorphism, environmental factors and their interaction in ischemic stroke. Neurosci Lett 398(3):172–177
Hameed B, Syed NA (2006) Prognostic indicators in cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. J Pak Med Assoc 56(11):551–554
Lamy C, Hamou JB, Coste J, Mas JL (2000) Ischemic stroke in young women: risk of recurrence during subsequent pregnancies. Franch study group on stroke in pregnancy. Neurology 55(2):269–274
Mehraein S, Ortwein H, Busch M, Weih M, Einhaupl K, Masuhr F (2003) Risk of recurrence of cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis during subsequent pregnancy and puerperium. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74(6):814–816
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Titlic, M., Pavelin, S., Tonkic, A. et al. Thrombosis of sinus sagitalis during puerperium caused by thrombophilic gene mutation. J Thromb Thrombolysis 25, 270–272 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-007-0061-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-007-0061-5