Abstract
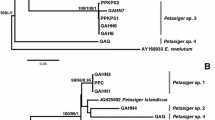
Metacercariae of two species of Posthodiplostomum Dubois, 1936 (Digenea: Diplostomidae) were subjected to morphological and molecular studies: P. brevicaudatum (von Nordmann, 1832) from Gasterosteus aculeatus (L.) (Gasterosteiformes: Gasterosteidae), Bulgaria (morphology, cox1 and ITS1-5.8S-ITS2) and Perca fluviatilis L. (Perciformes: Percidae), Czech Republic (morphology, cox1, ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 and 28S); and P. centrarchi Hoffman, 1958 from Lepomis gibbosus (L.) (Perciformes: Centrarchidae), Bulgaria (morphology, cox1 and ITS1-5.8S-ITS2) and Slovakia (cox1 and ITS1-5.8S-ITS2). In addition, cercariae of P. cuticola (von Nordmann, 1832) from Planorbis planorbis (L.) (Mollusca: Planorbidae), Lithuania (morphology and cox1) and metacercariae of Ornithodiplostomum scardinii (Schulman in Dubinin, 1952) from Scardinius erythrophthalmus (L.) (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae), Czech Republic, were examined (morphology, cox1, ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 and 28S). These represent the first molecular data for species of Posthodiplostomum and Ornithodiplostomum Dubois, 1936 from the Palaearctic. Phylogenetic analyses based on cox1 and ITS1-5.8S-ITS2, using O. scardinii as the outgroup and including the three newly-sequenced Posthodiplostomum spp. from Europe and eight published unidentified (presumably species-level) lineages of Posthodiplostomum from Canada confirmed the distinct status of the three European species (contrary to the generally accepted opinion that only P. brevicaudatum and P. cuticola occur in the Palaearctic). The subspecies Posthodiplostomum minimum centrarchi Hoffmann, 1958, originally described from North America, is elevated to the species level as Posthodiplostomum centrarchi Hoffman, 1958. The undescribed “Posthodiplostomum sp. 3” of Locke et al. (2010) from centrarchid fishes in Canada has identical sequences with the European isolates of P. centrarchi and is recognised as belonging to the same species. The latter parasite, occurring in the alien pumpkinseed sunfish Lepomis gibbosus in Europe, is also supposed to be alien for this continent. It is speculated that it colonised Europe long ago and is currently widespread (recorded in Bulgaria, Slovakia and Spain); based on the cox1 sequence of an adult digenean isolate from the Ebro Delta, Spain, only the grey heron (Ardea cinerea L.) (Ciconiiformes: Ardeidae) is known to be its definitive host in Europe.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray, R. A., Waeschenbach, A., Cribb, T. H., Weedall, G. D., Dyal, P., & Littlewood, D. T. J. (2009). The phylogeny of the Lepocreadioidea (Platyhelminthes, Digenea) inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial genes: Implications for their systematics and evolution. Acta Parasitologica, 54, 310–329.
Darriba, D., Taboada, G. L., Doallo, R., & Posada, D. (2012). jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Methods, 9, 772.
Davis, S. R., & Miller, G. C. (1989). Parasites of some fishes from B. Everett Jordan Reservoir, North Carolina. Journal of the Elisha Mitchell Scientific Society, 105, 97–114.
Dönges, J. (1964). Der Lebenszyklus von Posthodiplostomum cuticola (v. Nordmann, 1832) Dubois, 1936 (Trematoda, Diplostomatidae). Zeitschrift für Parasitenkunde, 24, 169–248.
Dönges, J. (1965). Der Lebenszyklus von Posthodiplostomum brevicaudatum (Trematoda), eines Parasiten in den Augen von Süßwasserfischen. Zoologica, 114, 1–39.
Dronen, N. O., & Chen, H.-W. (2002). Endohelminths from the little blue heron Egretta caerulea from the Texas Gulf Coast. Comparative Parasitology, 69, 96–99.
Dubois, G. (1938). Monographie des Strigeida (Trematoda). Mémoires de la Société Neuchâteloise des Sciences Naturelles, 6, 1–535.
Dubois, G. (1970). Synopsis des Strigeidae et des Diplostomatidae (Trematoda). Mémoires de la Société Neuchâteloise des Sciences Naturelles, 10, 1–727.
Edgar, R. C. (2004). MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research, 32, 1792–1797.
Galazzo, D. E., Dayanandan, S., Marcogliese, D. J., & McLaughlin, J. D. (2002). Molecular systematics of some North American species of Diplostomum (Digenea) based on rDNA-sequence data and comparisons with European congeners. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 80, 2207–2217.
Georgieva, S., Selbach, C., Faltýnková, A., Soldánová, M., Sures, B., Skírnisson, K., & Kostadinova, A. (2013). New cryptic species of the “revolutum” group of Echinostoma (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) revealed by molecular and morphological data. Parasites & Vectors, 6, 64.
Georgieva, S., Faltýnková, A., Brown, R., Blasco-Costa, I., Soldánová, M., Sitko, J., Scholz, T., & Kostadinova, A. (2014). Echinostoma “revolutum” (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) species complex revisited: species delimitation based on novel molecular and morphological data gathered in Europe. Parasites & Vectors, 7, 520.
Gibson, D. I. (1996). Trematoda. In: Margolis, L. & Kabata, Z. (Eds). Guide to the parasites of fishes of Canada. Part IV. Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 124, 363 pp.
Grabda-Kazubska, B., Baturo-Warszawska, B., & Pojmańska, T. (1987). Dynamics of parasite infestation of fish in lakes Dgał Wielki and Warniak in connection with introduction of phytophagous species. Acta Parasitologica Polonica, 32, 1–28.
Guindon, S., & Gascuel, O. (2003). A simple, fast and accurate method to estimate large phylogenies by maximum-likelihood. Systematic Biology, 52, 696–704.
Guindon, S., Dufayard, J. F., Lefort, V., Anisimova, M., Hordijk, W., & Gascuel, O. (2010). New algorithms and methods to estimate Maximum-Likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Systematic Biology, 59, 307–321.
Hoffman, G. L. (1958). Experimental studies on the cercaria and metacercaria of a strigeoid trematode, Posthodiplostomum minimum. Experimental Parasitology, 7, 23–50.
Hoffman, G. L. (1998). Parasites of North American freshwater fishes. Second Edition. Ithaca & London: Cornell University Press, 539 pp.
Hughes, R. C. (1928). Studies on the trematode family Strigeidae (Holostomidae). No. IX. Neascus van-cleavei (Agersborg). Transactions of the American Microscopical Society, 47, 320–341.
Hurvich, C. M., & Tsai, C.-L. (1989). Regression and time series model selection in small samples. Biometrika, 76, 297–307.
Jančev, J., Vassilev, I., Isskova, N., & Genov, T. (1984). A contribution to the trematode fauna of the wild birds in Bulgaria. In: Vassilev, I. (Ed.) [Fauna, taksonomiya i ekologiya na khelminti po ptitisi.] Sofia: Publishing House of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, pp. 188–205 (In Bulgarian).
Kostadinova, A. (1993). [Trematodes and trematode communities of the fish-eating birds from the Bulgarian Black Sea coast.] PhD Thesis, Sofia: Institute of Parasitology, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, 227 pp (In Bulgarian).
Kostadinova, A. (1995). Trematodes of birds of the family Ardeidae from the Bulgarian Black Sea coast. Comptes Rendus de l’Académie Bulgare des Sciences, 48, 89–91.
Kottelat, M., & Freyhof, J. (2007). Handbook of European freshwater fishes. Kottelat, Cornol, Switzerland and Freyhof, Berlin, Germany, 646 pp.
Lane, B., Spier, T., Wiederholt, J., & Meagher, S. (2015). Host specificity of a parasitic fluke: Is Posthodiplostomum minimum a centrarchid-infecting generalist or specialist? Journal of Parasitology, 101, 6–17.
Locke, S. A., McLaughlin, J. D., & Marcogliese, D. J. (2010). DNA barcodes show cryptic diversity and a potential physiological basis for host specificity among Diplostomoidea (Platyhelminthes: Digenea) parasitizing freshwater fishes in the St. Lawrence River, Canada. Molecular Ecology, 19, 2813–2827.
Luton, K., Walker, D., & Blair, D. (1992). Comparison of ribosomal internal transcribed spacers from two congeneric species of flukes (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda: Digenea). Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 56, 323–328.
Miller, M. A., Pfeiffer, W., & Schwartz, T. (2010). Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In: Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), 14 Nov. 2010, New Orleans, LA pp. 1–8.
Moszczynska, A., Locke, S. A., McLaughlin, J. D., Marcogliese, D. J., & Crease, T. J. (2009). Development of primers for the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase I gene in digenetic trematodes (Platyhelminthes) illustrates the challenge of barcoding parasitic helminths. Molecular Ecology Resources, 9, 75–82.
Niewiadomska, K. (2002). Superfamily Diplostomoidea Poirier, 1886. In Gibson, D. I., Jones, A. & Bray, R. A. (Eds.), Keys to the Trematoda, Vol. 1. Wallingford - London, UK: CABI Publishing and The Natural History Museum, pp. 159–242.
Niewiadomska, K. (2003). Monografie Parazytologiczne. 15. Pasozyty ryb Polski (klucze do oznaczania): Przywry - Digenea. Warszawa: Polskie Towarzystwo Parazytologiczne, 169 pp.
Pleijel, F., Jondelius, U., Norlinder, E., Nygren, A., Oxelman, B., Schander, C., Sundberg, P., & Thollesson, M. (2008). Phylogenies without roots? A plea for the use of vouchers in molecular phylogenetic studies. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 48, 369–371.
Pugachev, O.N. (2003). Trematoda. In: Alimov, A. F. (Ed.) Checklist of the freshwater fish parasites of the Northern Asia. Trudy Zoologichekogo Instituta Rossiyskoy Akademii Nauk, 298, pp. 1–224 (In Russian).
Rambaut, A. (2012). FigTree v. 1.4. Molecular evolution, phylogenetics and epidemiology. Edinburgh, UK: University of Edinburgh, Institute of Evolutionary Biology, http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/.
Rambaut, A., & Drummond, A. J. (2009). Tracer 1.5. Available from http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer.
Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., van der Mark, P., Ayres, D. L., Darling, A., Hohna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L, Suchard, M. A., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2012). MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61, 539–542.
Sudarikov, V. E. (1971). Order Strigeidida (La Rue, 1926) Sudarikov, 1959, Suborder Strigeata La Rue, 1926. In: Skrjabin, K. I. (Ed.). [Trematodes of animals and man.] Osnovy Trematodologii, 24. Moscow: Nauka, pp. 69–227 (In Russian).
Sudarikov, V. E., Shigin, A. A., Kurochkin, Yu. V., Lomakin, V. V., Sten’ko, R. P., & Yurlova, N. I. (2002). [Metacercariae of trematodes parasitic in freshwater hydrobionts of central Russia.] In: Freze, V. I. (Ed.), [Trematode metacercariae parasitic in hydrobionts of Russia, Vol. 1.] Moscow: Nauka, 296 pp (In Russian).
Sugiura, N. (1978). Further analysis of the data by Akaike’s information criterion and the finite corrections. Communication in Statistics Theory and Methods, A, 7, 13–26.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., & Kumar, S. (2013). MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2725–2729.
Telford, M. J., Herniou, E. A., Russell, R. B., & Littlewood, D. T. J. (2000). Changes in mitochondrial genetic codes as phylogenetic characters: two examples from the flatworms. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 97, 11359–11364.
Tkach, V. V., Littlewood, D. T. J., Olson, P. D., Kinsella, J. M., & Swiderski, Z. (2003). Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the Microphalloidea Ward, 1901 (Trematoda: Digenea). Systematic Parasitology, 56, 1–15.
Vassilev, V., Vassilev, R., Yankov, P., Kamburova, N., Uzunov, Y., Pehlivanov, L., Georgiev, B. B., Popgeorgiev, G., Assyov, B., Avramov, S., Tzenova, R., & Kornilev, Y. (2013). National action plan for conservation of wetlands of high significance in Bulgaria, 2013–2022. Sofia: Bulgarian Biodiversity Foundation, 104 pp.
Wisniewski, W. L. (1958). The development cycle of Posthodiplostomum brevicaudatum (v. Nordmann, 1832) Kozicka, 1958. Acta Parasitologica Polonica, 6, 251–271.
Acknowledgements
BS, PP and BBG are grateful to the Ministry of Environment and Waters of the Republic of Bulgaria for licenses (NCZP-151/11.05.2012 and NCZP-168/29.04.2013) to carry out studies in Atanasovsko Lake Reserve. The field study was based at Atanasovsko Lake Field Station of the Institute of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Research, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences; the assistance of the staff of this station as well as of Dr Gergana P. Vasileva, Konstantin Popov and Dr Pavel Nikolov is acknowledged. AK and SG are grateful to Dr Mikuláš Oros (Institute of Parasitology, Slovak Academy of Sciences) for help with sampling logistics along River Danube and Professor Tomáš Scholz (Institute of Parasitology, Czech Academy of Sciences) for providing fish from Lake Mácha. The constructive suggestions of an anonymous reviewer helped to improve the present article.
Funding
This study was partially supported by the Czech Science Foundation (project ECIP P505/12/G112) to AK, OK and SG. SG profits from a postdoctoral fellowship of the Czech Academy of Sciences. BS, PP and BBG used facilities developed in the frames of the projects WETLANET (FP7 CAPACITIES Grant 229802), CEBDER (National Science Fund, Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Bulgaria, Grant DO 02-15/2009). Field work was partially implemented on expenses of Grant YS DO 02-271/18.12.2008 (NSF, Bulgaria).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Borislav Stoyanov and Simona Georgieva have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoyanov, B., Georgieva, S., Pankov, P. et al. Morphology and molecules reveal the alien Posthodiplostomum centrarchi Hoffman, 1958 as the third species of Posthodiplostomum Dubois, 1936 (Digenea: Diplostomidae) in Europe. Syst Parasitol 94, 1–20 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-016-9680-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-016-9680-6