Abstract
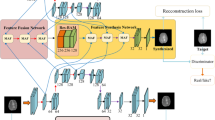
Magnetic resonance imaging is a widely used medical imaging technology, which can provide different contrasts between the tissues in human body. To use the complementary information from multiple imaging modalities and shorten the time of MR scanning, cross-modality magnetic resonance image synthesis has recently aroused extensive interests in literature. Most existing methods improve the quality of image synthesis by artificially designing loss on the basis of minimizing pixel-wise intensity error, even though it can improve the quality of the synthesized image, it is still difficult to balance the hyperparameters of different loss functions. In this paper, we propose a generative adversarial network (Trans-cGAN) based on transformer and unet for cross-modality magnetic resonance image synthesis. Specifically, transformer block is added into the network to enhance the model’s understanding of the overall semantics of the image as well as to implicitly integrate the edge information. Moreover, spectral normalization is added to the generator and discriminator to avoid mode collapse and ensure the stability of training. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed Trans-cGAN is superior to the most of the cross-modality MR image synthesis methods in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. Furthermore, Trans-cGAN also shows excellent generality in the generic image synthesis task of the benchmark datasets of maps and cityscapes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data associated with this work can be availed from the corresponding author upon formal request.
References
Abiko, R., Ikehara, M.: Channel attention GAN trained with enhanced dataset for single-image shadow removal. IEEE Access 10, 12322–12333 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3147063
Arjovsky, M., Chintala, S., Bottou, L.: Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, pp. 214–223 (2017)
Armanious, K., Jiang, C., Fischer, M., et al.: MedGAN: medical image translation using GANs. Comput. Med. Imaging Graphics 79(101), 684 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2019.101684
Benzakoun, J., Deslys, M.A., Legrand, L., et al.: Synthetic flair as a substitute for flair sequence in acute ischemic stroke. Radiology 303(1), 153–159 (2022)
Bi, L., Kim, J., Kumar, A., et al.: Synthesis of positron emission tomography (PET) images via multi-channel generative adversarial networks (gans). In: Cardoso, M.J., Arbel, T., Gao, F., et al. (eds.) Molecular Imaging, Reconstruction and Analysis of Moving Body Organs, and Stroke Imaging and Treatment—Fifth International Workshop, CMMI 2017, Second International Workshop,RAMBO 2017, and First International Workshop, SWITCH 2017, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2017, Québec City, QC, Canada, September 14, 2017, Proceedings, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 10555, pp 43–51. Springer (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67564-0_5
Chai, Y., Xu, B., Zhang, K., et al.: MRI restoration using edge-guided adversarial learning. IEEE Access 8, 83858–83870 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2992204
Chartsias, A., Joyce, T., Giuffrida, M.V., et al.: Multimodal MR synthesis via modality-invariant latent representation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(3), 803–814 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2017.2764326
Chen, J., Lu, Y., Yu, Q., et al.: Transunet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. CoRR arxiv:2102.04306 (2021)
Clarke, L., Velthuizen, R., Camacho, M., et al.: MRI segmentation: methods and applications. Magn. Reson. Imaging 13(3), 343–368 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0730-725X(94)00124-L
Cordier, N., Delingette, H., Lê, M., et al.: Extended modality propagation: image synthesis of pathological cases. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(12), 2598–2608 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2589760
Cordts, M., Omran, M., Ramos, S., et al.: The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. CoRR arxiv:1604.01685 (2016)
Dar, S.U.H., Yurt, M., Karacan, L., et al.: Image synthesis in multi-contrast MRI with conditional generative adversarial networks. CoRR arxiv:1802.01221 (2018)
Despotovic, I., Goossens, B., Philips, W.: MRI segmentation of the human brain: Challenges, methods, and applications. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 450341:1-450341:23 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/450341
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., et al.: An image is worth 16 x 16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. CoRR arxiv:2010.11929 (2020)
Goodfellow, I.J., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., et al.: Generative adversarial networks. CoRR arxiv:1406.2661 (2014)
Gulrajani, I., Ahmed, F., Arjovsky, M., et al.: Improved training of Wasserstein GANs. CoRR arxiv:1704.00028 (2017)
Henry, T., Carré, A., Lerousseau, M., et al.: Brain tumor segmentation with self-ensembled, deeply-supervised 3d U-net neural networks: a brats 2020 challenge solution. In: Crimi, A., Bakas, S., (eds.) Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries—6th International Workshop, BrainLes 2020, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2020, Lima, Peru, October 4, 2020, Revised Selected Papers, Part I, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 12658, pp. 327–339. Springer (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_30
Hiasa, Y., Otake, Y., Takao, M., et al.: Cross-modality image synthesis from unpaired data using cyclegan: effects of gradient consistency loss and training data size. CoRR arxiv:1803.06629 (2018)
Isola, P., Zhu, J., Zhou, T., et al.: Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, July 21–26, 2017, pp. 5967–5976. IEEE Computer Society (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.632
Jiang, Y., Chang, S., Wang, Z.: Transgan: two pure transformers can make one strong GAN, and that can scale up. In: Ranzato, M., Beygelzimer, A., Dauphin, Y.N., et al. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, NeurIPS 2021, December 6–14, 2021, virtual, pp. 14745–14758 (2021)
Jog, A., Carass, A., Roy, S., et al.: Random forest regression for magnetic resonance image synthesis. Med. Image Anal. 35, 475–488 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2016.08.009
Kim, T., Cha, M., Kim, H., et al.: Learning to discover cross-domain relations with generative adversarial networks. (2017) arxiv:1703.05192
Lê, M., Delingette, H., Kalpathy-Cramer, J., et al.: Personalized radiotherapy planning based on a computational tumor growth model. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 36(3), 815–825 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2626443
Liu, X., Yu, A., Wei, X., et al.: Multimodal MR image synthesis using gradient prior and adversarial learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 14(6), 1176–1188 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTSP.2020.3013418
Liu, Z., Lin, Y., Cao, Y., et al.: Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows (2021). CoRR arxiv:2103.14030
Mirza, M., Osindero, S.: Conditional generative adversarial nets (2014). CoRR arxiv:1411.1784
Miyato, T., Kataoka, T., Koyama, M., et al.: Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks (2018). CoRR arxiv:1802.05957
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation (2015). CoRR arxiv:1505.04597
Schlemper, J., Oktay, O., Schaap, M., et al.: Attention gated networks: learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med. Image Anal. 53, 197–207 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.01.012
Sui, Y., Afacan, O., Jaimes, C., et al.: Scan-specific generative neural network for MRI super-resolution reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 41(6), 1383–1399 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2022.3142610
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., et al.: Attention is all you need (2017). CoRR arxiv:1706.03762
Wang, X., Girshick, R.B., Gupta, A., et al.: Non-local neural networks. In: 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, June 18–22, 2018, pp. 7794–7803. Computer Vision Foundation/IEEE Computer Society, (2018a). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00813
Wang, Y., Ma, G., An, L., et al.: Semisupervised tripled dictionary learning for standard-dose PET image prediction using low-dose PET and multimodal MRI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64(3), 569–579 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2016.2564440
Wang, Y., Yu, B., Wang, L., et al.: 3d conditional generative adversarial networks for high-quality PET image estimation at low dose. NeuroImage 174, 550–562 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.03.045
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., et al.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
Wu, C., Zou, Y., Yang, Z.: U-GAN: Generative adversarial networks with U-net for retinal vessel segmentation. In: 2019 14th International Conference on Computer Science & Education (ICCSE), pp. 642–646 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCSE.2019.8845397
Yang, Q., Li, N., Zhao, Z., et al.: MRI image-to-image translation for cross-modality image registration and segmentation (2018). CoRR arxiv:1801.06940
Ye, D.H., Zikic, D., Glocker, B., et al.: Modality propagation: coherent synthesis of subject-specific scans with data-driven regularization. In: Mori, K., Sakuma, I., Sato, Y., et al. (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2013—16th International Conference, Nagoya, Japan, September 22–26, 2013, Proceedings, Part I, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 8149, pp. 606–613. Springer (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40811-3_76
Yi, X., Babyn, P.S.: Sharpness-aware low-dose CT denoising using conditional generative adversarial network. J. Digit. Imaging 31(5), 655–669 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-018-0056-0
Yu, B., Zhou, L., Wang, L., et al.: Ea-GANs: edge-aware generative adversarial networks for cross-modality MR image synthesis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(7), 1750–1762 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2895894
Yu, Y., Xie, Y., Thamm, T., et al.: Use of deep learning to predict final ischemic stroke lesions from initial magnetic resonance imaging. JAMA Network Open 3(3), e200772–e200772 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.0772, https://arxiv.org/abs/https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/articlepdf/2762679/yu_2020_oi_200050_1602778823.39892.pdf
Zeiler, M.D., Fergus, R.: Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In: Fleet, D.J., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., et al. (eds.) Computer Vision—ECCV 2014—13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6–12, 2014, Proceedings, Part I, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 8689, pp. 818–833. Springer (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1_53
Zhang, H., Goodfellow, I.J., Metaxas, D.N., et al.: Self-attention generative adversarial networks (2018). CoRR arxiv:1805.08318
Zhao, H., Jiang, L., Jia, J., et al.: Point transformer (2020). CoRR arxiv:2012.09164
Zhu, J., Park, T., Isola, P., et al.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks (2017). CoRR arxiv:1703.10593
Zhu, X., Su, W., Lu, L., et al.: Deformable DETR: deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection (2020). CoRR arxiv:2010.04159
Funding
Financial support:The work was supported by grands from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11971214, 81960309).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL: Conceptualization, data curation, methodology, software, writing—original draft. NH: Resources, data curation. YQ: Data curation. JZ: Validation, supervision. JS: Validation, supervision, writing—review and editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experimental protocols were approved by Medical Ethics Committee of Lanzhou University Second Hospital (approval number: 2022A-650, dated 20 October 2022), all methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Informed consent
All informed consent was obtained from all subjects and their legguardian.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Han, N., Qin, Y. et al. Trans-cGAN: transformer-Unet-based generative adversarial networks for cross-modality magnetic resonance image synthesis. Stat Comput 33, 113 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-023-10282-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-023-10282-8