Abstract
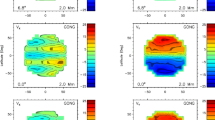
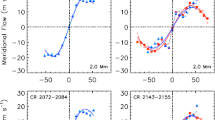
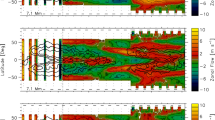
We study the subsurface meridional flow and its divergence from the surface to a depth of about 16 Mm at the equator and its variation with the solar cycle derived with ring-diagram analysis applied to Michelson Doppler Imager (MDI) Dynamics Program, Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG), and Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) Dopplergrams. The meridional flow at the equator is small but nonzero and is mainly negative (southward) during Solar Cycle 23 with an average of \(-1.1 \pm 0.2~\text{m}\,\text{s}^{-1}\) at depths shallower than 7 Mm and positive (northward) during Solar Cycle 24 with an average of \(+1.3 \pm 0.1~\text{m}\,\text{s}^{-1}\) over the same depth range derived from supersynoptic maps of combined HMI and GONG data (scaled to match HMI flow amplitudes). The divergence in supersynoptic maps is positive at all times and clearly varies with the solar cycle with large values during cycle maxima and small values during minima. On time scales of synoptic maps, we found that at depths shallower than 10 Mm the cross-equatorial flow is, on average, toward the hemisphere with the larger amount of flux. The meridional flow at the equator has broad distributions with widths that are at least five times larger than the mean values. The distributions of Solar Cycles 23 and 24 overlap but are distinguishable. For a high-activity subset, the cross-equatorial flow is predominantly toward locations with high activity and the divergence is greater than average. The nonzero cross-equatorial flow is in this case a consequence of the inflows present near active regions and the imbalance of activity between the hemispheres. For a quiet-region subset, the cross-equatorial flow is, on average, in the same direction as the average flow over a solar cycle with a similar broad distribution, while the quiet-region divergence is smaller than the grand average.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The original flow maps are available at jsoc.stanford.edu for SDO/HMI and at gong.nso.edu/data for GONG data, while NSO/NISP magnetograms are available at nso.edu/data/nisp-data/. The processed data are available on reasonable application to the author.
References
Baldner, C.S., Schou, J.: 2012, Effects of asymmetric flows in solar convection on oscillation modes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 760, L1. DOI. ADS.
Basu, S., Antia, H.M., Bogart, R.S.: 2004, Ring-diagram analysis of the structure of solar active regions. Astrophys. J. 610, 1157. DOI. ADS.
Bisoi, S.K., Janardhan, P.: 2020, A new tool for predicting the solar cycle: correlation between flux transport at the equator and the poles. Solar Phys. 295, 79. DOI. ADS.
Bogart, R.S., Baldner, C., Basu, S., Haber, D.A., Rabello-Soares, M.C.: 2011a, HMI ring diagram analysis I. The processing pipeline. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 271, 012008. DOI. ADS.
Bogart, R.S., Baldner, C., Basu, S., Haber, D.A., Rabello-Soares, M.C.: 2011b, HMI ring diagram analysis II. Data products. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 271, 012009. DOI. ADS.
Braun, D.C.: 2019, Flows around averaged solar active regions. Astrophys. J. 873, 94. DOI. ADS.
Bumba, V., Howard, R.: 1969, Solar activity and recurrences in magnetic-field distribution. Solar Phys. 7, 28. DOI. ADS.
Cally, P.S.: 2007, What to look for in the seismology of solar active regions. Astron. Nachr. 328, 286. DOI. ADS.
Cameron, R.H., Schüssler, M.: 2012, Are the strengths of solar cycles determined by converging flows towards the activity belts? Astron. Astrophys. 548, A57. DOI. ADS.
Cameron, R.H., Dasi-Espuig, M., Jiang, J., Işık, E., Schmitt, D., Schüssler, M.: 2013, Limits to solar cycle predictability: cross-equatorial flux plumes. Astron. Astrophys. 557, A141. DOI. ADS.
Cameron, R.H., Jiang, J., Schüssler, M., Gizon, L.: 2014, Physical causes of solar cycle amplitude variability. J. Geophys. Res. 119, 680. DOI. ADS.
Charbonneau, P.: 2020, Dynamo models of the solar cycle. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 17, 4. DOI. ADS.
Chen, R., Zhao, J.: 2018, Temporal evolution of solar meridional flow in the deep interior during 2010 – 2018. In: Catalyzing Solar Connections, 55. ADS.
Corbard, T., Toner, C., Hill, F., Hanna, K.D., Haber, D.A., Hindman, B.W., Bogart, R.S.: 2003, Ring-diagram analysis with GONG++. In: Sawaya-Lacoste, H. (ed.) GONG+ 2002. Local and Global Helioseismology: The Present and Future, ESA SP 517, 255. ADS.
Couvidat, S., Schou, J., Hoeksema, J.T., Bogart, R.S., Bush, R.I., Duvall, T.L., Liu, Y., Norton, A.A., Scherrer, P.H.: 2016, Observables processing for the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager instrument on the Solar Dynamics Observatory. Solar Phys. 291, 1887. DOI. ADS.
Gizon, L., Cameron, R.H., Pourabdian, M., Liang, Z.-C., Fournier, D., Birch, A.C., Hanson, C.S.: 2020, Meridional flow in the Sun’s convection zone is a single cell in each hemisphere. Science 368, 1469. DOI. ADS.
Gottschling, N., Schunker, H., Birch, A.C., Löptien, B., Gizon, L.: 2021, Evolution of solar surface inflows around emerging active regions. Astron. Astrophys. 652, A148. DOI. ADS.
Haber, D.A., Hindman, B.W., Toomre, J., Bogart, R.S., Thompson, M.J., Hill, F.: 2000, Solar shear flows deduced from helioseismic dense-pack samplings of ring diagrams. Solar Phys. 192, 335. DOI. ADS.
Haber, D.A., Hindman, B.W., Toomre, J., Bogart, R.S., Larsen, R.M., Hill, F.: 2002, Evolving submerged meridional circulation cells within the upper convection zone revealed by ring-diagram analysis. Astrophys. J. 570, 855. DOI. ADS.
Harvey, J., Tucker, R., Britanik, L.: 1998, High resolution upgrade of the GONG instruments. In: Korzennik, S. (ed.) Structure and Dynamics of the Interior of the Sun and Sun-Like Stars, ESA Special Publication 418, 209. ADS.
Harvey, J.W., Hill, F., Hubbard, R.P., Kennedy, J.R., Leibacher, J.W., Pintar, J.A., Gilman, P.A., Noyes, R.W., Title, A.M., Toomre, J., Ulrich, R.K., Bhatnagar, A., Kennewell, J.A., Marquette, W., Patron, J., Saa, O., Yasukawa, E.: 1996, The Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG) project. Science 272, 1284. DOI. ADS.
Harvey, K.L., Zwaan, C.: 1993, Properties and emergence of bipolar active regions. Solar Phys. 148, 85. DOI. ADS.
Hill, F.: 1988, Rings and trumpets – three-dimensional power spectra of solar oscillations. Astrophys. J. 333, 996. DOI. ADS.
Hoeksema, J.T., Baldner, C.S., Bush, R.I., Schou, J., Scherrer, P.H.: 2018, On-orbit performance of the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager instrument onboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory. Solar Phys. 293, 45. DOI. ADS.
Howe, R., Komm, R.W., Hill, F., Haber, D.A., Hindman, B.W.: 2004, Activity-related changes in local solar acoustic mode parameters from Michelson Doppler imager and global oscillations network group. Astrophys. J. 608, 562. DOI. ADS.
Jiang, J., Işik, E., Cameron, R.H., Schmitt, D., Schüssler, M.: 2010, The effect of activity-related meridional flow modulation on the strength of the solar polar magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 717, 597. DOI. ADS.
Jiang, J., Hathaway, D.H., Cameron, R.H., Solanki, S.K., Gizon, L., Upton, L.: 2014, Magnetic flux transport at the solar surface. Space Sci. Rev. 186, 491. DOI. ADS.
Komm, R., Gosain, S.: 2019, Kinetic helicity and lifetime of activity complexes during solar cycle 24. Astrophys. J. 887, 192. DOI. ADS.
Komm, R., Howe, R., Hill, F.: 2011, Subsurface velocity of emerging and decaying active regions. Solar Phys. 268, 407. DOI. ADS.
Komm, R., Howe, R., Hill, F.: 2017, Solar-cycle variation of subsurface-flow divergence: a proxy of magnetic activity? Solar Phys. 292, 122. DOI. ADS.
Komm, R., Howe, R., Hill, F.: 2018, Subsurface zonal and meridional flow during cycles 23 and 24. Solar Phys. 293, 145. DOI. ADS.
Komm, R., Howe, R., Hill, F.: 2020, Solar-cycle variation of the subsurface flows of active- and quiet-region subsets. Solar Phys. 295, 47. DOI. ADS.
Komm, R., Howe, R., Hill, F.: 2021, Divergence and vorticity of subsurface flows during solar cycles 23 and 24. Solar Phys. 296, 73. DOI. ADS.
Komm, R.W., Howard, R.F., Harvey, J.W.: 1993, Meridional flow of small photospheric magnetic features. Solar Phys. 147, 207. DOI. ADS.
Komm, R., González Hernández, I., Howe, R., Hill, F.: 2015a, Solar-cycle variation of subsurface meridional flow derived with ring-diagram analysis. Solar Phys. 290, 3113. DOI. ADS.
Komm, R., González Hernández, I., Howe, R., Hill, F.: 2015b, Subsurface zonal and meridional flow derived from GONG and SDO/HMI: a comparison of systematics. Solar Phys. 290, 1081. DOI. ADS.
Liang, Z.-C., Gizon, L., Birch, A.C., Duvall, T.L., Rajaguru, S.P.: 2018, Solar meridional circulation from twenty-one years of SOHO/MDI and SDO/HMI observations. Helioseismic travel times and forward modeling in the ray approximation. Astron. Astrophys. 619, A99. DOI. ADS.
Liu, Y., Zhao, J., Schuck, P.W.: 2013, Horizontal flows in the photosphere and subphotosphere of two active regions. Solar Phys. 287, 279. DOI. ADS.
Löptien, B., Birch, A.C., Duvall, T.L., Gizon, L., Proxauf, B., Schou, J.: 2017, Measuring solar active region inflows with local correlation tracking of granulation. Astron. Astrophys. 606, A28. DOI. ADS.
Mackay, D.H., Yeates, A.R.: 2012, The sun’s global photospheric and coronal magnetic fields: observations and models. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 9, 6. DOI. ADS.
Martin-Belda, D., Cameron, R.H.: 2016, Surface flux transport simulations: effect of inflows toward active regions and random velocities on the evolution of the Sun’s large-scale magnetic field. Astron. Astrophys. 586, A73. DOI. ADS.
Martin-Belda, D., Cameron, R.H.: 2017, Inflows towards active regions and the modulation of the solar cycle: a parameter study. Astron. Astrophys. 597, A21. DOI. ADS.
Norton, A.A., Charbonneau, P., Passos, D.: 2014, Hemispheric coupling: comparing dynamo simulations and observations. Space Sci. Rev. 186, 251. DOI. ADS.
Pesnell, W.D., Thompson, B.J., Chamberlin, P.C.: 2012, The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 3. DOI. ADS.
Petrovay, K.: 2020, Solar cycle prediction. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 17, 2. DOI. ADS.
Poulier, P.-L.: 2022, Helioseismic diagnostics of solar surface dynamics in the near-surface layers. PhD thesis, Georg August University of Gottingen, Germany. ADS.
Rabello-Soares, M.C., Bogart, R.S., Scherrer, P.H.: 2016, Statistical analysis of acoustic wave parameters near solar active regions. Astrophys. J. 827, 140. DOI. ADS.
Scherrer, P.H., Bogart, R.S., Bush, R.I., Hoeksema, J.T., Kosovichev, A.G., Schou, J., Rosenberg, W., Springer, L., Tarbell, T.D., Title, A., Wolfson, C.J., Zayer, I. (MDI Engineering Team): 1995, The solar oscillations investigation – Michelson Doppler imager. Solar Phys. 162, 129. DOI. ADS.
Scherrer, P.H., Schou, J., Bush, R.I., Kosovichev, A.G., Bogart, R.S., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Duvall, T.L., Zhao, J., Title, A.M., Schrijver, C.J., Tarbell, T.D., Tomczyk, S.: 2012, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) investigation for the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 207. DOI. ADS.
Schou, J., Scherrer, P.H., Bush, R.I., Wachter, R., Couvidat, S., Rabello-Soares, M.C., Bogart, R.S., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Duvall, T.L., Akin, D.J., Allard, B.A., Miles, J.W., Rairden, R., Shine, R.A., Tarbell, T.D., Title, A.M., Wolfson, C.J., Elmore, D.F., Norton, A.A., Tomczyk, S.: 2012, Design and ground calibration of the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) instrument on the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 229. DOI. ADS.
Toner, C.G.: 2001, On the absolute alignment of GONG images. In: Wilson, A., Pallé, P.L. (eds.) SOHO 10/GONG 2000 Workshop: Helio- and Asteroseismology at the Dawn of the Millennium, ESA Special Publication 464, 355. ADS.
Toner, C., Goodrich, J., Shroff, C., Kneale, R.: 2004, A first look at the June 8, 2004 Venus transit as observed by GONG. In: Danesy, D. (ed.) SOHO 14 Helio- and Asteroseismology: Towards a Golden Future, ESA Special Publication 559, 657. ADS.
Wang, Y.-M., Nash, A.G., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 1989, Magnetic flux transport on the Sun. Science 245, 712. DOI. ADS.
Zhao, J., Nagashima, K., Bogart, R.S., Kosovichev, A.G., Duvall, T.L. Jr.: 2012, Systematic center-to-limb variation in measured helioseismic travel times and its effect on inferences of solar interior meridional flows. Astrophys. J. Lett. 749, L5. DOI. ADS.
Acknowledgments
The data used here are courtesy of NASA/SDO and the HMI Science Team. This work also utilizes GONG data obtained by the NSO Integrated Synoptic Program (NISP), managed by the National Solar Observatory, which is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA), Inc. under a cooperative agreement with the National Science Foundation. I thank Mark DeRosa whose presentation about flux transport gave me the idea for this study.
Funding
This work was supported by NASA grants 80NSSC18K1206, 80NSSC19K0261, and 80NSSC20K0194 to the National Solar Observatory and by NASA grant NNH18ZDA001N-DRIVE to Stanford University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The author declares that he has no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to the Topical Collection:
Celebrating a Solar Cycle of Discovery with SDO
Guest Editors: Dean Pesnell, Ryan Milligan and Shin Toriumi
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Komm, R. Is the Subsurface Meridional Flow Zero at the Equator?. Sol Phys 297, 99 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-022-02027-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-022-02027-z