Abstract
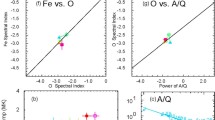
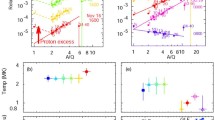
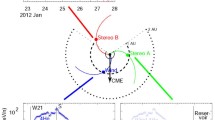
In solar energetic particle (SEP) events, the power-law dependence of element abundance enhancements on their mass-to-charge ratios [\(A/Q\)] provides a new tool that measures the combined rigidity dependences from both acceleration and transport. Distinguishing between these two processes can be challenging. However, the effects of acceleration dominate when SEP events are small or when the ions propagate scatter-free, and transport can dominate the temporal time evolution of large events with streaming-limited intensities. Magnetic reconnection in solar jets produces positive powers of \(A/Q\) from +2 to +7 and shock acceleration produces mostly negative powers from −2 to +1 in small and moderate SEP events where transport effects are minimal. This variation in the rigidity dependence of shock acceleration may reflect the non-planar structure, complexity, and temporal time variation of coronal shocks themselves. Wave amplification by streaming protons in the largest SEP events suppresses the escape of ions with low \(A/Q\), creating observed powers of \(A/Q\) from +1 to +3 upstream of the accelerating shock, decreasing to small negative powers downstream. For shock acceleration, the powers of \(A/Q\) are correlated with the energy spectral indices of He, O, and Fe, yet unexplained departures exist.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afanasiev, A., Battarbee, M., Vainio, R.: 2016, Self-consistent Monte Carlo simulations of proton acceleration in coronal shocks: effect of anisotropic pitch-angle scattering of particles. Astron. Astrophys. 584, 81. DOI.
Bell, A.R.: 1978a, The acceleration of cosmic rays in shock fronts. I. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 182, 147. DOI.
Bell, A.R.: 1978b, The acceleration of cosmic rays in shock fronts. II. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 182, 443. DOI.
Breneman, H.H., Stone, E.C: 1985, Solar coronal and photospheric abundances from solar energetic particle measurements. Astrophys. J. Lett. 299, L57. DOI.
Bučík, R.: 2020, 3He-rich solar energetic particles: solar sources. Space Sci. Rev. 216, 24. DOI.
Bučík, R., Innes, D.E., Mall, U., Korth, A., Mason, G.M., Gómez-Herrero, R.: 2014, Multi-spacecraft observations of recurrent 3He-rich solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. 786, 71. DOI.
Bučík, R., Innes, D.E., Chen, N.H., Mason, G.M., Gómez-Herrero, R., Wiedenbeck, M.E.: 2015, Long-lived energetic particle source regions on the Sun. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 642, 012002. DOI.
Bučík, R., Innes, D.E., Mason, G.M., Wiedenbeck, M.E., Gómez-Herrero, R., Nitta, N.V.: 2018a, 3He-rich solar energetic particles in helical jets on the Sun. Astrophys. J. 852, 76. DOI.
Bučík, R., Wiedenbeck, M.E., Mason, G.M., Gómez-Herrero, R., Nitta, N.V., Wang, L.: 2018b, 3He-rich solar energetic particles from sunspot jets. Astrophys. J. Lett. 869, L21. DOI.
Chen, N.H., Bučík, R., Innes, D.E., Mason, G.M.: 2015, Case studies of multi-day 3He-rich solar energetic particle periods. Astron. Astrophys. 580, 16. DOI.
Cliver, E.W., Kahler, S.W., Reames, D.V.: 2004, Coronal shocks and solar energetic proton events. Astrophys. J. 605, 902. DOI.
Cohen, C.M.S., Mason, G.M., Mewaldt, R.A., Wiedenbeck, M.E.: 2014, The longitudinal dependence of heavy-ion composition in the 2013 April 11 solar energetic particle event. Astrophys. J. 794, 35. DOI.
Desai, M.I., Giacalone, J.: 2016, Large gradual solar energetic particle events. Liv. Rev. Solar Phys. DOI.
Desai, M.I., Mason, G.M., Dwyer, J.R., Mazur, J.E., Gold, R.E., Krimigis, S.M., Smith, C.W., Skoug, R.M.: 2003, Evidence for a suprathermal seed population of heavy ions accelerated by interplanetary shocks near 1 AU. Astrophys. J. 588, 1149. DOI.
Drake, J.F., Cassak, P.A., Shay, M.A., Swisdak, M., Quataert, E.: 2009, A magnetic reconnection mechanism for ion acceleration and abundance enhancements in impulsive flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 700, L16. DOI.
Ellison, D.C., Möbius, E., Paschmann, G.: 1990, Particle injection and acceleration at Earth’s bow shock: comparison of upstream and downstream events. Astrophys. J. 352, 376. DOI.
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P., Usoskin, I.G.: 2012, Properties of Ground level enhancement events and the associated solar eruptions during solar cycle 23. Space Sci. Rev. 171, 23. DOI.
Gosling, J.T.: 1993, The solar flare myth. J. Geophys. Res. 98, 18937. DOI.
Hu, J., Li, G., Ao, X., Verkhoglyadova, O., Zank, G.: 2017, Modeling particle acceleration and transport at a 2D CME-driven shock. J. Geophys. Res. 122, 10,938. DOI.
Hu, J., Li, G., Fu, S., Zank, G., Ao, X.: 2018, Modeling a single SEP event from multiple vantage points using the iPATH model. Astrophys. J. Lett. 854, L19. DOI.
Jones, F.C., Ellison, D.C.: 1991, The plasma physics of shock acceleration. Space Sci. Rev. 58, 259. DOI.
Kahler, S.W., Reames, D.V., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 2001, Coronal mass ejections associated with impulsive solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. 562, 558. DOI.
Kahler, S.W., Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Michels, D.J.: 1984, Associations between coronal mass ejections and solar energetic proton events. J. Geophys. Res. 89, 9683. DOI.
Kajdič, P., Preisser, L., Blanco-Cano, X., Burgess, D., Trotta, D.: 2019, First observations of irregular surface of interplanetary shocks at ion scales by Cluster. Astrophys. J. Lett. 874, L13. DOI.
Kouloumvakos, A., Rouillard, A.P., Wu, Y., Vainio, R., Vourlidas, A., Plotnikov, I., Afanasiev, A., Önel, H.: 2019, Connecting the properties of coronal shock waves with those of solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. 876, 80. DOI.
Laming, J.M.: 2015, The FIP and inverse FIP effects in solar and stellar coronae. Liv. Rev. Solar Phys. 12, 2. DOI.
Laming, J.M., Vourlidas, A., Korendyke, C., Chua, D., Cranmer, S.R., Ko, Y.-K., et al.: 2019, Element abundances: a new diagnostic for the solar wind. Astrophys. J. 879, 124. DOI.
Lario, D., Decker, R.B., Roelof, E.C., Viñas, A.-F.: 2015, Energetic particle pressure at interplanetary shocks: STEREO-A observations. Astrophys. J. 813, 85. DOI.
Lee, M.A.: 1983, Coupled hydromagnetic wave excitation and ion acceleration at interplanetary traveling shocks. J. Geophys. Res. 88, 6109. DOI.
Lee, M.A.: 2005, Coupled hydromagnetic wave excitation and ion acceleration at an evolving coronal/interplanetary shock. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 158, 38. DOI.
Lee, M.A., Mewaldt, R.A., Giacalone, J.: 2012, Shock acceleration of ions in the heliosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 173, 247. DOI.
Mason, G.M.: 2007, 3He-rich solar energetic particle events. Space Sci. Rev. 130, 231. DOI.
Mason, G.M., Gloeckler, G., Hovestadt, D.: 1984, Temporal variations of nucleonic abundances in solar flare energetic particle events. II – Evidence for large-scale shock acceleration. Astrophys. J. 280, 902. DOI.
Mason, G.M., Mazur, J.E., Dwyer, J.R.: 1999, 3He enhancements in large solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. Lett. 525, L133. DOI.
Mason, G.M., Ng, C.K., Klecker, B., Green, G.: 1989, Impulsive acceleration and scatter-free transport of about 1 MeV per nucleon ions in 3He-rich solar particle events. Astrophys. J. 339, 529. DOI.
Mason, G.M., Mazur, J.E., Dwyer, J.R., Jokippi, J.R., Gold, R.E., Krimigis, S.M.: 2004, Abundances of heavy and ultraheavy ions in 3He-rich solar flares. Astrophys. J. 606, 555. DOI.
Mazzotta, P., Mazzitelli, G., Colafrancesco, S., Vittorio, N.: 1998, Ionization balance for optically thin plasmas: Rate coefficients for all atoms and ions of the elements H to Ni. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 133, 403. DOI.
Mewaldt, R.A., Cohen, C.M.S., Leske, R.A., Christian, E.R., Cummings, A.C., Stone, E.C., von Rosenvinge, T.T., Wiedenbeck, M.E.: 2002, Fractionation of solar energetic particles and solar wind according to first ionization potential. Adv. Space Res. 30, 79. DOI.
Meyer, J.-P.: 1985, The baseline composition of solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 57, 151. DOI.
Mostafavi, P., Zank, G.P., Webb, G.M.: 2017, Structure of energetic particle mediated shocks revisited. Astrophys. J. 841, 4. DOI.
Ng, C.K., Reames, D.V.: 2008, Shock acceleration of solar energetic protons: the first 10 minutes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 686, L123. DOI.
Ng, C.K., Reames, D.V., Tylka, A.J.: 1999, Effect of proton-amplified waves on the evolution of solar energetic particle composition in gradual events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 2145. DOI.
Ng, C.K., Reames, D.V., Tylka, A.J.: 2001, Abundances, spectra, and anisotropies in the 1998 Sep 30 and 2000 Apr 4 large SEP events. In: Kampert, K.-H., Hainzelmann, G., Spiering, C., Simon, M., Lorenz, E., Pohl, M., Droege, W., Kunow, H., Scholer, M. (eds.) Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic-Ray Conf., Hamburg, 8, Copernicus, Katlenburg-Lindau, 3140.
Ng, C.K., Reames, D.V., Tylka, A.J.: 2003, Modeling shock-accelerated solar energetic particles coupled to interplanetary Alfvén waves. Astrophys. J. 591, 461. DOI.
Ng, C.K., Reames, D.V., Tylka, A.J.: 2012, Solar energetic particles: shock acceleration and transport through self-amplified waves. AIP Conf. Proc. 1436, 212. DOI.
Parker, E.N.: 1963, Interplanetary Dynamical Processes, Interscience, New York.
Post, D.E., Jensen, R.V., Tarter, C.B., Grasberger, W.H., Lokke, W.A.: 1977, Steady-state radiative cooling rates for low-density, high temperature plasmas. Atom. Data Nucl. Data Tables 20, 397. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 1988, Bimodal abundances in the energetic particles of solar and interplanetary origin. Astrophys. J. Lett. 330, L71. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 1990, Acceleration of energetic particles by shock waves from large solar flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 358, L63. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 1995a, Coronal abundances determined from energetic particles. Adv. Space Res. 15(7), 41.
Reames, D.V.: 1995b, Solar energetic particles: a paradigm shift. Rev. Geophys. 33, 585. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 1999, Particle acceleration at the sun and in the heliosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 90, 413. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2000, Abundances of trans-iron elements in solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. Lett. 540, L111. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2009, Solar energetic-particle release times in historic ground-level events. Astrophys. J. 706, 844. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2013, The two sources of solar energetic particles. Space Sci. Rev. 175, 53. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2014, Element abundances in solar energetic particles and the solar corona. Solar Phys. 289, 977. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2015, What are the sources of solar energetic particles? Element abundances and source plasma temperatures. Space Sci. Rev. 194, 303. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2016, Temperature of the source plasma in gradual solar energetic particle events. Solar Phys. 291, 911. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2017, Solar Energetic Particles, Lec. Notes Phys. 932, Springer, Berlin. DOI. ISBN 978-3-319-50870-2.
Reames, D.V.: 2018a, The “FIP effect” and the origins of solar energetic particles and of the solar wind. Solar Phys. 293, 47. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2018b, Abundances, ionization states, temperatures, and FIP in solar energetic particles. Space Sci. Rev. 214, 61. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2019a, Hydrogen and the abundances of elements in impulsive solar energetic-particle events. Solar Phys. 294, 37. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2019b, Hydrogen and the abundances of elements in gradual solar energetic-particle events. Solar Phys. 294, 69. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2019c, Excess H, suppressed He, and the abundances of elements in solar energetic particles. Solar Phys. 294, 141. DOI.
Reames, D.V.: 2020, Four distinct pathways to the element abundances in solar energetic particles. Space Sci. Rev. 216, 20. DOI.
Reames, D.V., Barbier, L.M., Ng, C.K.: 1996, The spatial distribution of particles accelerated by coronal mass ejection-driven shocks. Astrophys. J. 466, 473. DOI.
Reames, D.V., Cliver, E.W., Kahler, S.W.: 2014a, Abundance enhancements in impulsive solar energetic-particle events with associated coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 289, 3817. DOI.
Reames, D.V., Cliver, E.W., Kahler, S.W.: 2014b, Variations in abundance enhancements in impulsive solar energetic-particle events and related CMEs and flares. Solar Phys. 289, 4675. DOI.
Reames, D.V., Meyer, J.P., von Rosenvinge, T.T.: 1994, Energetic-particle abundances in impulsive solar flare events. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 90, 649. DOI.
Reames, D.V., Ng, C.K.: 1998, Streaming-limited intensities of solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. 504, 1002. DOI.
Reames, D.V., Ng, C.K.: 2004, Heavy-element abundances in solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. 610, 510. DOI.
Reames, D.V., Ng, C.K.: 2010, Streaming-limited intensities of solar energetic particles on the intensity plateau. Astrophys. J. 723, 1286. DOI.
Reames, D.V., Ng, C.K., Berdichevsky, D.: 2001, Angular distributions of solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. 550, 1064. DOI.
Trotta, D., Burgess, D., Prete, G., Perri, S., Zimbardo, G.: 2020, Particle transport in hybrid PIC shock simulations: a comparison of diagnostics. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 491, 580. DOI.
Tylka, A.J., Lee, M.A.: 2006, Spectral and compositional characteristics of gradual and impulsive solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. 646, 1319. DOI.
Tylka, A.J., Reames, D.V., Ng, C.K.: 1999, Observations of systematic temporal evolution in elemental composition during gradual solar energetic particle events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 2141. DOI.
Tylka, A.J., Cohen, C.M.S., Dietrich, W.F., Lee, M.A., Maclennan, C.G., Mewaldt, R.A., Ng, C.K., Reames, D.V.: 2005, Shock geometry, seed populations, and the origin of variable elemental composition at high energies in large gradual solar particle events. Astrophys. J. 625, 474. DOI.
von Rosenvinge, T.T., Barbier, L.M., Karsch, J., Liberman, R., Madden, M.P., Nolan, T., Reames, D.V., Ryan, L., Singh, S., Trexel, H.: 1995, The Energetic Particles: Acceleration, Composition, and Transport (EPACT) investigation on the Wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 152. DOI.
Webber, W.R.: 1975, Solar and galactic cosmic ray abundances – a comparison and some comments. In: Pinkau, K. (ed.) Proc. 14th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf., Munich, 5, 1597. ADS.
Zank, G.P., Rice, W.K.M., Wu, C.C.: 2000, Particle acceleration and coronal mass ejection driven shocks: a theoretical model. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 25079. DOI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The author declares he has no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reames, D.V. Distinguishing the Rigidity Dependences of Acceleration and Transport in Solar Energetic Particles. Sol Phys 295, 113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01680-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01680-6