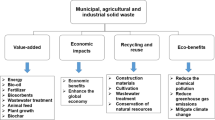
Abstract
Large quantities of sludge produced from acid mine drainage (AMD) treatment require proper disposal due to their potential environmental impacts. Sludge handling and disposal practices are used to address the environmental concerns, and they represent significant economic liability. As a sustainable management strategy, utilization of AMD sludge for beneficial applications can not only eliminate or alleviate the need of disposal, but create value from the materials. In particular, coal mine drainage sludge (CMDS) can potentially be used for various applications due to its high ferric content. However, conventional coal mine drainage (CMD) treatment and sludge disposal practices do not necessarily produce sludge with optimal properties for the applications. This calls for development and implementation of application-driven treatment and sludge management practices to generate sludge materials tailored for the target applications. This study systematically characterized causal linkages between various CMD treatment and sludge disposal factors and sludge properties reported in literature. It also reviewed and documented optimum sludge properties for beneficial applications including adsorptive pollution control, microbially facilitated ferric reduction, and catalytic degradation of wastes. The systematic understanding was then used to develop CMD treatment and sludge disposal guidelines that would facilitate production of application-specific sludge materials. Such an application-driven CMDS management approach, if successfully implemented, is expected to bring about modernization of waste management infrastructure and create values in mineral producing regions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed SN, Almuktar SA, Scholz M (2017) Treatment of contaminated greywater usingpelletised mine water sludge. J Environ Manage 197:10–23
Ahmed M, Lin L-S (2017) Ferric reduction in organic matter oxidation and its applicability for anaerobic wastewater treatment: a review and future aspects. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 16:273–287
Ahmed M, Lin O, Saup CM, Wilkins MJ, Lin L-S (2019) Effects of Fe/S ratio on the kinetics and microbial ecology of an Fe(III)-dosed anaerobic wastewater treatment system. J Hazard Mater 369:593–600
Ahmed M, Saup CM., Wilkins MJ, Lin L-S (2020) Continuous ferric iron-dosed anaerobic wastewater treatment: Treatment performance, sludge characteristics, and microbial composition. J Environ Chem Eng 8(2):103537
Ahmed M, Aziziha M, Anwar R, Johnson MB, Lin L-S (2021) Magnetic sludge byproducts for adsorptive phosphorus removal: resource recovery from iron-based anaerobic sewage sludge. Waste Manage 120:269–276
Alfaya E, Iglesias O, Pazos M, Sanrom´an MA (2015) Environmental application of an industrial waste as catalyst for the electro-Fenton-like treatment of organic pollutants. RSC Adv 5:14416–14424
Amanda N, Moersidik SS (2019) Characterization of sludge generated from acid mine drainage treatment plants. J Phys 1351:012113
Amos RT, Bekins BA, Cozzarelli IM, Voytek M, Kirshtein JD, Jones EJ, Blowes DW (2012) Evidence for iron-mediated anaerobic methane oxidation in a crude oil-contaminated aquifer. Geobiology 10(6):506–517
Andersen SL, Flores RG, Madeira VS, José HJ, Moreira RF (2012) Synthesis and characterization of acicular iron oxide particles obtained from acid mine drainage and their catalytic properties in toluene oxidation. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(2):767–774
Arslan-Alaton I (2007) Degradation of a commercial textile biocide with advanced oxidation processes and ozone. J Environ Manage 82:145–154
Aube BC & Zinck JM (1999) Comparison of AMD treatment processes and their impact on sludge characteristics. In: Mining and the environment II. Proceedings for Sudbury, pp 261–270
Azam HM, Finneran KT (2013) Ferric iron amendment increases Fe(III)-reducing microbial diversity and carbon oxidation in on-site wastewater systems. Chemosphere 90(4):1435–1443
Babuponnusami A, Muthukumar K (2014) A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 2:557–572
Badawy M, Ghalyb M, Gad-Allah T (2006) Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of organophosphorus pesticides from wastewater. Desalination 194:166–175
Badulis G, Tokoro C, Sasaki H (2006) Sludge generation in the treatment of acid mine drainage (amd) by high-density sludge (hds) recycling method. Min Mater Process Inst Japan 122:406–414
Baltpurvins KA, Burns RC, Lawrance GA (1996) Effect of pH and anion type on the aging of freshly precipitated iron(iii) hydroxide sludges. Environ Sci Technol 30(3):939–944
Barreiro JC, Capelato MD, Martin-Neto L, Christian H, Hansen B (2007) Oxidative decomposition of atrazine by a Fenton-like reaction in a H2O2/ferrihydrite system. Water Res 41(1):55–62
Bautista P, Mohedano A, Gilarranz M, Casas J, Rodriguez J (2007) Application of Fenton oxidation to cosmetic wastewater treatment. J Hazardous Mater 143:128–134
Beal EJ, House CH, Orphan VJ (2009) Manganese- and iron-dependent marine methane oxidation. Science 325(5937):184–187
Bianco B, Michelis I, Vegliò F (2011) Fenton treatment of complex industrial wastewater: optimization of process conditions by surface response method. J Hazardous Mater 186:1733–1738
Bonneville S (2005) Kinetics of microbial Fe(III) oxyhydroxide reduction: The role of mineral properties. Doctoral dissertation, Utrecht University, Department of Earth-Sciences – Geochemistry
Bonneville S, Behrends T, Cappellen PV (2009) Solubility and dissimilatory reduction kinetics of iron(III) oxyhydroxides: a linear free energy relationship. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:5273–5282
Bosch J, Heister K, Hofmann T, Meckenstock RU (2010) Nanosized iron oxide colloids strongly enhance microbial iron reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(1):184–189
Breidenbach AW, Schaffer RB (1976) Development document for interim final effluent limitations guidelines and new source performance standardsfor the coal mining. Environmental Protection Agency, U.S
Catalkaya E, Kargi F (2007) Color, TOC and AOX removals from pulp mill effluent by advanced oxidation processes: a comparative study. J Hazardous Mater 139:244–253
Chapelle FH, Bradley PM, Lovley DR, O’Neill K, Landmeyer JE (2005) Rapid evolution of redox processes in a petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifer. Groundwater 40(4):353–360
Chase ME (2018) Iron hydroxide from coal mine drainage to remove and reuse phosphorus from greenhouse and plant nursery runoff, Masters thesis, Clemson University, USA
Chen T, Yana B, Lei C, Xiao X (2014) Pollution control and metal resource recovery for acid mine drainage. Hydrometallurgy 147:112–119
Chitrakar R, Tezuka S, Sonoda A, Sakane K, Ooi K, Hirotsu T (2006) Phosphate adsorption on synthetic goethite and akaganeite. J Colloid Interface Sci 298(2):602–608
Clement J-C, Shrestha J, Ehrenfeld JG, Jaffe PR (2005) Ammonium oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron under anaerobic conditions in wetland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 37:2323–2328
Cui M, Jang M, Cho S-H (2011) Potential application of sludge produced from coal mine drainage treatment for removing Zn(II) in an aqueous phase. Environ Geochem Health 33:103–112
Cui M, Jang M, Cho S-H, Khim J, Cannon FS (2012) A continuous pilot-scale system using coal-mine drainage sludge to treat acid mine drainage contaminated with high concentrations of Pb, Zn, and other heavy metals. J Hazard Mater 215:122–128
Cummings DE, March AW, Bostick B, Spring S, Frank Caccavo J, Fendorf S, Rosenzweig RF (2000) Evidence for microbial fe(iii) reduction in anoxic, mining-impacted lake sediments (lake coeur d’alene, idaho). Appl Environ Microbiol 66(1):154–162
Dempsey BA, Jeon B-H (2001) Characteristics of sludge produced from passive treatment of mine drainage. Geochem: Explor Environ, Anal 1:89–94
Ding L-J, An X-L, Li S, Zhang G-L, Zhu Y-G (2014) Nitrogen loss through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction from paddy soils in a chronosequence. Environ Sci Technol 48:10641–10647
Ding B, Li Z, Qin Y (2017) Nitrogen loss from anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to Iron(III) reduction in a riparian zone. Environ Pollut 231:379–386
Dobbie K, Heal K, Smith K (2006) Assessing the performance of phosphorus-saturated ochre as a fertilizer and its environmental acceptability. Soil Use Manag 21(2):231–239
Dobbie KE, Heal KV, Aumonier J, Smith KA, Johnstone A, Younger PL (2009) Evaluation of iron ochre from mine drainage treatment for removal of phosphorus from wastewater. Chemosphere 75(6):795–800
Elliott H, Dempsey B (1991) Agronomic effects of land application of water treatment sludges. Am Water Works Assoc 83(4):126–131
Ettwig KF, Zhu B, Speth D, Keltjens JT, Jetten MS, Kartal B (2016) Archaea catalyze iron-dependent anaerobic oxidation of methane. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(45):12792–12796
Evenson CJ, Nairn R (2000) Enhancing phosphorous sorption capacity with treatment wetland iron oxyhydroxides. Am Soc Min Reclam 2000:421–426
Feng J, Hu X, Yue P (2006) Effect of initial solution pH on the degradation of Orange II using clay-based Fe nanocomposites as heterogeneous photo Fenton catalyst. Water Res 40:641–646
Firpo BA, Weiler J, Schneider IA (2020) Technosol made from coal waste as a strategy to plant growth and environmental control. Energy Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engeos.2020.09.006
Firpo BA, Weiler J, Schneider IA (2021) Technosol made from coal waste as a strategy to plant growth and environmental control. Energy Geosci 2(2):160–166
Fish CL, Hedin R, Partezana JM (1996) Chemical characterization of iron oxide precipitates from wetlands constructed to treat polluted mine drainage. In: Proceedings America society of mining and reclamation. Knoxville, USA, pp 541–549
Florence K, Sapsford D, Johnson D, Kay C, Wolkersdorfer C (2016) Iron-mineral accretion from acid mine drainage and its application in passive treatment. Environ Technol 37(11):1428–1440
Florencea K, Sapsford D, Johnson D, Kay C, Wolkersdorfer C (2016) Iron-mineral accretion from acid mine drainage and its application in passive treatment. Environ Technol 37(11):1428–1440
Flores RG, Andersen SL, Maia LK (2012) Recovery of iron oxides from acid mine drainage and their application as adsorbent or catalyst. J Environ Manage 111:53–60
Georgaki I, Dudeney A, Monhemius A (2004) Characterisation of iron-rich sludge: correlations between reactivity, density and structure. Miner Eng 17:305–316
Ha NT, Anh BT (2017) The removal of heavy metals by iron mine drainage sludge and Phragmites australis. 2nd Transdisciplinary Research on Environmental Problems in Southeast Asia.71. IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science
Hacherl EL, Kosson DS, Cowan RM (2003) A kinetic model for bacterial Fe(III) oxide reduction in batch cultures. Water Resour Res 39(4):1098
Hakkou R, Benzaazoua M, Bussière B (2008) Acid mine drainage at the abandoned kettara mine (morocco): 1 environmental characterization. Mine Water Environ 27(3):145–159
He Z, Zhang Q, Feng Y, Luo H, Pana X, Gadd GM (2018) Microbiological and environmental significance of metal-dependent anaerobic oxidation of methane. Sci Total Environ 610:759–768
Heal KV, Dobbie KE, Bozika E, McHaffie H, Simpson AE, Smith KA (2005) Enhancing phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands with ochre from mine drainage treatment. Water Sci Technol 51(9):275–282
Hedin RS (2006) Sustainable mine drainage treatment through the passive production of saleable iron oxide solids. In: 7th international conference on acid rock drainage (ICARD). American Society of Mining and Reclamation (ASMR), Lexington, KY
Huang S, Jaffe PR (2018) Isolation and characterization of an ammonium-oxidizing iron reducer: Acidimicrobiaceae sp A6. PLoS ONE 13(4):e0194007
Ivanov V, Stabnikov V, Zhuang W, Tay J, Tay STL (2005) Phosphate removal from the returned liquor of municipal wastewater treatment plant using iron-reducing bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 98:1152–1161
Jang M (2014) Coal mine drainage sludge and its application for treating metallic mine effluent. Rev Environ Health 29(1):95–100
Kalin M, Fyson A, Wheeler NW (2006) The chemistry of conventional and alternative treatment systems for the neutralization of acid mine drainage. Sci Total Environ 366(2):395–408
Kefeni KK, Msagati TM, Maree JP, Mamba BB (2015) Metals and sulphate removal from acid mine drainage in two steps via ferrite sludge and barium sulphate formation. Miner Eng 81:79–87
Kirby CS, Decker SM, Macander NK (1999) Comparison of color, chemical and mineralogical compositions of mine drainage sediments to pigment. Environ Geol 37(3):243–254
Ko M-S, Kim J-Y, Lee J-S, Ko J-I, Kim K-W (2013) Arsenic immobilization in water and soil using acid mine drainage sludge. Appl Geochem 35:1–6
Komlos J, Jaffe PR (2004) Effect of iron bioavailability on dissolved hydrogen concentrations during microbial iron reduction. Biodegradation 15:315–325
Kwan WP, Voelker BM (2002) Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide and organic compounds in the presence of dissolved iron and ferrihydrite. Environ Sci Technol 36(7):1467–1476
Larsen O, Postma D (2001) Kinetics of reductive bulk dissolution of lepidocrocite, ferrihydrite, and goethite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65(9):1367–1379
Lee H, Kim D, Kim J, Ji M-K, Han Y-S, Park Y-T, Choi J (2015) As(III) and As(V) removal from the aqueous phase via adsorption onto acid mine drainage sludge (AMDS) alginate beads and goethite alginate beads. J Hazard Mater 292:146–154
Lewis EE (2014) Utilization of ferric compounds from acid mine drainage treatment sludge in anaerobic wastewater treatment. Doctoral Dissertation, West Virginia University, Civil and Environmental Engineering
Lin S-S, Gurol MD (1998) Catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide on iron oxide: kinetics, mechanism, and implications. Environ Sci Technol 32:1417–1423
Lovely D, Holmes D, Nevin K (2004) Dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. Adv Microb Physiol 49:219–286
Lovley D, Baedecker M, Lonergan D, Cozzarelli I, Phillips E, Siegel D (1989) Oxidation of aromatic contaminants coupled to microbial iron reduction. Nature 339:297–299
Marcello RR, Galato S, Peterson M, Riella HG, Bernardin AM (2008) Inorganic pigments made from the recycling of coal mine drainage treatment sludge. Environ Manage 88:1280–1284
Matavos-Aramyan S, Moussavi M (2017) Advances in fenton and fenton based oxidation processes for industrial effluent contaminants control-a review. Int J Environ Sci Nat Resour 2(4)
Mayes W, Potter H, Jarvis A (2009) Novel approach to zinc removal from circum-neutral mine waters using pelletised recovered hydrous ferric oxide. J Hazard Mater 162(1):512–520
McDonald DM, Webb JA, Musgrave RJ (2006) The effect of neutralization method and reagent on the rate of Cu and Zn release from acid rock drainage treatment sludges. ASMR, Lexington, KY
Mohana D, Chander S (2006) Removal and recovery of metal ions from acid mine drainage using lignite—A low cost sorbent. J Hazard Mater 137:1545–1553
Munch J, Ottow J (1983) Reductive transformation mechanism of ferric oxides in hydromorphic soils. Environ Biogeochem 35:383–394
Netpradit S, Thiravetyan P, Towprayoon S (2003) Application of waste metal hydroxide sludge for adsorption of azo reactive dyes. Water Res 37:763–772
Nielsen JL, Juretschko S, Wagner M, Nielsen PH (2002) Abundance and phylogenetic affiliation of iron reducers in activated sludge as assessed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and microautoradiography. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(9):4629–4636
Olds WE, Tsang DC, Weber PA, Weisener CG (2013) Nickel and zinc removal from acid mine drainage: roles of sludge surface area and neutralising agents. J Min. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/698031
Oni OE, Friedrich MW (2017) Metal oxide reduction linked to anaerobic methane oxidation. Trends Microbiol 25(2):88–90
Panagopoulos A, Haralambous K-J (2020a) Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD) and Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) strategies for wastewater management and resource recovery - analysis, challenges and prospects. J Environ Chem Eng 8(5):104418
Panagopoulos A, Haralambous K-J (2020b) Environmental impacts of desalination and brine treatment - Challenges and mitigation measures. Marine Pollut Bullet 161:111773
Park W, Nam Y-K, Lee M-J, Kim T-H (2009) Anaerobic ammonia-oxidation coupled with fe3+ reduction by an anaerobic culture from a piggery wastewater acclimated to NH4. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 14:680–685
Penn CJ, Bryant RB, Kleinman PJ, Allen AL (2007) Removing dissolved phosphorus from drainage ditch water with phosphorus sorbing materials. J Soil Water Conserv 62(4):269–276
Postma D (1993) The reactivity of iron oxides in sediments: a kinetic approach. Geochimica Et Cosmochirnwa Acta 57:5027–5034
Rakotonimaro TV, Neculita CM, Bussière B, Benzaazoua M, Zagury GJ (2017) Recovery and reuse of sludge from active and passive treatment of mine drainage-impacted waters: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:73–91
Riedinger N, Formolo MJ, Lyons TW, Henkel S, Beck A, Kasten S (2014) An inorganic geochemical argument for coupled anaerobic oxidation of methane and iron reduction in marine sediments. Geobiology 12(2):172–181
Roden E, Zachara JM (1996) Microbial reduction of crystalline iron(iii) oxides: influence of oxide surface area and potential for cell growth. Environ Sci Technol 30:1618–1628
Sapsford D, Santonastaso M, Thorn P, Kershaw S (2015) Conversion of coal mine drainage ochre to water treatment reagent: production, characterisation and application for P and Zn removal. J Environ Manage 160:7–15
Sawayama S (2006) Possibility of anoxic ferric ammonium oxidation. J Biosci Bioeng 101(1):70–72
Schewertmann U, Murad E (1983) Effect of pH on the formation of goethite and hematite from ferrihydrite. Clays Clay Miner 31(4):277–284
Seo E, Cheong Y, Yim G, Min K, Geroni J (2017) Recovery of Fe, Al and Mn in acid coal mine drainage by sequential selective precipitation with control of pH. CATENA 148:11–16
Sharma S, Mukhopadhyay M, Murthy Z (2013) Treatment of chlorophenols from wastewaters by advanced oxidation processes. Sep Purif Rev 42:263–295
Shim MJ, Choi BY, Lee G, Hwang YH, Yang J-S, O’Loughlin EJ, Kwon MJ (2015) Water quality changes in acid mine drainage streams in Gangneung, Korea, 10 years after treatment with limestone. J Geochem Explor 159:234–242
Shokes T, Molle G (1999) Removal of dissolved heavy metals from acid rock drainage using iron metal. Environ Sci Technol 33:282–287
Sibrell PL, Tucker TW (2012) Fixed bed sorption of phosphorus from wastewater using iron oxide-based media derived from acid mine drainage. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(8):5105–5117
Sibrell PL, Watten BJ (2003) Evaluation of sludge produced by limestone neutralization of AMD at the Friendship Hill National Historic Site. In: 9th billings land reclamation symposium. American Society of Mining and Reclamation, Billings MT
Sibrell PL, Montgomery GA, Ritenour KL, Tucker TW (2009) Removal of phosphorus from agricultural wastewaters using adsorption media prepared from acid mine drainage sludge. Water Res 43:2240–2250
Silva R, Secco MP, Lermen RT, Schneider IA, Hidalgo GE, Sampaio CH (2019) Optimizing the selective precipitation of iron to produce yellow pigment from acid mine drainage. Miner Eng 135:111–117
Skousen JG, Sexstone A, Ziemkiewicz P (2000) Acid mine drainage control and treatment. In: Daniels RI (ed) Reclamation of drastically disturbed lands. American Society of Agronomy and American Society for Surface Mining and Reclamation
Sorensen MA (2001) Iron oxides as a stabilizing agent for heavy metals - in the context of treating residues from waste incineration. Doctoral dissertation, Technical University of Denmark, Environment & Resources
Sorensen MA, Stackpoole MM, Frenkel AI, Bordia RK, Korshin GV, Christensen TH (2000) Aging of Iron (Hydr)oxides by heat treatment and effects on heavy metal binding. Environ Sci Technol 34(18):3991–4000
Tekin H, Bilkay O, Ataberk S, Balta T, Ceribasi I, Sanin F, Yetis U (2006) Use of Fenton oxidation to improve the biodegradability of a pharmaceutical wastewater. J Hazardous Mater 136:258–265
Tony MA, Lin L-S (2020a) Iron recovery from acid mine drainage sludge as Fenton source for municipal wastewater treatment. Int J Environ Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1734196
Tony MA, Lin L-S (2020b) Attenuation of organics contamination in polymers processing effluent using iron-based sludge: process optimization and oxidation mechanism. Environ Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2020.1803417
Trumm D (2010) Selection of active and passive treatment systems for AMD—flow charts for New Zealand conditions. NZ J Geol Geophys 53(2):195–210
USEPA (2008) Coal mining detailed study (821-R-08-012). USEPA
Valentine BR, Wang HC (1998) Iron oxide surface catalyzed oxidation of quinoline by hydrogen peroxide. J Environ Eng 124(1):31–38
Viadero RC, Wei X, Buzby K (2006) Characterization and dewatering evaluation of acid mine drainage sludge from ammonia neutralization. Environ Eng Sci 23(4):734–743
Viadero RC, Wei X, Buzby KM (2006) Characterization and dewatering evaluation of acid mine drainage sludge from ammonia neutralization. Environ Eng Sci 23(4):734–743
Wang YR, Daniel T (2013) Utilizing acid mine drainage sludge and coal fly ash for phosphate removal from dairy wastewater. Environ Technol 34(21):3177–3182
Wang N, Zheng T, Zhang G, Wang P (2016) A review on Fenton-like processes for organic wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 4:762–787
Watts RJ, Foget MK, Kong S-H, Teel AL (1999) Hydrogen peroxide decomposition in model subsurface systems. J Hazardous Mater B 69:229–243
Webb P (2009) Innovative enhanced metals recovery from acid mine drainage. Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection, Ebensburg, PA
Weber KA, Achenbach LA, Coates JD (2006) Microorganisms pumping iron: anaerobic microbial iron oxidation and reduction. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:752–764
Wei X (2005) Acid mine drainage: Sludge dewatering, metal recovery and synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles, Graduate Theses, Dissertations, and Problem Reports. West Virginia University, Morgantown
Wei X, Viadero RC Jr (2007) Adsorption and precoat filtration studies of synthetic dye removal by acid mine drainage sludge. J Environ Eng 133(6):633–640
Wei X, Viadero RC, Buzby KM (2005) Recovery of iron and aluminum from acid mine drainage by selective precipitation. Environ Eng Sci 22(6):745–755
Wei X, Viadero R, Bhojappa S (2008) Phosphorus removal by acid mine drainage sludge from secondary effluents of municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 42:3275–3284
Yang WH, Weber KA, Silver WL (2012) Nitrogen loss from soil through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction. Nat Geosci 5:538–541
Yang J-S, Kim Y-S, Park S-M, Baek K (2014) Removal of As(III) and As(V) using iron-rich sludge produced from coal mine drainage treatment plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:10878–10889
Yang J-S, Kwon MJ, Park Y-T, Choi J (2015) Adsorption of arsenic from aqueous solutions by iron oxide coated sand fabricated with acid mine drainage. Sep Sci Technol 50(2):267–275
Yang Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhao H, Peng H (2018) Nitrogen removal during anaerobic digestion of wasted activated sludge under supplementing Fe(III) compounds. Chem Eng J 332:711–716
Zhang M-H, Dong H, Zhao L, Wang D-X, Meng D (2019) A review on Fenton process for organic wastewater treatment based on optimization perspective. Sci Total Environ 670:110–121
Zhou G-W, Yang X-R, Li H, Marshall CW, Zheng B-X, Yan Y, Zhu Y-G (2016) Electron shuttles enhance anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron(iii) reduction. Environ Sci Technol 50:9298–9307
Zinck J (2006) Disposal, reprocessing and reuse options for acidic drainage treatment sludge. In: 7th international conference on acid rock drainage (ICARD). American Society of Mining and Reclamation (ASMR), St. Louis MO, pp 2604–2617
Zinck J, Wilson L, Chen T, Griffith W, Mikhail S & Turcotte A (1997) Characterization and stability of acid mine drainage treatment sludges. Mining and Mineral Sciences Laboratories
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Science Foundation [grant number OIA-1458952]. The authors are thankful for the support.
Funding
This research is supported by the National Science Foundation [grant number OIA-1458952].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anwar, R., Ahmed, M., Seats, P. et al. Prospect of utilizing coal mine drainage sludge as an iron source for value-creating applications. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 20, 679–695 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-021-09584-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-021-09584-y