Abstract
Purpose
The aim was to assess perceived health status and health-related quality of life (HRQL) according to persistence of and variation in weight status among children from the age of 4 to 6 years.
Methods
Longitudinal study of 1883 participants in the ELOIN cohort (Madrid Region, Spain), with physical examination at ages 4 and 6 years. Perceived health status and HRQL were assessed using parent-reported Kidscreen-10 scores, with excess weight being defined on the basis of body mass index (BMI) using the WHO reference tables (z-BMI > 1 standard deviation), and abdominal obesity being defined on the basis of waist circumference (percentile ≥ 90) using the tables proposed by Fernández et al. Variation in these two parameters at age 6 years was associated with incident cases of suboptimal health by logistic regression, and with HRQL by linear regression.
Results
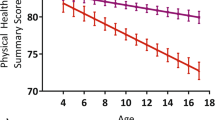
Compared to children without excess weight or abdominal obesity in both periods, incident cases of excess weight or abdominal obesity had odds ratios (ORs) of suboptimal health of 2.41 (95% CI 1.21 to 4.80) and 2.99 (95% CI 1.31 to 6.84) respectively. In terms of HRQL, children with remission of excess weight had a higher Kidscreen-10 score: β coefficient = 2.02 (95% CI 0.36 to 3.68), whereas new cases of abdominal obesity had a lower Kidscreen-10 score: β = − 2.22 (95% CI − 4.40 to − 0.03).
Conclusions
Incident cases of excess weight and abdominal obesity had a higher risk of suboptimal health. Incident cases of abdominal obesity were also associated with worse HRQL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ng, M., Fleming, T., Robinson, M., Thomson, B., Graetz, N., Margono, C., et al. (2014). Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. The Lancet,384(9945), 766–781.
Ahrens, W., Pigeot, I., Pohlabeln, H., De Henauw, S., Lissner, L., Molnár, D., et al. (2014). Prevalence of overweight and obesity in European children below the age of 10. International Journal of Obesity,38(2), S99–S107.
Abarca-Gómez, L., Abdeen, Z. A., Hamid, Z. A., Abu-Rmeileh, N. M., Acosta-Cazares, B., Acuin, C., et al. (2017). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. The Lancet,390(10113), 2627–2642.
Pérez-Farinós, N., López-Sobaler, A. M., Dal Re, M. A., Villar, C., Labrado, E., Robledo, T., et al. (2013). The ALADINO study: A national study of prevalence of overweight and obesity in Spanish children in 2011. BioMed Research International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/163687.
Agencia Española de Consumo, Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutrición (AECOSAN). Ministerio de Sanidad Servicios, Sociales e Igualdad. Estudio ALADINO 2015: Estudio de Vigilancia del Crecimiento, Alimentación, Actividad Física, Desarrollo Infantil y Obesidad en España. (2015). Madrid http://www.aecosan.msssi.gob.es/AECOSAN/docs/documentos/nutricion/observatorio/Estudio_ALADINO_2015.pdf.
Han, J. C., Lawlor, D. A., & Kimm, S. Y. (2010). Childhood obesity. The Lancet. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736.
Tsiros, M., Olds, T., Buckley, J., Grimshaw, P., Brennan, L., Walkley, J., et al. (2009). Health-related quality of life in obese children and adolescents. International Journal of Obesity,33(4), 387.
Buttitta, M., Iliescu, C., Rousseau, A., & Guerrien, A. (2014). Quality of life in overweight and obese children and adolescents: A literature review. Quality of Life Research,23(4), 1117–1139.
Griffiths, L. J., & Parsons, T. H. (2010). Self-esteem and quality of life in obese children and adolescents: A systematic review. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity,5(4), 282–304.
Ul-Haq, Z., Mackay, D. F., Fenwick, E., & Pell, J. P. (2013). Meta-analysis of the association between body mass index and health-related quality of life among children and adolescents, assessed using the pediatric quality of life inventory index. The Journal of Pediatrics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.07.049.
Hunsberger, M., Lehtinen-Jacks, S., Mehlig, K., Gwozdz, W., Russo, P., Michels, N., et al. (2016). Bidirectional associations between psychosocial well-being and body mass index in European children: Longitudinal findings from the IDEFICS study. BMC Public Health,16(1), 949.
Jansen, P. W., Mensah, F. K., Clifford, S., Nicholson, J. M., & Wake, M. (2013). Bidirectional associations between overweight and health-related quality of life from 4–11 years: Longitudinal study of Australian children. International Journal of Obesity. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.71.
Sawyer, M. G., Harchak, T., Wake, M., & Lynch, J. (2011). Four-year prospective study of BMI and mental health problems in young children. Pediatrics. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.20103132.
Williams, J. W., Canterford, L., Hesketh, K. D., Hardy, P., Waters, E. B., Patton, G. C., et al. (2011). Changes in body mass index and health related quality of life from childhood to adolescence. I. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity. https://doi.org/10.3109/17477166.2010.526226.
Parkinson, K. N., Adamson, A. J., Basterfield, L., Reilly, J. K., Le Couteur, A., & Reilly, J. J. (2015). Influence of adiposity on health-related quality of life in the gateshead millennium study cohort: Longitudinal study at 12 years. Archives of Disease in Childhood. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2014-307498.
Smith, K. W., Avis, N. E., & Assmann, S. F. (1999). Distinguishing between quality of life and health status in quality of life research: A meta-analysis. Quality of Life Research,8(5), 447–459.
Turer, C. B., Lin, H., & Flores, G. (2013). Health status, emotional/behavioral problems, health care use, and expenditures in overweight/obese US children/adolescents. Academic Pediatrics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2013.02.005.
Vingilis, E. R., Wade, T. J., & Seeley, J. S. (2002). Predictors of adolescent self-rated health. Analysis of the National Population Health Survey. Canadian Journal of Public Health/Revue Canadienne de Sante’e Publique, pp. 193–197
Ortiz-Marrón, H., Cuadrado-Gamarra, J. I., Esteban-Vasallo, M., Cortés-Rico, O., Sánchez-Díaz, J., Sánchez-Díaz, J., et al. (2016). Estudio longitudinal de Obesidad Infantil (ELOIN): diseño, participación y características de la muestra. Revista Española de Cardiología,69(5), 521–523.
de Onis, M., Onyango, A. W., Borghi, E., Siyam, A., Nishidaa, C., Siekmann, J., et al. (2007). Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bulletin of the World Health Organization,85(9), 660–667.
Fernández, J. R., Redden, D. T., Pietrobelli, A., & Allison, D. B. (2004). Waist circumference percentiles in nationally representative samples of African-American, European-American, and Mexican-American children and adolescents. The Journal of Pediatrics,145(4), 439–444.
Zimmet, P., Alberti, G., Kaufman, F., Tajima, N., Silink, M., Arslanian, S., et al. (2007). The IDF consensus definition of the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. The Lancet,8(5), 299–306.
Ravens-Sieberer, U., Erhart, M., Rajmil, L., Herdman, M., Auquier, P., Bruil, J., et al. (2010). Reliability, construct and criterion validity of the KIDSCREEN-10 score: A short measure for children and adolescents’ well-being and health-related quality of life. Quality of Life Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-010-9706-5.
Erhart, M., Ottova, V., Gaspar, T., Jericek, H., Schnohr, C., Alikasifoglu, M., et al. (2009). Measuring mental health and well-being of school-children in 15 European countries using the KIDSCREEN-10 Index. International Journal of Public Health,54(2), 160–166.
Boyce, W., Torsheim, T., Currie, C., & Zambon, A. (2006). The family affluence scale as a measure of national wealth: Validation of an adolescent self-report measure. Social Indicators Research,78(3), 473–487.
Breidablik, H. J., Meland, E., & Lydersen, S. (2008). Self-rated health in adolescence: A multifactorial composite. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health,36(1), 12–20.
Dobashi, K. (2016). Evaluation of obesity in school-age children. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.29397.
Ortiz-Marrón, H., Ortiz-Pinto, M. A., Cuadrado-Gamarra, J. I., Esteban-Vasallo, M., Cortés-Rico, O., Rey-Gallo, L., et al. (2018). Persistencia y variación del sobrepeso y la obesidad en la población preescolar de la Comunidad de Madrid tras dos años de seguimiento. Cohorte ELOIN: Revista Española Cardiología. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.recesp.2017.12.007.
Ahrens, W., Bammann, K., Siani, A., Buchecker, K., De Henauw, S., Iacoviello, L., et al. (2011). The IDEFICS cohort: Design, characteristics and participation in the baseline survey. International Journal of Obesity,35(S1), S3.
Espín-Ríos, M. I., Pérez-Flores, D., Sánchez-Ruíz, J. F., & Salmerón-Martínez, D. (2013). Prevalence of childhood obesity in the Murcia Region; an assessment of different references for body mass index. In Anales de pediatría (Barcelona, Spain: 2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anpedi.2012.09.007.
González-García, A., Álvarez-Bueno, C., de la Cruz, L., Sánchez-López, M., Solera-Martínez, M., Díez-Fernández, A., et al. (2015). Prevalence of thinness, overweight and obesity among 4-to-6-year-old Spanish schoolchildren in 2013; situation in the European context. Nutricion Hospitalaria,32(4), 1476–1482.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the following participants: the families; the paediatricians belonging to the Madrid Regional Sentinel Primary-care Physician Network and the staff of Demométrica SL and Sondaxe SL who conducted the family interviews.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Madrid’s Ramón y Cajal Hospital, and informed consent in writing was given by the parents of all child participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortiz-Pinto, M.A., Ortiz-Marrón, H., Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A. et al. Parental perception of child health status and quality of life associated with overweight and obesity in early childhood. Qual Life Res 29, 163–170 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-019-02313-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-019-02313-7