Abstract
In this paper, we evaluate the economic cost of the Islamic State on the Syrian and Iraqi economies from 2010 to 2016. To do so, we use the Post-Terrorism Final Economic Damage Simulator—PTFED-Simulator. The PTFED-Simulator assesses the economic damage of terrorism based on ten different indicators: (1) total regional terrorism tension (∆Tt); (2) harmonized anti-terrorist strategy (AT+); (3) war losses from terrorism (−πt); (4) total economic leakage from terrorism (−Ψt); (5) economic desgrowth from terrorism (−δt); (6) military dimension of terrorism (MDt); (7) post-terrorism economic damage (−Πt); (8) post terrorism economic damage evaluation; (9) post-terrorism reconstruction plan (PTRt); and (10) terrorism effect on mega-disk networks mapping. Overall, we seek to evaluate the impact of terrorism on economic performance from a multi-dimensional perspective in both the short run and long run.

Source: GTD (2014)

Source: GTD (2014)

Source: GTD (2014)












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
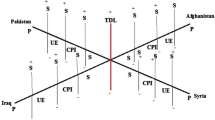
We applied a new mathematical framework to explain how a terrorist conflict evolves in different phases. To elaborate the process, we employed supportive mathematical approaches such as complexity along with advanced geometry, calculus i.e. differential equations, and matrix calculus. In addition, the same model proposes a series of multidimensional mathematical propositions and assumptions to generate favorable conditions to conduct systematic simulations of different scenarios and time periods.
References
Abadie, A., Gardeazabal, J.: The economic costs of conflict: a case study of the Basque country. Am. Econ. Rev. 93(1), 113–132 (2003)
Blomberg, S.B., Hess, G.D., Orphanides, A.: The macroeconomic consequences of terrorism. J. Monet. Econ. 51(5), 1007–1032 (2004)
Chen, A.H., Siems, T.F.: The effects of terrorism on global capital markets. Eur. J. Polit. Econ. 20(2), 249–266 (2004)
CIA Fact Book (2016). http://www.globalfirepower.com/countries comparison detail.asp?form = form&country1 = Official Forces (G1)&country2 = Regional Terrorist Groups (G2)&Submit = CMPARE
Danios. (2012). Most victims of Islamic terrorism are muslims. And why America is to blame for it. feature, loon politics Report.http://www.loonwatch.com/2012/06/most-victims-of-islamic-terrorism-are-muslims and-why-america-is-to-blame-for-it/
Frey, B.S., Luechinger, S., Stutzer, A.: Calculating tragedy: assessing the costs of terrorism. J. Econ. Surv. 21(1), 1–24 (2007)
Gaibulloev, K., Sandler, T.: Growtrh consequences of terrorism in Western Europe. Kyklos Int. Rev. Soc. Sci. 61(3), 411–424 (2008)
Global Terrorism Database (GTD). (2014). https://www.start.umd.edu/gtd/
Global Terrorism Index (GTI). (2016). https://www.start.umd.edu/gtd/
Ianchovichina, E., Ivanic, M. (2014). The economic impact of the Syrian war and the spread of ISIS: Who loses & how much? http://blogs.worldbank.org/arabvoices/economic-impact-syrian-war-and spread-isis-who loses-how-much
Khan, A.: How does terrorism matter at state-level of a country? evidence from Islamic countries. Qual. Quant. (2017). doi:10.1007/s11135-017-0494-7
Khan, A., Ruiz Estrada, M.A.: The effects of terrorism on economic performance: the case of Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS). Qual. Quant. 50(4), 1645–1661 (2015)
Khan, A., Ruiz Estrada, M.A.: Globalization and terrorism: an overview. Qual. Quant. (2016). doi:10.1007/s11135-016-0367-5
Ruiz Estrada, M.A., Park, D.: Korean unification: How painful and how costly? J. Policy Model. 30(1), 87–100 (2008)
Ruiz Estrada, M.A.: Policy modeling: definition, classification, and evaluation. J. Policy Model. 33(4), 523–536 (2011)
Ruiz Estrada, M.A., Yap, S.F.: The origins and evolution of policy modeling. J. Policy Model. 35(1), 170–182 (2013)
Ruiz Estrada, M.A., Yap, S.F.: The origins and evolution of policy modeling. J. Policy Model. 35(1), 170–182 (2013)
Ruiz Estrada, M.A., Park, D., Kim, J.S., Khan, A.: The economic impact of terrorism: a new model and its application to Pakistan. J. Policy Model. 33(4), 523–536 (2015)
Ruiz Estrada, M.A., Koutronas, E.: Terrorist attack assessment: Paris November 2015 and Brussels March 2016. J. Policy Model. 38(3), 553–571 (2016)
Ruiz Estrada, M.A.: An alternative graphical modeling for economics: econographicology. Qual. Quant. (2017). doi:10.1007/s11135-015-0280-3
Sandler, T., Enders, W.: Economic consequences of terrorism in developed and developing countries: An overview. In: Keefer, P., Loayza, N. (eds.) Terrorism, Economic Development, and Political Openness. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge (2008)
Shahbaz, M., Shabbir, M.S.: Military spending and economic growth in Pakistan: new evidence from rolling window approach. Ekonomska istrazˇivanja 25(1), 144–159 (2012)
Shahzad, J., Rehman, M.U., Ahmad, T., Fida, B.: Relationship between FDI, terrorism and economic growth in Pakistan. Soc. Indic. Res. (2015). doi:10.1007/s11205-015-0950-5
World Bank. (2009). Interim strategy note fort Republic of Iraq for the Period Mid FY09 FY11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz Estrada, M.A., Khan, A. & Park, D. The economic cost of the Islamic State on the Syrian and Iraqi economies. Qual Quant 52, 1707–1730 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-017-0549-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-017-0549-9