Abstract
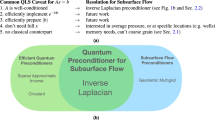
It was recently shown that certain subsurface hydrological inverse problems—here framed as determining the composition of an aquifer from pressure readings—can be solved on a quantum annealer. However, the quantum annealer performance suffered when solving problems where the aquifer was composed of materials with vastly different permeability, which is often encountered in practice. In this paper, we study why this regime is difficult and use several pre- and post-processing tools to address these issues. This study has three benefits: it improves quantum annealing performance for real-world problems in hydrology, it studies the scaling behavior for these problems (which were previously studied at a fixed size), and it elucidates a challenging class of problems that are amenable to quantum annealers.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
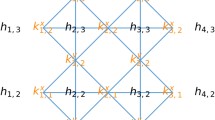
Of course, the values determined by FV did not necessarily agree with the actual values of \({\mathbf {k}}_{\mathrm{true}}\) due to the effects of noise.
References
O’Malley, D.: An approach to quantum-computational hydrologic inverse analysis. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 6919 (2018)
Lu, Z., Robinson, B.A.: Parameter identification using the level set method. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, 6 (2006)
Class, H., Ebigbo, A., Helmig, R., Dahle, H.K., Nordbotten, J.M., Celia, M.A., Audigane, P., Darcis, M., Ennis-King, J., Fan, Y., et al.: A benchmark study on problems related to co 2 storage in geologic formations. Comput. Geosci. 13(4), 409 (2009)
Harp, D.R., Stauffer, P.H., O’Malley, D., Jiao, Z., Egenolf, E.P., Miller, T.A., Martinez, D., Hunter, K.A., Middleton, R.S., Bielicki, J.M., et al.: Development of robust pressure management strategies for geologic co2 sequestration. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 64, 43–59 (2017)
Mackay, D.M., Cherry, J.A.: Groundwater contamination: pump-and-treat remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 23(6), 630–636 (1989)
O’Malley, D., Vesselinov, V.V.: A combined probabilistic/nonprobabilistic decision analysis for contaminant remediation. SIAM/ASA J. Uncertain. Quantif. 2(1), 607–621 (2014)
O’Malley, D., Karra, S., Currier, R.P., Makedonska, N., Hyman, J.D., Viswanathan, H.S.: Where does water go during hydraulic fracturing? Groundwater 54(4), 488–497 (2016)
Hyman, J.D., Jiménez-Martínez, J., Viswanathan, H.S., Carey, J.W.W.M., Porter, M.L., Rougier, E., Karra, S., Kang, Q., Chen, L., et al.: Understanding hydraulic fracturing: a multi-scale problem. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 374(2078), 20150426 (2016)
Lee, J., Kitanidis, P.K.: Large-scale hydraulic tomography and joint inversion of head and tracer data using the principal component geostatistical approach (PCGA). Water Resour. Res. 50(7), 5410–5427 (2014)
Lin, Y., O’Malley, D., Vesselinov, V.V.: A computationally efficient parallel Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm for highly parameterized inverse model analyses. Water Resour. Res. 52(9), 6948–6977 (2016)
Lin, Y., Le, E.B., O’Malley, D., Vesselinov, V.V., Bui-Thanh, T.: Large-scale inverse model analyses employing fast randomized reduction. Water Resour. Res. 53(8), 6784–6801 (2017)
Mo, S., Zabaras, N., Shi, X., Jichun, W.: Deep autoregressive neural networks for high-dimensional inverse problems in groundwater contaminant source identification. Water Resour. Res. 55(5), 3856–3881 (2019)
O’Malley, D., Golden, J.K., Vesselinov, V.V.: Learning to regularize with a variational autoencoder for hydrologic inverse analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.02401 (2019)
Boros, E., Hammer, P.L., Sun, R., Tavares, G.: Preprocessing of unconstrained quadratic binary optimization. Technical report, Rutgers University, Center for Operations Research (2006)
Boros, E., Hammer, P.L., Sun, R., Tavares, G.: A max-flow approach to improved lower bounds for quadratic unconstrained binary optimization (qubo). Discrete Optim. 5(2), 501–529 (2008)
Dorband, J.E.: A method of finding a lower energy solution to a qubo/ising objective function. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.04849 (2018)
Ajagekar, A., You, F.: Quantum computing for energy systems optimization: challenges and opportunities. Energy 179, 76–89 (2019)
Rosenberg, G., Haghnegahdar, P., Goddard, P., Carr, P., Wu, K., de Prado, M.L.: Solving the optimal trading trajectory problem using a quantum annealer. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 10, 1053–1060 (2016)
D-Wave Systems: D-Wave User Manual: Postprocessing Methods on D-Wave Systems. D-Wave Systems
Karimi, H., Rosenberg, G.: Boosting quantum annealer performance via sample persistence. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(7), 166 (2017)
Sax, I., Feld, S., Zelinski, S., Gabor, T., Linnhoff-Popien, C., Maurer, W.: Approximate approximation on a quantum annealer. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM International Conference on Computing Frontiers, pp. 108–117 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golden, J.K., O’Malley, D. Pre- and post-processing in quantum-computational hydrologic inverse analysis. Quantum Inf Process 20, 176 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03115-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03115-y