Abstract
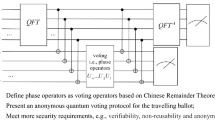
Motivated by the revealing topological structures of continuous-variable graph state (CVGS), we investigate the design of quantum voting scheme, which has serious advantages over the conventional ones in terms of efficiency and graphicness. Three phases are included, i.e., the preparing phase, the voting phase and the counting phase, together with three parties, i.e., the voters, the tallyman and the ballot agency. Two major voting operations are performed on the yielded CVGS in the voting process, namely the local rotation transformation and the displacement operation. The voting information is carried by the CVGS established before hand, whose persistent entanglement is deployed to keep the privacy of votes and the anonymity of legal voters. For practical applications, two CVGS-based quantum ballots, i.e., comparative ballot and anonymous survey, are specially designed, followed by the extended ballot schemes for the binary-valued and multi-valued ballots under some constraints for the voting design. Security is ensured by entanglement of the CVGS, the voting operations and the laws of quantum mechanics. The proposed schemes can be implemented using the standard off-the-shelf components when compared to discrete-variable quantum voting schemes attributing to the characteristics of the CV-based quantum cryptography.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum computation and quantum information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Lucamarini, M., Mancini, S.: Secure deterministic communication without entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(14), 140501 (2005)
Hillery, M., Ziman, M., Bužek, V., Bieliková, M.: Towards quantum-based privacy and voting. Phys. Lett. A. 349(1), 75–81 (2006)
Dolev, S., Pitowsky, I., Tamir, B.: A quantum secret ballot. preprint arXiv:quant-ph/0602087 (2006)
Vaccaro, J.A., Spring, J., Chefles, A.: Quantum protocols for anonymous voting and surveying. Phys. Rev. A. 75(1), 012333 (2007)
Horoshko, D., Kilin, S.: Quantum anonymous voting with anonymity check. Phys. Lett. A. 375(8), 1172–1175 (2011)
Li, Y., Zeng, G.: Quantum anonymous voting systems based on entangled state. Opt. Rev. 15(5), 219–223 (2008)
Jiang, L., He, G., Nie, D., Xiong, J., Zeng, G.: Quantum anonymous voting for continuous variables. Phys. Rev. A 85(4), 042309 (2012)
Hein, M., Eisert, J., Briegel, H.J.: Multiparty entanglement in graph states. Phys. Rev. A. 69(6), 062311 (2004)
Yu, S., Chen, Q., Lai, C.H., Oh, C.H.: Nonadditive quantum error-correcting code. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101(9), 090501 (2008)
Dr, W., Aschauer, H., Briegel, H.J.: Multiparticle entanglement purification for graph states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91(10), 107903 (2003)
Ghne, O., Tth, G., Hyllus, P., Briegel, H.J.: Bell inequalities for graph states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(12), 120405 (2005)
Qian, Y., Shen, Z., He, G., Zeng, G.: Quantum-cryptography network via continuous-variable graph states. Phys. Rev. A. 86(5), 052333 (2012)
Guo, Y., Lv, G., Zeng, G.: Balancing continuous-variable quantum key distribution with source-tunable linear optics cloning machine. Quant. Infor. Proces. 14(11), 4323–4338 (2015)
Braunstein, S.L., van Loock, P.: Quantum information with continuous variables. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77(2), 513–577 (2005)
Braunstein, S.L., Pati, A.K.: Quantum Information with Continuous Variables. Springer Science and Business Media, Berlin (2012)
Zhang, J., Braunstein, S.L.: Continuous-variable Gaussian analog of cluster states. Phys. Rev. A. 73(3), 032318 (2006)
van Loock, P., Weedbrook, C., Gu, M.: Building Gaussian cluster states by linear optics. Phys. Rev. A. 76(3), 032321 (2007)
Menicucci, N.C., Flammia, S.T., Zaidi, H., Pfister, O.: Ultracompact generation of continuous-variable cluster states. Phys. Rev. A. 76(1), 010302 (2007)
Su, X., Tan, A., Jia, X., Zhang, J., Xie, C., Peng, K.: Experimental preparation of quadripartite cluster and Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger entangled states for continuous variables. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(7), 070502 (2007)
Yukawa, M., Ukai, R., van Loock, P., Furusawa, A.: Experimental generation of four-mode continuous-variable cluster states. Phys. Rev. A. 78(1), 012301 (2008)
Wu, Y., Cai, R., He, G., Zhang, J.: Quantum secret sharing with continuous variable graph state. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(5), 1085–1102 (2014)
Lau, H.K., Weedbrook, C.: Quantum secret sharing with continuous-variable cluster states. Phys. Rev. A. 88(4), 042313 (2013)
Wang, G.Y., Li, T., Deng, F.G.: High-efficiency atomic entanglement concentration for quantum communication network assisted by cavity QED. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(4), 1305–1320 (2015)
Wang, M., Xiang, Y., He, Q., Gong, Q.: Detection of quantum steering in multipartite continuous-variable Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger Clike states. Phys. Rev. A. 91(1), 012112 (2015)
Menicucci, N.C., Demarie, T.F., Brennen, G.K.: Anonymous broadcasting with a continuous-variable topological quantum code. arXiv preprint arXiv:1503.00717 (2015)
Hein, M., Dr, W., Eisert, J., Raussendorf, R., Van den Nest, M., Briegel, H.-J.: Entanglement in graph states and its applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:quant-ph/0602096 (2006)
Guo, Y., Qiu, D., Huang, P., Zeng, G.: Controlling continuous-variable quantum key distribution with tuned linear optics cloning machines. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 84, 094003 (2015)
Wang, M., Sun, Y.: A practical, precise method for frequency tracking and phasor estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Del. 19(4), 1547–1552 (2004)
Wang, M., Sun, Y.: A practical method to improve phasor and power measurement accuracy of DFT algorithm. IEEE Trans. Power Del. 21(3), 1054–1062 (2006)
Briegel, H.J., Raussendorf, R.: Persistent entanglement in arrays of interacting particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86(5), 910 (2001)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61379153, 61572529), and partly by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 2013M542119, 2014T70772), Science and Technology Planning Project of Hunan Province, China (Grant No. 2015RS4032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Feng, Y. & Zeng, G. Quantum anonymous voting with unweighted continuous-variable graph states. Quantum Inf Process 15, 3327–3345 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1349-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1349-1