Abstract
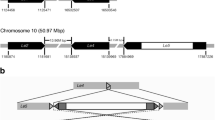
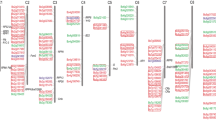
Lectins are proteins that bind specifically to carbohydrates and are active in plant defence and many other physiological processes. The sequencing of the flax (Linum usitatissimum) genome showed that it was unusually rich in genes predicted to encode one or more agglutinin domains (Pfam PF07468). This domain is characteristic of the amaranthin-type lectin family, and thus the 19 predicted flax genes that contained this domain were named L. usitatissimum amaranthin-like lectins (LuALLs). Six LuALLs were predicted to contain a lectin domain and also either a Bet v I domain or an aerolysin domain, both of which have also been found in defence-related proteins. To investigate the function of these genes, transcript expression of 19 LuALLs was measured using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Most LuALLs were expressed throughout vegetative and floral tissues, while two were highly enriched in late-stage embryos, and two others were detected exclusively in stems or cotyledons. Transcripts of six LuALLs increased as much as 3,000-fold in seedlings treated with methyl jasmonate, and six LuALLs were induced by salicylic acid, although only one gene was common to both groups of hormone-responsive genes. These studies form a basis for further research on evolution of plant defences, with potential application in enhancing crop protection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee R, Das K, Ravishankar R, Suguna K, Surolia A, Vijayan M (1996) Conformation, protein-carbohydrate interactions and a novel subunit association in the refined structure of peanut lectin-lactose complex. J Mol Biol 259(2):281–296
Buckley JT, Halasa LN, Lund KD, Macintyre S (1981) Purification and some properties of the hemolytic toxin aerolysin. Can J Biochem 59(6):430–435
Caramelo JJ, Parodi AJ (2008) Getting in and out from calnexin/calreticulin cycles. J Biol Chem 283(16):10221–10225
Chauhan JS, Rao A, Raghava GPS (2013) In silico platform for prediction of N-, O- and C-Glycosites in eukaryotic protein sequences. Plos One 8(6):e67008
Day A, Fenart S, Neutelings G, Hawkins S, Rolando C, Tokarski C (2013) Identification of cell wall proteins in the flax (Linum usitatissimum) stem. Proteomics 13(5):812–825
De Hoff PL, Brill LM, Hirsch AM (2009) Plant lectins: the ties that bind in root symbiosis and plant defense. Mol Genet Genomics 282(1):1–15
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, Brunak S, von Heijne G (2000) Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence. J Mol Biol 300(4):1005–1016
Fahrenkrog B, Aebi U (2003) The nuclear pore complex: nucleocytoplasmic transport and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(10):757–766
Fragniere C, Serrano M, Abou-Mansour E, Metraux JP, L’Haridon F (2011) Salicylic acid and its location in response to biotic and abiotic stress. FEBS Lett 585(12):1847–1852
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud S, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In the proteomics protocols handbook. Walker JM (ed). Humana Press, p 571–607
Hirokawa T, Boon-Chieng S, Mitaku S (1998) SOSUI: classification and secondary structure prediction system for membrane proteins. Bioinformatics 14(4):378–379
Huis R, Hawkins S, Neutelings G (2010) Selection of reference genes for quantitative gene expression normalization in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). Bmc Plant Biol 10:71
Jiang SY, Ma ZG, Ramachandran S (2010) Evolutionary history and stress regulation of the lectin superfamily in higher plants. BMC Evol Biol 10:79
Krishnaswamy SS, Srivastava S, Mohammadi M, Rahman MH, Deyholos MK, Kav NNV (2008) Transcriptional profiling of pea ABR17 mediated changes in gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 8:91
Lannoo N, Van Damme EJM (2010) Nucleocytoplasmic plant lectins. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1800(2):190–201
Levchuk AN, Voitovich EN, Lyakh VA (2013) Lectins of oil-seed flax plants exposed to abiotic stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 60(1):77–83
Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AKM (2006) The family 10 of plant pathogenesis-related proteins: their structure, regulation, and function in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 68(1–3):3–13
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(−Delta Delta C) method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Markovic-Housley Z, Degano M, Lamba D, von Roepenack-Lahaye E, Clemens S, Susani M, Ferreira F, Scheiner O, Breiteneder H (2003) Crystal structure of a hypoallergenic isoform of the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1 and its likely biological function as a plant steroid carrier. J Mol Biol 325(1):123–133
Mitaku S, Hirokawa T (1999) Physicochemical factors for discriminating between soluble and membrane proteins: hydrophobicity of helical segments and protein length. Protein Eng 12(11):953–957
Nielsen H, Engelbrecht J, Brunak S, von Heijne G (1997) Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their cleavage sites. Protein Eng 10(1):1–6
Parker MW, van der Goot FG, Buckley JT (1996) Aerolysin—the ins and outs of a model channel-forming toxin. Mol Microbiol 19(2):205–212
Peumans WJ, Van Damme EJM (1995) Lectins as plant defense proteins. Plant Physiol 109(2):347–352
Punta M, Coggill PC, Eberhardt RY, Mistry J, Tate J, Boursnell C, Pang N, Forslund K, Ceric G, Clements J et al (2012) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 40(D1):D290–D301
Puthoff DP, Sardesai N, Subramanyam S, Nemacheck JA, Williams CE (2005) Hfr-2, a wheat cytolytic toxin-like gene, is up-regulated by virulent Hessian fly larval feeding. Mol Plant Pathol 6(4):411–423
Radauer C, Lackner P, Breiteneder H (2008) The Bet v 1 fold: an ancient, versatile scaffold for binding of large, hydrophobic ligands. BMC Evol Biol 8:286
Rinderle SJ, Goldstein IJ, Matta KL, Ratcliffe RM (1989) Isolation and characterization of amaranthin, a lectin present in the seeds of amaranthus-caudatus, that recognizes the T-antigen (or cryptic-T)-antigen. J Biol Chem 264(27):16123–16131
Roach MJ, Deyholos MK (2007) Microarray analysis of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) stems identifies transcripts enriched in fibre-bearing phloem tissues. Mol Genet Genomics 278(2):149–165
Srivastava S, Fristensky B, Kav NNV (2004) Constitutive expression of a PR10 protein enhances the germination of Brassica napus under saline conditions. Plant Cell Physiol 45(9):1320–1324
Tai H, Pelletier C, Beardmore T (2004) Total RNA isolation from Picea mariana dry seed. Plant Mol Biol Report 22:93a–93e
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Transue TR, Smith AK, Mo HQ, Goldstein IJ, Saper MA (1997) Structure of benzyl T-antigen disaccharide bound to Amaranthus caudatus agglutinin. Nat Struct Biol 4(10):779–783
Van Damme EJM, Lannoo N, Peumans WJ (2008) Plant Lectins. In: Kader JC, Delseny M (ed), Adv Bot Res 48:107–209
Van Damme EJ, Fouquaert E, Lannoo N, Vandenborre G, Schouppe D, Peumans WJ (2011) Novel concepts about the role of lectins in the plant cell. In the molecular immunology of complex carbohydrates. Springer, Verlag, p 271–294
van Loon LC, Rep M, Pieterse CMJ (2006) Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44:135–162
Venglat P, Xiang DQ, Qiu SQ, Stone SL, Tibiche C, Cram D, Alting-Mees M, Nowak J, Cloutier S, Deyholos M et al (2011) Gene expression analysis of flax seed development. BMC Evol Biol 11:74
Wang ZW, Hobson N, Galindo L, Zhu SL, Shi DH, McDill J, Yang LF, Hawkins S, Neutelings G, Datla R et al (2012) The genome of flax (Linum usitatissimum) assembled de novo from short shotgun sequence reads. Plant J 72(3):461–473
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by funding from Genome Canada, Genome Alberta and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faruque, K., Begam, R. & Deyholos, M.K. The Amaranthin-Like Lectin (LuALL) Genes of Flax: a Unique Gene Family with Members Inducible by Defence Hormones. Plant Mol Biol Rep 33, 731–741 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-014-0791-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-014-0791-4