Abstract
Aims
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) straw decomposition and nutrient release (N, K, and P) processes were investigated using a 3-pool model (labile, intermediate, and resistant) to understand the determinant factors.
Methods
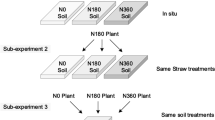
A two-year field experiment was carried out with a split-plot design: the main plot contained two irrigation regimes, while the subplot contained three peanut straw incorporation rates. A total of 216 nylon-mesh bags consisting of peanut straw were buried at a depth of 20 cm, and were removed at 6 winter wheat growth stages (overwintering, double ridge, jointing, flowering, grain filling, and maturity), and the nutrient release (N, P and K) from the peanut straw was measured.
Results
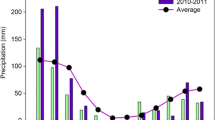
The decomposition dynamics of the labile and intermediate pools were similar in both years. The straw incorporation rate, rather than the irrigation regime, controlled the decomposition process, which increased with increased straw incorporation rates. At a high incorporation rate, the released N, P, and K from the peanut straw were approximately 39%, 30%, and 87% of the required regional fertilizer input for winter wheat, respectively. Furthermore, the N released from straw decomposition was strongly related to the released K as indicated by the stoichiometry ratio. The random forest model predicted that temperature, precipitation, and initial straw nutrients were the main drivers of peanut straw decomposition.
Conclusions
We determined the nutrient stoichiometry and release characteristics of peanut straw decomposition, and found that in comparison to irrigation, the straw incorporation rate exhibits a more profound effect on the peanut straw decomposition process.
Graphical abstract

Highlights
-
Peanut straw decomposition increases with incorporation rate than irrigation.
-
The relative N release is synergistic with relative K release.
-
High straw incorporation rate provides 30–40% of required N and P for wheat growth.
-
Temperature, precipitation, and initial nutrient amount are the main drivers of straw decomposition.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
If requested.
Code availability
If requested.
References
Akhtar K, Wang WY, Khan A, Ren GX, Afridi MZ, Feng YZ, Yang GH (2019) Wheat straw mulching offset soil moisture deficient for improving physiological and growth performance of summer sown soybean. Agric Water Manag 211:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.09.031
Bao SD (2000) Soil agro-chemistrical analysis, 3rd edn. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Bao YY, Feng YZ, Stegen JC, Wu M, Chen RR, Liu WJ, Zhang JW, Li ZP, Lin XG (2020) Straw chemistry links the assembly of bacterial communities to decomposition in paddy soils. Soil Biol Biochem 148:107866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.107866
Berg B, Meentemeyer V (2002) Litter quality in a north European transect versus carbon storage potential. Plant Soil 242:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019637807021
Chen YT, Ma SQ, Jiang HM, Hu Y, Lu XY (2020) Influences of litter diversity and soil moisture on soil microbial communities in decomposing mixed litter of alpine steppe species. Geoderma 377:114577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114577
Chen ZM, Wang HY, Liu XL, Zhao XL, Lu DJ, Zhou JM, Li CZ (2017) Changes in soil microbial community and organic carbon fractions under short-term straw return in a rice-wheat cropping system. Soil till Res 165:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2016.07.018
Cong P, Li YY, Wang J, Gao ZJ, Pang HC, Zhang L, Liu N, Dong JX (2019) Increasing straw incorporation rates improves subsoil fertility and crop yield in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China. Arch Agron Soil Sci 66:1976–1990. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2019.1704735
Cong P, Wang J, Li YY, Liu N, Dong JX, Pang HC, Zhang L, Gao ZJ (2020) Changes in soil organic carbon and microbial community under varying straw incorporation strategies. Soil till Res 204:104735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104735
Cui YX, Zhang YL, Duan CJ, Wang X, Zhang XC, Ju WJ, Chen HS, Yue SC, Wang YQ, Li SQ, Fang LC (2020) Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation decreases the nitrogen cycling potential of soils in semi-arid agricultural ecosystems. Soil till Res 197:104463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104463
Djukic I, Kepfer-Rojas S, Schmidt IK, Larsen KS, Beier C, Berg B, Verheyen K (2018) Early stage litter decomposition across biomes. Sci Total Environ 628–629:1369–1394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.012
Fan HG, Gu J, Wang YZ, Yuan HR, Chen Y, Luo B (2021) Effect of potassium on the pyrolysis of biomass components: Pyrolysis behaviors, product distribution and kinetic characteristics. Waste Manage 121:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.12.023
Feng WT, Shi Z, Jiang J, Xia JY, Liang JY, Zhou JZ, Luo YQ (2016) Methodological uncertainty in estimating carbon turnover times of soil fractions. Soil Biol Biochem 100:118–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.06.003
Fortes C, Trivelin PCO, Vitti AC (2012) Long-term decomposition of sugarcane harvest residues in Sao Paulo state, Brazil. Biomass Bioenergy 42:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.03.011
Garcia-Palacios P, Maestre FT, Kattge J, Wall DH (2013) Climate and litter quality differently modulate the effects of soil fauna on litter decomposition across biomes. Ecol Lett 16:1045–1053. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12137
Grossman JJ, Cavender-Bares J, Hobbie SE (2020) Functional diversity of leaf litter mixtures slows decomposition of labile but not recalcitrant carbon over two years. Ecol Monogr 90:e01407. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1407
Guan XK, Wei L, Turner NC, Ma SC, Yang MD, Wang TC (2020) Improved straw management practices promote in situ straw decomposition and nutrient release, and increase crop production. J Clean Prod 250:119514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119514
Guenet B, Danger M, Abbadie L, Lacroix G (2010) Priming effect: bridging the gap between terrestrial and aquatic ecology. Ecology 304:271–307. https://doi.org/10.1890/09-1968.1
He RR, Zhu D, Chen XW, Cao Y, Chen YQ, Wang XL (2019) How the trade barrier changes environmental costs of agricultural production: An implication derived from China’s demand for soybean caused by the US-China trade war. J Clean Prod 227:578–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.192
He SN, Chen Y, Xiang W, Chen XW, Wang XL, Chen Y (2021) Carbon and nitrogen footprints accounting of peanut and peanut oil production in China. J Clean Prod 291:125964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125964
Huang SQ, Zeng X, Wei YN, Bai X, Jin ZH, Zhang M, Wang ZH, Wang HM, Qu JJ, Di H (2020) Decomposition of betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase transgenic maize straw and its effects on soil microbial biomass and microbiota diversity. Appl Soil Ecol 153:103582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103582
Jensen LS, Salo T, Palmason F, Breland TA, Henriksen TM, Stenberg B, Pedersen A, Lundström C, Esala M (2005) Influence of biochemical quality on C and N mineralisation from a broad variety of plant materials in soil. Plant Soil 273:307–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-8128-y
Jiang WJ, Yan TW, Chen B (2021) Impact of media channels and social interactions on the adoption of straw return by Chinese farmers. Sci Total Environ 756:144078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144078
Ju XT, Kou CL, Zhang FS, Christie P (2006) Nitrogen balance and groundwater nitrate contamination: comparison among three intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain. Environ Pollut 143:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.11.005
Keuskamp JA, Dingemans BJJ, Lehtinen T, Sarneel JM, Hefting MM, Muller-Landau H (2013) Tea Bag Index: a novel approach to collect uniform decomposition data across ecosystems. Methods Ecol Evol 4:1070–1075. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12097
Lang AK, Jevon FV, Vietorisz CR, Ayres MP, Hatala-Matthes J (2021) Fine roots and mycorrhizal fungi accelerate leaf litter decomposition in a northern hardwood forest regardless of dominant tree mycorrhizal associations. New Phytol 230:316–326. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17155
Latifmanesh H, Deng L, Li L, Chen ZJ, Zheng YT, Bao XT, Zheng CY, Zhang WJ (2020) How incorporation depth of corn straw effects straw decomposition rate and C&N release in the wheat-corn cropping system. Agric Ecosyst Environ 300:107000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.107000
Liu SR, Hu RG, Cai GC, Lin S, Zhao JS, Li YY (2014) The role of UV-B radiation and precipitation on straw decomposition and topsoil C turnover. Soil Biol Biochem 77:197–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.06.009
Lin LJ, Liao MA, Ren YJ, Luo L, Zhang X, Yang DY, He J (2014) Effects of mulching tolerant plant straw on soil surface on growth and cadmium accumulation of Galinsoga parviflora. PLoS ONE 9:e114957. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114957
Liu XJ, Ju XT, Zhang FS, Pan JR, Christie P (2003) Nitrogen dynamics and budgets in a winter wheat-maize cropping system in the North China Plain. Field Crop Res 83:111–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(03)00068-6
Liu ZX, Gao F, Liu Y, Yang JQ, Zhen XY, Li XX, Li Y, Zhao JH, Li JR, Qian BC, Yang DQ, Li XD (2019) Timing and splitting of nitrogen fertilizer supply to increase crop yield and efficiency of nitrogen utilization in a wheat-peanut relay intercropping system in China. Crop J 7:101–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2018.08.006
Martínez-García LB, Korthals GW, Brussaard L, Mainardi G, De Deyn GB (2021) Litter quality drives nitrogen release, and agricultural management (organic vs. conventional) drives carbon loss during litter decomposition in agro-ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 153:108115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.108115
NBSC (2020) National Bureau of statistics-China. http://www.stats.gov.cn/. Accessed 10 Mar 2021
Parton W, Silver WL, Burke IC, Grassens L, Harmon ME, Currie WS, King JY, Adair EC, Brandt LA, Hart SC, Fasth B (2007) Global scale similarities in nitrogen release patterns during long-term decomposition. Science 315:1134853. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1134853
Paul PLC, Bell RW, Barrett-Lennard EG, Kabir E (2020) Straw mulch and irrigation affect solute potential and sunflower yield in a heavy textured soil in the Ganges Delta. Agric Water Manag 239:106211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106211
Pimentel LG, Cherubin MR, Oliveira DMS, Cerri CEP, Cerri CC (2019) Decomposition of sugarcane straw: Basis for management decisions for bioenergy production. Biomass Bioenergy 122:133–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.01.027
Singh L, Thakur D, Sharma MK, Chawla A (2021) Dynamics of leaf litter decomposition in the timberline zone of western Himalaya. Acta Oecol 111:103715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actao.2021.103715
Sparks DL, Page AL, Helmke PA, Loeppert RH, Soltanpour PN, Tabatabai MA, Johnston CT, Sumner ME (1996) Methods of soil analysis. Part 3-chemical methods. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.3
Sun B, Wang XY, Wang F, Jiang YJ, Zhang XX (2013) Assessing the relative effects of geographic location and soil type on microbial communities associated with straw decomposition. Appl Environ 79:3327–3335. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00083-13
Tang QY, Zhang CX (2013) Data Processing System (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research. Insect Sci 20:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7917.2012.01519.x
Wang C, Zhao JC, Feng YP, Shang MF, Bo XZ, Gao ZZ, Chen F, Chu QQ (2021a) Optimizing tillage method and irrigation schedule for greenhouse gas mitigation, yield improvement, and water conservation in wheat-maize cropping systems. Agric Water Manag 248:106762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106762
Wang XQ, Nie JW, Wang PX, Zhao J, Yang YD, Wang S, Zeng ZH, Zang HD (2021b) Does the replacement of chemical fertilizer nitrogen by manure benefit water use efficiency of winter wheat-summer maize systems? Agric Water Manag 243:106428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106428
Wang YN, Li FYH, Song X, Wang XS, Suri G, Baoyin T (2020) Changes in litter decomposition rate of dominant plants in a semi-arid steppe across different land-use types: Soil moisture, not home-field advantage, plays a dominant role. Agric Ecosyst Environ 303:107119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.107119
Wu J, Guo XS, Lu JW, Wan SX, Wang YQ, Xu ZY, Zhang XL (2013) Decomposition characteristics of wheat straw and effects on soil biological properties and nutrient status under different rice cultivation. Acta Ecol Sin 33:565–575. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201111201769 (in Chinese)
Yadvinder S, Gupta RK, Jagmohan S, Gurpreet S, Gobinder S, Ladha JK (2010) Placement effects on rice residue decomposition and nutrient dynamics on two soil types during wheat cropping in rice-wheat system in northwestern India. Nutr Cycl Agroecosystems 88:471–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-010-9370-8
Zeng DH, Mao R, Chang SX, Li LJ, Yang D (2010) Carbon mineralization of tree leaf litter and crop residues from poplar-based agroforestry systems in Northeast China: A laboratory study. Appl Soil Ecol 44:133–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2009.11.002
Zhang K (2017) Water/Nitrogen utilization and nitrogen translocation of cereal-legume multi-cropping systems in the North China Plain: a case study on wheat-peanut double cropping. China Agricultural University, Beijing
Zhao J, Zhang XP, Yang YD, Zang HD, Yan P, Meki MN, Doro L, Sui P, Jeong J, Zeng ZH (2021) Alternative cropping systems for groundwater irrigation sustainability in the North China Plain. Agric Water Manag 250:106867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106867
Zhou GP, Gao SJ, Chang DN, Rees RM, Cao WD (2021) Using milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) to promote rice straw decomposition by regulating enzyme activity and bacterial community. Bioresour Technol 319:124215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124215
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31901470) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0300205-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lei Yang: Methodology, Visualization and Writing. Jie Zhou: Reviewing and Editing. Kazem Zamanian: Reviewing and Editing. Kai Zhang: Methodology and Investigation. Jie Zhao: Investigation, Reviewing and Editing. Huadong Zang: Conceptualization, Supervision, Reviewing and Editing. Yadong Yang: Conceptualization, Supervision, Reviewing, Editing and Funding. Zhaohai Zeng: Conceptualization, Supervision, Reviewing and Funding. The authors acknowledge the editors and reviewers for their great help for improving the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
None.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kadambot Hamsa Mohamed Siddique.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Zhou, J., Zamanian, K. et al. Peanut straw application rate had a greater effect on decomposition and nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus release than irrigation. Plant Soil 499, 193–205 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05614-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05614-y