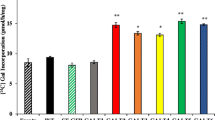
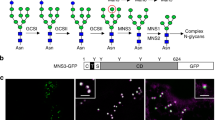
Abstract
Endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidases (ENGases) cleave N-glycans from proteins and/or peptides by hydrolyzing the O-glycosidic linkage between the two core-N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) residues. Although, two homologous genes potentially encoding ENGases have been identified in Arabidopsis thaliana, their respective substrate specificity, their subcellular and their organ specific localization was hitherto unknown. In order to investigate the role of ENGases in this model plant species, we transiently expressed the two A. thaliana genes in Nicotiana benthamiana and determined the substrate specificities, as well as the Km values, of the purified recombinant enzymes. The assumed predominantly cytosolic localisation of both enzymes, here referred to as AtENGase85A and AtENGase85B, was determined by confocal microscopy of plant leaves expressing the respective GFP-fusion constructs. For the individual characterization of the two enzymes expression patterns in planta, single knock-out plants were selected for both genes. Although both enzymes are present in most organs, only AtENGase85A (At5g05460) was expressed in stems and no ENGase activity was detected in siliques. A double knock-out was generated by crossing but—like single knock-out plants—no apparent phenotype was observed. In contrast, in this double knock-out, free N-glycans carrying a single GlcNAc at the reducing end are completely absent and their counterparts with two GlcNAc—visible only at a trace level in wild type—accumulated dramatically.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ENGase:
-
Endo-N-acetylglucosaminidase
- PNGase:
-
Peptide-N 4-(N-acetyl-β-glucosaminyl)asparagine amidase
References
Adar R, Streicher H, Rozenblatt S, Sharon N (1997) Synthesis of soybean agglutinin in bacterial and mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem 249(3):684–689
Altmann F, Schweiszer S, Weber C (1995) Kinetic comparison of peptide: N-glycosidases F and A reveals several differences in substrate specificity. Glycoconj J 12:84–93
Altmann F, Paschinger K, Dalik T, Vorauer K (1998) Characterisation of peptide-N4-(N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminyl)asparagine amidase A and its N-glycans. Eur J Biochem 252:118–123
Anumula KR (1994) Quantitative determination of monosaccharides in glycoproteins by high-performance liquid chromatography with highly sensitive fluorescence detection. Anal Biochem 220:275–283
Barreaud JP, Bourgerie S, Julien R, Guespin-Michel JF, Karamanos Y (1995) An endo-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase, acting on the di-N-acetylchitobiosyl part of N-linked glycans, is secreted during sporulation of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol 177:916–920
Bourgerie S, Karamanos Y, Grard T, Julien R (1994) Purification and characterization of an endo-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase from the culture medium of Stigmatella aurantiaca DW4. J Bacteriol 176:6170–6174
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Bernard T, Lombard V, Henrissat B (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res Database issue: D233–238
Chantret I, Fasseu M, Zaoui K, Le Bizec C, Yayé HS, Dupré T, Moore SE (2010) Identification of roles for peptide: N-glycanase and endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase (Engase1p) during protein N-glycosylation in human HepG2 cells. PLoS One 5(7):e11734
Diepold A, Li G, Lennarz WJ, Nürnberger T, Brunner F (2007) The Arabidopsis AtPNG1 gene encodes a peptide: N-glycanase. Plant J 52:94–104
Kim I, Ahn J, Liu C, Tanabe K, Apodaca J, Suzuki T, Rao H (2006) The Png1-Rad23 complex regulates glycoprotein turnover. J Cell Biol 172:211–219
Kimura Y (2007) Structural and functional features of plant glycoprotein glycans. In: Kamerling JP (ed) Comprehensive Glycoscience, Elsevier, Amsterdam, vol 3, pp 61–78
Kimura Y, Tokuda T, Ohno A, Tanaka H, Ishiguro Y (1998) Enzymatic properties of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases from developing tomato fruits and soybean seeds: substrate specificity of plant origin endoglycosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1381:27–36
Kimura Y, Matsuo S, Tsurusaki S, Kimura M, Hara-Nishimura I, Nishimura M (2002) Subcellular localization of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase and high-mannose type free N-glycans in plant cell. Biochim Biophys Acta 1570:38–46
Ma Y, Wang T (2010) Deactivation of Soybean Agglutinin by Enzymatic and Other Physical Treatments. J Agric Food Chem 58:11413–11419
Maeda M, Kimura M, Kimura Y (2010) Intracellular and extracellular free N-glycans produced by plant cells: occurrence of unusual plant complex-type free N-glycans in extracellular spaces. J Biochem 148:681–692
Masaoka H, Shibata K, Yamaguchi H (1999) Topological and functional characterization of the N-Glycans of Soybean (Glycine max) agglutinin. J Biochem 126:212–217
Nakamura K, Inoue M, Maeda M, Nakano R, Hosoi K, Fujiyama K, Kimura Y (2009) Molecular cloning and gene expression analysis of tomato endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase, an endoglycosidase involved in the production of high-mannose type free N-glycans during tomato fruit ripening. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:461–464
Pabst M, Bondili JS, Stadlmann J, Mach L, Altmann F (2007) Mass + retention time = structure: a strategy for the analysis of N-glycans by carbon LC-ESI-MS and its application to fibrin N-glycans. Anal Chem 79:5051–5057
Packer NH, Lawson MA, Jardine DR, Redmond JW (1998) A general approach to desalting oligosaccharides released from glycoproteins. Glycoconj J 15:737–747
Rademacher T, Sack M, Arcalis E, Stadlmann J, Balzer S, Altmann F, Quendler H, Stiegler G, Kunert R, Fischer R, Stoger E (2008) Recombinant antibody 2G12 produced in maize endosperm efficiently neutralizes HIV-1 and contains predominantly single-GlcNAc N-glycans. Plant Biotechnol J 6:189–201
Seibel NM, Eljouni J, Nalaskowski MM, Hampe W (2007) Nuclear localization of enhanced green fluorescent protein homomultimers. Anal Biochem 368(1):95–99
Suzuki T, Park H, Hollingsworth NM, Sternglanz R, Lennarz WJ (2000) PNG1, a yeast gene encoding a highly conserved peptide: N-glycanase. J Cell Biol 149:1039–1052
Suzuki T, Yano K, Sugimoto S, Kitajima K, Lennarz WJ, Inoue S, Inoue Y, Emori Y (2002) Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase, an enzyme involved in processing of free oligosaccharides in the cytosol. PNAS 99:9691–9696
Takegawa K, Yamabe K, Fujita K, Tabuchi M, Mita M, Izu H, Watanabe A, Asada Y, Sano M, Kondo A, Kato I, Iwahara S (1997) Cloning, sequencing, and expression of Arthrobacter protophormiae endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase in Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys 338:22–28
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the Fonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung (P20132-B16 to Renaud Léonard). We thank Clemens Gruber for the MS analysis of N-glycosylation sites, Richard Strasser (BOKU, Vienna, Austria) for supplying p21GT and Sabine Lhernould (Université de Limoges, France) for her guidance in free N-glycan preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischl, R.M., Stadlmann, J., Grass, J. et al. The two endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase genes from Arabidopsis thaliana encode cytoplasmic enzymes controlling free N-glycan levels. Plant Mol Biol 77, 275–284 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9808-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9808-7