Abstract
Purpose
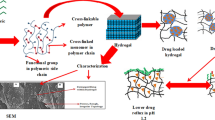
To investigate influence of ion induced mesophasic transformation on pharmaceutical performance of in situ gelling system consisting of glyceryl monooleate.
Methods
The prepared system showed mesophasic transformation during its conversion from sol to gel upon controlled hydration. The process of mesophasic transformation was studied by SAXS, DSC, rheology and plane polarized light microscopy. Further the influence of additives i.e. naproxen salts (sodium and potassium) and naproxen (base) on the process of mesophasic transformation was also elucidated.
Results
It was observed that addition of salt form of naproxen transformed W/O emulsions into cubic mesophase whereas addition of base form of naproxen formed reverse hexagonal (HII) phase upon controlled hydration. The cubic mesophase formed by naproxen salts retarded the drug release for initial 3 h whereas HII phase showed sustained drug release characteristics for naproxen base following Higuchi drug release kinetics.
Conclusion
The current work suggests that formulations with tailor made pharmaceutical performance can be developed by selecting proper additives in the system so as to obtain the desired mesophase ‘on demand’ thereby controlling drug release characteristics.

ᅟ






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fahr A, van Hoogevest P, May S, Bergstrand N, Leigh M. Transfer of lipophilic drugs between liposomal membranes and biological interfaces: consequences for drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005;26:251–65.
Shan-Yang L, Hsiu-Li L, Mei-Jane L. Adsorption of binary liquid crystals onto cellulose membrane for thermo-responsive drug delivery. Adsorption. 2002;8:197–202.
Jensen J, Schutzbach J. Activation of mannosyltransferase II by nonbilayer phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1984;23:1115–9.
Caboi F, Nylander T, Razumas V, Talaikyte Z, Monduzzi M, Larsson K. Structural effects, mobility, and redox behavior of vitamin K1 hosted in the monoolein/water liquid crystalline phases. Langmuir. 1997;13:5476–83.
Lindblom G, Rilfors L. Cubic phases and isotropic structures formed by membrane lipids—possible biological relevance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989;988:221–56.
Larsson K. Cubic lipid-water phases: structures and biomembrane aspects. J Phys Chem. 1989;93:7304–14.
Seddon J. Lyotropic phase behaviour of biological amphiphiles. Ber Bunsenges Phys Chem. 1996;100:380–93.
Chang C, Bodmeier R. Effect of dissolution media and additives on the drug release from cubic phase delivery systems. J Control Release. 1997;46:215–22.
Isrealachvilli J, Mitchell D, Ninham B. Theory of self-assembly of hydrocarbon amphiphiles into micelles and bilayers. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans II. 1976;72:1525–68.
Patton J, Carey M. Watching fat digestion. Science. 1979;204:145–8.
Chernik G. Phase studies of surfactant-water systems. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci. 2000;4:381–90.
Larsson K. Two cubic phases in monoolein/water system. Nature. 1983;304:664.
Lutton E. Phase behavior of aqueous systems of monoglycerides. JAOCS. 1965;42:1068–70.
Qiu H, Caffrey M. The phase diagram of the monoolein/water system: metastability and equilibrium aspects. Biomaterials. 2000;21:223–34.
Rappolt M, Di Gregorio G, Almgren M, Amenitsch H, Pabst G. Non-equilibrium formation of the cubic Pn3m phase in a monoolein/water system. Europhy Lett. 2006;75:267–73.
Drummond C, Fong C. Surfactant self-assembly objects as novel drug delivery vehicles. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci. 2000;4:449–56.
Caboi F, Murgia S, Monduzzi M, Lazzari P. NMR investigation on Melaleuca Alternifolia essential oil dispersed in the monoolein aqueous system: phase behavior and dynamics. Langmuir. 2002;18:7916–22.
Shah M, Paradkar A. Cubic liquid crystalline glyceryl monooleate matrices for oral delivery of enzyme. Int J Pharm. 2005;294(1–2):161–71.
Sadhale Y, Shah J. Glyceryl monooleate cubic phase gel as chemical stability enhancer of cefazolin and cefuroxime. Pharm Dev Tech. 1998;3(4):549–56.
Fong W, Hanley T, Boyd B. Stimuli responsive liquid crystals provide ‘on-demand’ drug delivery in vitro and in vivo. J Control Rel. 2009;135(3):218–26.
Yaghmur A, Laggner P, Zhang S, Rappolt M. Tuning curvature and stability of monoolein bilayers by designer lipid-like peptide surfactants. PLoS One. 2007;2(5):e479.
Patil S, Venugopal E, Bhat S, Mahadik K, Paradkar A. Probing influence of mesophasic transformation in self-emulsifying system: effect of ion. Mol Pharm. 2012;9(2):318–24.
Patil S, Venugopal E, Bhat S, Mahadik K, Paradkar A. Microstructural elucidation of self-emulsifying system: effect of chemical structure. Pharm Res. 2012;29:2180–8.
Biradar S, Dhumal R, Paradkar A. Rheological investigation of self-emulsification process. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2009;12(1):17–31.
Rosevear F. The microscopy of the liquid crystalline neat and middle phases of soaps and synthetic detergents. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1954;31:628–39.
Clogston J, Craciun G, Hart D, Caffrey M. Controlling release from the lipidic cubic phase by selective alkylation. J Control Release. 2005;102:441–61.
Glatter O, Orthaber D, Stradner A, Scherf G, Fanun M, Garti N, et al. Sugar-Ester nonionic microemulsion :structural characterization. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2001;241:215–25.
Salonen A, Muller F, Glatter O. Dispersions of internally liquid crystalline systems stabilized by charged disklike particles as pickering emulsions: basic properties and time-resolved behavior. Langmuir. 2008;24(10):5306–14.
Yariv D, Efrat R, Libster D, Aserin A, Garti N. In vitro permeation of diclofenac salts from lyotropic liquid crystalline systems. Colloid Surfaces B. 2010;78:185–92.
Collins K, Washabaugh M. The Hofmeister effect and the behaviour of water at interfaces. Q Rev Biophys. 1985;18(4):323–422.
Cacace M, Landau E, Ramsden J. The Hofmeister series: salt and solvent effects on interfacial phenomena. Q Rev Biophys. 1997;30:241–77.
Dong R, Hao J. Complex fluids of Polyoxyethylene Monoalkyl Ether nonionic surfactants. Chem Rev. 2010;110:4978–5022.
Borne J, Nylander T, Khan A. Phase behavior and aggregate formation for the aqueous monoolein system mixed with sodium oleate and oleic acid. Langmuir. 2001;17:7742–51.
Li S, Yamashita Y, Yamazaki M. Effect of Electrostatic Interactions on Phase Stability of Cubic Phases of Membranes of Monoolein/Dioleoylphosphatidic Acid Mixtures. Biophys J. 2001;81:983–93.
Senatra D, Lendinara L, Giri M. W/O microemulsions as model systems for the study of water confined in microenvironments: low resolution 1H magnetic resonance relaxation analysis. Prog Colloid Polym Sci. 1991;84:122–8.
Schulz P, Puig J, Barreiro G, Torres L. Thermal transitions in surfactant-based lyotropic liquid crystals. Thermochim Acta. 1994;231:239–56.
Kogan A, Shalev D, Raviv U, Aserin A, Garti N. Formation and Characterization of ordered bicontinuous microemulsions. J Phys Chem B. 2009;113:10669–78.
Ulrich A, Watts A. Molecular response of the lipid headgroup to bilayer hydration monitored by 2H-NMR. Biophys J. 1994;66:1441–9.
Mezzenga R, Meyer C, Servais C, Romoscanu A, Sagalowicz L, Hayward R. Shear rheology of Lyotropic liquid crystals: a case study. Langmuir. 2005;21(8):3322–33.
Tadros T. Application of rheology for assessment and prediction of the long-term physical stability of emulsions. Adv Colloid Interface. 2007;109:227–58.
Negrini R, Mezzenga R. pH-responsive lyotropic liquid crystals for controlled drug delivery. Langmuir. 2011;27:5296–303.
Acknowledgments And Disclosures
The authors thank Dr. Guruswamy Kumaraswamy, Scientist, Polymer Chemistry, National Chemical Laboratory, Pune for providing facility of Small Angle X ray Scattering and for extending his cooperation in SAXS data analysis and discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, S.S., Venugopal, E., Bhat, S. et al. Mapping Ion-Induced Mesophasic Transformation in Lyotropic In Situ Gelling System and its Correlation with Pharmaceutical Performance. Pharm Res 30, 1906–1914 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-1033-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-1033-4