Abstract
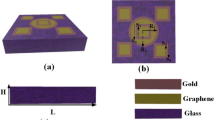
This manuscript presents the development and analysis of a highly sensitive surface plasmonic biosensor tailored for forensic applications, with a specific focus on the precise identification of illegal drugs. The sensor employs a synergistic combination of graphene, glass(fused silica), and gold as fundamental building materials, harnessing their unique properties to enhance detection capabilities. By integrating glass as the substrate, the sensor benefits from its excellent transparency, mechanical stability, and chemical inertness. This provides a solid foundation for the graphene layer, allowing for precise and reliable sensing interactions. A comparative evaluation with existing technologies highlights the sensor's competitive edge in terms of both sensitivity and accuracy. The application of glass as the substrate plays a pivotal role in providing a robust platform for the graphene layer, thereby contributing significantly to the sensor's overall performance and applicability in forensic scenarios. The proposed sensor demonstrates remarkable sensitivity, achieving a maximum relative sensitivity of 4889 GHz/RIU enabling the detection of even the slightest shifts in refractive index—a crucial aspect in the identification of illicit drugs. The sensor's wide range of FOM values, ranging from 15.138 to 54.932 RIU−1, further highlights its adaptability across a diverse spectrum of refractive index measurements.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data supporting the findings in this work are available from the corresponding author with a reasonable request.
References
Ahmad, F., et al.: Advances in graphene-based electrode materials for high-performance supercapacitors: a review. J. Energy Storage (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2023.108731
Aliqab, K., Wekalao, J., Alsharari, M., Armghan, A., Agravat, D., Patel, S.K.: Designing a graphene metasurface organic material sensor for detection of organic compounds in wastewater. Biosensors 13(8), 1–16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13080759
Almawgani, A.H.M., et al.: A graphene-metasurface-inspired optical sensor for the heavy metals detection for efficient and rapid water treatment. Photonics 10(1), 56 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10010056
Alsalman, O., Wekalao, J., Arun Kumar, U., Agravat, D., Parmar, J., Patel, S.K.: Design of split ring resonator graphene metasurface sensor for efficient detection of brain tumor. Plasmonics (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02002-9
Andrade, J., et al.: A novel method for the determination of illicit drugs in wastewater and surface watersbased on a new semi-automated liquid-liquid microextraction device. SSRN Electron. J. (2023). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4313958
Anzar, N., Suleman, S., Parvez, S., Narang, J.: A review on Illicit drugs and biosensing advances for its rapid detection. Process Biochem. 113, 113–124 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2021.12.021
Atta, N.F., Galal, A., Azab, S.M.: Determination of morphine at gold nanoparticles/Nafion® carbon paste modified sensor electrode. Analyst 136(22), 4682–4691 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1an15423k
Atta, N.F., Ahmed, R.A., Amin, H.M.A., Galal, A.: Monodispersed gold nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotubes as an enhanced sensing platform for nanomolar detection of tramadol. Electroanalysis 24(11), 2135–2146 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201200344
Berardinelli, D., Tini, A., Montanari, E., Berretta, P., Di Trana, A.: Liquid chromatography in forensic toxicology. Liq. Chromatogr. Appl. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-99969-4.00010-3
Chen, C.H., Wang, C.C., Ko, P.Y., Chen, Y.L.: Nanomaterial-based adsorbents and optical sensors for illicit drug analysis. J. Food Drug Anal. 28(4), 654–676 (2020). https://doi.org/10.38212/2224-6614.1137
Chen, Y., et al.: Surface and interface engineering: Graphene-based freestanding electrodes for electrochemical energy storage. Coord. Chem. Rev. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215411
“COMSOL,” IEEE Microw. Mag., vol. 22, no. 12, pp. 7–7, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/mmm.2021.3119712.
Dashtian, K., et al.: Biosensors for drug of abuse detection advanced sensor technology: biomedical. Environ. Constr. Appl. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-90222-9.00018-2
de Campos, E.G., et al.: Alternative matrices in forensic toxicology: a critical review. Forensic Toxicol. 40(1), 1–18 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-021-00596-5
Deji, R., Rahul, Choudhary, B.C., Sharma, R.K.: Role of graphene-based materials in gas sensing applications: from synthesis to device fabrication. Mater. Horizons: from Nat. to Nanomater (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7188-4_18
Grover, C., How, J., Close, R.: Fentanyl, etizolam, and beyond: a feasibility study of a community partnership using handheld Raman spectrometry to identify substances in the local illicit drug supply. J. Public Health Res. 12(2), 22799036231166310 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1177/22799036231166313
Haddad, A., Comanescu, M.A., Green, O., Kubic, T.A., Lombardi, J.R.: Detection and quantitation of trace fentanyl in heroin by surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 90(21), 12678–12685 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02909
Hu, Y., Li, M., Liu, H., Li, B.: Broadband manipulation of flexural waves based on phase-modulated elastic metasurfaces. Eng. Struct. 275, 115209 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2022.115209
Hu, B., et al.: Dual-encapsulated phase change composites with hierarchical MXene-graphene monoliths in graphene foam for high-efficiency thermal management and electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Part B Eng. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2023.110998
Izdebski, M., Ledzion, R., Kucharczyk, W.: Prediction of refractive index in inorganic crystals based on averaged atomic mass. Opt. Mater. (amst) (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2023.113697
Jadeja, R., Surve, J., Parmar, T., Patel, S.K., Al-Zahrani, F.A.: Detection of peptides employing a THz metasurface based sensor. Diam. Relat. Mater. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109675
Li, F., et al.: The terahertz metamaterials for sensitive biosensors in the detection of ethanol solutions. Opt. Commun. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126287
Loch, A.S., Burn, P.L., Shaw, P.E.: Fluorescent sensors for the detection of free-base illicit drugs—Effect of tuning the electronic properties. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 387, 133766 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.133766
Lodha, A., Pandya, A., Sutariya, P.G., Menon, S.K.: A smart and rapid colorimetric method for the detection of codeine sulphate, using unmodified gold nanoprobe. RSC Adv. 4(92), 50443–50448 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra06269h
Monir, M.K., Uddin, M.S., Sen, S.: Design of a novel photonic crystal fiber and numerical analysis of sensitivity for the detection of illegal drugs in terahertz regime. Sens. Bio-Sensing Res. 39, 100551 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2023.100551
Muthuvinayagam, M., Ashok Kumar, S.S., Ramesh, K., Ramesh, S.: Introduction of graphene: the ‘Mother’ of all carbon allotropes. Eng. Mater. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1206-3_2
Naresh, V., Lee, N.: A review on biosensors and recent development of nanostructured materials-enabled biosensors. Sens. (switzerland) 21(4), 1–35 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041109
Norian, E., Astinchap, B.: The effect of an external magnetic field, doping, and bias voltage on the thermoelectric and thermodynamic of S-graphene monolayer. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2022.107307
Norman, C., Marland, V., McKenzie, C., Ménard, H., NicDaéid, N.: Evaluation of fentanyl immunoassay test strips for rapid in-situ detection of fentanyl and fentanyl analogs in seized samples and alternative matrices. Int. J. Drug Policy. Drug Policy 118, 104102 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2023.104102
Patel, S.K., Surve, J., Parmar, J.: Detection of cancer with graphene metasurface-based highly efficient sensors. Diam. Relat. Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109367
Patel, S.K., et al.: Encoding and tuning of THz metasurface-based refractive index sensor with behavior prediction using XGBoost Regressor. IEEE Access (2022a). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3154386
Patel, S.K., et al.: Graphene based highly sensitive refractive index sensor using double split ring resonator metasurface. Opt. Quantum Electron. (2022b). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-03600-3
Patel, S.K., Wekalao, J., Alsalman, O., Surve, J., Parmar, J., Taya, S.A.: Development of surface plasmon resonance sensor with enhanced sensitivity for low refractive index detection. Opt. Quantum Electron. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05265-y
Santana-Viera, S., Lara-Martín, P.A., González-Mazo, E.: High resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) determination of drugs in wastewater and wastewater based epidemiology in Cadiz Bay (Spain). J. Environ. Manage. 341, 11800 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118000
Shuaibu, L., Audu, A.A., Igenepo, K.J.: The application of nanosensors in illicit drugs determination: a review. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.9734/cjast/2021/v40i2231477
Sternbach, A.J., et al.: Negative refraction in hyperbolic hetero-bicrystals. Science (80-. ) 379(6632), 555–557 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adf1065
Subaihi, A., Muhamadali, H., Mutter, S.T., Blanch, E., Ellis, D.I., Goodacre, R.: Quantitative detection of codeine in human plasma using surface-enhanced Raman scattering: Via adaptation of the isotopic labelling principle. Analyst 142(7), 1099–1105 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7an00193b
Sun, Y.S.: Label-free sensing on microarrays. Method. Mol. Biol. 1518, 81–108 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6584-7_7
Surve, J., Patel, S.K., Parmar, J.: Design of cost-efficient graphene metasurface based pregnancy test with NOR gate realization and parametric optimization. IEEE Sens. J. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2022.3218797
Tao, Y.: Spin hall conductivity based on the Drude model. Solid State Commun. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2021.114258
Taylor, R.D., MacCoss, M., Lawson, A.D.: Rings in drugs: Miniperspective. J. Med. Chemistry 57(14), 5845–5859 (2014)
Truta, F., et al.: Electrochemical rapid detection of methamphetamine from confiscated samples using a graphene-based printed platform. Sensors 23(13), 6193 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23136193
Uygun, Z.O.: Fundamentals of biological recognition elements. Fundam. Sens. Technol: Princ. Nov. Des. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-88431-0.00017-X
Weber, A., et al.: Innovative vibrational spectroscopy research for forensic application. Anal. Chem. 95(1), 167–205 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05094
Wekalao, J., Patel, S.K., Anushkannan, N.K., Alsalman, O., Surve, J., Parmar, J.: Design of ring and cross shaped graphene metasurface sensor for efficient detection of malaria and 2 bit encoding applications. Diam. Relat. Mater. 139, 110401 (2023a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2023.110401
Wekalao, J., Patel, S.K., Alsalman, O., Surve, J., Anushkannan, N.K., Parmar, J.: Waterborne bacteria detecting highly sensitive graphene metasurface based cost-efficient and efficient refractive index sensors. Plasmonics (2023b). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01983-x
Wekalao, J., Alsalman, O., Natraj, N.A., Surve, J., Parmar, J., Patel, S.K.: Design of graphene metasurface sensor for efficient detection of COVID-19. Plasmonics (2023c). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01946-2
Wekalao, J., et al.: Graphene-based thz surface plasmon resonance biosensor for hemoglobin detection applicable in forensic science. Plasmonics (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02146-8
Yang, J., Yang, Q., Zhang, Y., Wei, X., Shi, H.: Graphene nanowalls in photodetectors. RSC Adv. 13(33), 22838–22862 (2023a). https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ra03104g
Yang, H., et al.: Metasurface-empowered optical cryptography. Mater. Today 67, 424–445 (2023b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2023.06.003
Zahra, S., et al.: Electromagnetic metasurfaces and reconfigurable metasurfaces: a review. Front. Phys. 8, 593411 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2020.593411
Zhang, D., You, H., Zhang, L., Fang, J.: Facile surface modification of mesoporous au nanoparticles for highly sensitive SERS detection. Anal. Chem. 92(23), 15379–15387 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02781
Zhang, S., et al.: Metasurfaces for biomedical applications: Imaging and sensing from a nanophotonics perspective. Nanophotonics 10(1), 259–293 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1515/nanoph-2020-0373
Zhao, B., et al.: Green synthesis of multi-dimensional plasmonic coupling structures: graphene oxide gapped gold nanostars for highly intensified surface enhanced Raman scattering. Chem. Eng. J. 349, 581–587 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.127
Zhou, Q., Son, K., Liu, Y., Revzin, A.: Biosensors for cell analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 17, 165–190 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071114-040525
Zhu, Z.H., et al.: Metallic nanofilm half-wave plate based on magnetic plasmon resonance. Opt. Lett. 37(4), 698 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1364/ol.37.000698
Acknowledgements
Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R654), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Funding
Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R654), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
“Conceptualization, Shobhit K. Patel; methodology,, Shobhit K. Patel, Jacob Wekalao; Software, Jacob Wekalao, Shobhit K. Patel and Osamah Alsalman Validation, All authors writing—original draft preparation, Jacob Wekalao and Rinku Manvani; Formal Analysis, All Authors; writing—review and editing, All Authors; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wekalao, J., Alsalman, O., Manvani, R. et al. Graphene biosensor design based on glass substrate for forensic detection of illicit drugs. Opt Quant Electron 56, 819 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-024-06690-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-024-06690-3