Abstract
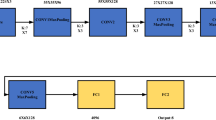
In this paper, a network model named DCC-Net based on infrared image sensor is developed for sports data management. Optical imaging plays an important role in the collection and analysis of sports data, but the traditional methods have limitations in the aspects of illumination change and motion blur. To solve these problems, we propose a DCC-net network model based on infrared image sensor. The background of this study is to improve the efficiency of collection and management of sports data in order to promote the improvement of athletes' training and competitive performance. We use a combination of convolutional neural networks and recurrent neural networks to extract and understand motion information in infrared images. The experimental results show that the DCC-net network model has better performance than the traditional optical method in the aspects of illumination variation and motion blur, and provides more accurate and stable motion data. Therefore, DCC-net network model based on infrared image sensor is an effective sports data management tool, which can provide more comprehensive and accurate training and competitive support for athletes and coaches.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be available upon request.
References
Belton, I., MacDonald, A., Wright, G., Hamlin, I.: Improving the practical application of the Delphi method in group-based judgment: A six-step prescription for a well-founded and defensible process. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 147, 72–82 (2019)
Bertills, K., Granlund, M., Dahlstrom, O., Augustine, L.: Relationships between physical education (PE) teaching and student self-efficacy, aptitude to participate in PE and functional skills: with a special focus on students with disabilities. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 23(4), 387–401 (2018)
Dodero, J.M., Gonzalez-Conejero, E.J., Gutierrez-Herrera, G., Peinado, S., Tocino, J.T., Ruiz-Rube, I.: Trade-off between interoperability and data collection performance when designing an architecture for learning analytics. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 68, 31–37 (2017)
Garcia-Garcia, A., Orts-Escolano, S., Oprea, S., Villena-Martinez, V., Martinez-Gonzalez, P., Garcia-Rodriguez, J.: A survey on deep learning techniques for image and video semantic segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 70, 41–65 (2018)
Guan, F., Peng, L., Perneel, L., Timmerman, M.: Open source FreeRTOS as a case study in real-time operating system evolution. J. Syst. Softw. 118, 19–35 (2016)
Harris, M.T., Metzler, M.: Online personal fitness course alignment with national guidelines for online physical education. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 38(3), 174–186 (2019)
Heide, F., Diamond, S., Nießner, M., Ragan-Kelley, J., Heidrich, W., Wetzstein, G.: Proximal: efficient image optimization using proximal algorithms. ACM Trans. Gr. (TOG) 35(4), 1–15 (2016)
Li, Y., Shi, T., Zhang, Y., Chen, W., Wang, Z., Li, H.: Learning deep semantic segmentation network under multiple weakly-supervised constraints for cross-domain remote sensing image semantic segmentation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 175, 20–33 (2021a)
Li, A., Jiao, L., Zhu, H., Li, L., Liu, F.: Multitask semantic boundary awareness network for remote sensing image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–14 (2021b)
Mazzi, Y., Gaga, A., Errahimi, F.: Benchmarking and comparison of two open-source RTOSs for embedded systems based on ARM Cortex-M4 MCU. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 14(16), 1261–1273 (2021)
Pence, J., Sakurahara, T., Zhu, X., Mohaghegh, Z., Ertem, M., Ostroff, C., Kee, E.: Data-theoretic methodology and computational platform to quantify organizational factors in socio-technical risk analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 185, 240–260 (2019)
Peng, C., Li, Y., Jiao, L., Chen, Y., Shang, R.: Densely based multi-scale and multi-modal fully convolutional networks for high-resolution remote-sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 12(8), 2612–2626 (2019)
Ramegowda, D., Lin, M.: Energy efficient mixed task handling on real-time embedded systems using FreeRTOS. J. Syst. Architect. 131, 102708–102713 (2022)
Zhang, Z., Min, H.: Analysis on the construction of personalized physical education teaching system based on a cloud computing platform. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2020, 1–8 (2020)
Zhao, L., Liu, X., Su, Y.S.: The differentiate effect of self-efficacy, motivation, and satisfaction on pre-service teacher students’ learning achievement in a flipped classroom: a case of a modern educational technology course. Sustainability 13(5), 2888–2895 (2021)
Zhou, W., Jin, J., Lei, J., Yu, L.: CIMFNet: Cross-layer interaction and multiscale fusion network for semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 16(4), 666–676 (2022)
Funding
This article was supported by the (1) Humanities and Social Sciences Project of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (Research on Collaborative Empowerment of School Sports under the Background of Double Reduction Policy), with the content being a series of research paper results, numbered (23SKGH005); (2)the Doctoral Student Support Project of Southwest University of Political Science and Law (Research on University Campus Network Construction), with the content being a series of research paper results, numbered (XZZX2019153).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WY has contributed to the paper’s analysis, discussion, writing, and revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yong, W. DCC-net network model for motion data management based on infrared light sensor. Opt Quant Electron 56, 600 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-06249-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-06249-8