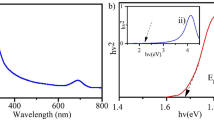
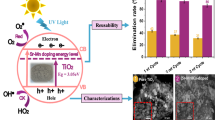
Abstract
Molybdenum Disulphide (MoS2) being an efficient photocatalyst due to its unique optical and structural properties, have attained the attention of researchers during last decade. However, poor absorption of light, fast recombination of charge carriers and low active sites are the barriers for its effective use as a photocatalyst. These constraints could be removed by the incorporation of transition metals in pure MoS2. To that end, we employed a facile and cost-effective hydrothermal method for preparation of pure and copper (Cu) doped (1, 3, 5, and 7%) MoS2 nanomaterials to investigate their degradation efficiency against methylene blue (MB) dye at different pH values (04–10) of reaction solution. Various characterization techniques like SEM, EDX, XRD, FTIR, UV–Vis, and PL were utilized to explore the morphological, compositional, structural, vibrational and optical properties of fabricated nanomaterials. The results revealed that 5% Cu doped MoS2 is an optimal sample among all other fabricated materials, having hexagonal structure, lowest band gap and recombination time of photogenerated charge carriers. This leads to its extraordinary performance in the degradation of MB (i.e.94%) in basic medium having pH 09. The outcomes of this research would be a valuable contribution toward advancing the development of exceptionally efficient TMDs photocatalysts for degradation of organic pollutants.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abdullah, H., Khan, M.M.R., Ong, H.R., Yaakob, Z.: Modified TiO2 photocatalyst for CO2 photocatalytic reduction: an overview. J CO2 Utilizat 22, 15–32 (2017)
Akhtar, J., et al.: Improved photocatalytic performance of Gd and Nd co-doped ZnO nanorods for the degradation of methylene blue. Ceram. Int. 46(8), 11955–11961 (2020)
Ameta, R., et al.: Photocatalysis. In: Advanced oxidation processes for waste water treatment, pp. 135–175. Elsevier (2018)
Benkhaya, S., El Harfi, A.: A critical review of surface water contaminated with dyes from textile industry effluent: possible approaches. Appl J Environ Eng Sci 4(1), 4–1 (2018)
Chowdhary, P., et al., Role of industries in water scarcity and its adverse effects on environment and human health. Environ. Concer. Sustain. Dev.: Vol. 1: Air, Water Energy Resour. pp. 235–256 (2020)
D’Sa, S. and D. Patnaik, The impact of the pharmaceutical industry of hyderabad in the pollution of the godavari river. Water Management in South Asia: Socio-Economic, Infrastructural, Environmental and Institutional Aspects, pp. 23–51 (2020)
Ebenstein, A.: The consequences of industrialization: evidence from water pollution and digestive cancers in China. Rev. Econ. Stat. 94(1), 186–201 (2012)
Farooq, M., Iqbal, T.: Facile hydrothermal synthesis of Cd doped MoS2 nanomaterials for degradation of organic pollutants: Correlation between experimental and COMSOL simulation. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 32(11), 4422–4433 (2022)
Farooq, M., et al.: Simple synthesis of Ni-doped MoS2 nanoparticles and their application as efficient photocatalyst: experiment and COMSOL simulation. Chem. Pap. 76(12), 7493–7506 (2022)
Ghimire, G., et al.: Local enhancement of exciton emission of monolayer MoS2 by copper phthalocyanine nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 122(12), 6794–6800 (2018)
Hashmi, G.J., et al.: Leather industry and environment: Pakistan scenario. Int J Appl Biol Foren 1(2), 20–25 (2017)
Heng, H., et al.: The visible-light-driven type III heterojunction H3PW12O40/TiO2-In2S3: a photocatalysis composite with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Alloy. Compd. 696, 51–59 (2017)
Hong, S., et al.: Earth abundant transition metal-doped few-layered MoS2 nanosheets on CdS nanorods for ultra-efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production. J Mater Chem A 5(39), 20851–20859 (2017)
Jeon, S.H., et al.: Hydrothermal synthesis of Nd2O3 nanorods. Ceram. Int. 43(1), 1193–1199 (2017)
Joseph, D., et al.: Thermoelectric performance of Cu-doped MoS2 layered nanosheets for low grade waste heat recovery. Appl. Surf. Sci. 505, 144066 (2020)
Joseph, D., Navaneethan, M., Abinaya, R., Harish, S., Archana, J., Ponnusamy, S., Hayakawa, Y.: Thermoelectric performance of Cu-doped MoS2 layered nanosheets for low grade waste heat recovery. Appl. Surf. Sci. 505, 144066 (2020)
Kamruzzaman, M., et al.: A comparative study of Ag doping effects on the electronic, optical, carrier conversion, photocatalytic and electrical properties of MoS2. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 273, 115442 (2021)
Katheresan, V., Kansedo, J., Lau, S.Y.: Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6(4), 4676–4697 (2018)
Khan, M., et al.: Effect of Ni doping on the structural, optical and photocatalytic activity of MoS2, prepared by Hydrothermal method. Mater Res Expr 7(1), 015061 (2020)
Khan, S. and A. Malik, Environmental and health effects of textile industry wastewater. Environmental deterioration and human health: Natural and anthropogenic determinants, pp. 55–71 (2014)
Krausmann, F., et al.: Growth in global materials use, GDP and population during the 20th century. Ecol. Econ. 68(10), 2696–2705 (2009)
Kumar, Y., et al.: Novel Z-Scheme ZnIn2S4-based photocatalysts for solar-driven environmental and energy applications: Progress and perspectives. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 87, 234–257 (2021)
Kumar, P., et al., Enhancing the adsorption capacity of green/chemical synthesized hematite nanoparticles by copper doping: removal of toxic Congo red dye and antioxidant activity. Appl Nanosci, pp. 1–14 (2023)
Kuo, S.-Y., et al.: Effects of doping concentration and annealing temperature on properties of highly-oriented Al-doped ZnO films. J. Cryst. Growth 287(1), 78–84 (2006)
Li, Z., Meng, X., Zhang, Z.: Recent development on MoS2-based photocatalysis: a review. J. Photochem. Photobiol., C 35, 39–55 (2018)
Li, Q., et al.: Noble-metal-free amorphous CoMoSx modified CdS core-shell nanowires for dramatically enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 498, 143863 (2019)
Mallesham, B., et al.: Crystal chemistry, band-gap red shift, and electrocatalytic activity of iron-doped gallium oxide ceramics. ACS Omega 5(1), 104–112 (2019)
Manzoor, J. and M. Sharma, Impact of textile dyes on human health and environment, in Impact of textile dyes on public health and the environment. 2020, IGI Global. p. 162–169 (2020)
Mukherjee, A., Goswami, N., Dhak, D.: Photocatalytic remediation of industrial dye waste streams using biochar and metal-biochar hybrids: a critical review. Chem Africa 6(2), 609–628 (2023)
Nachiyar, C.V., et al., Developments in treatment technologies of dye-containing effluent: a review. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, p. 100339 (2023)
Nagarajan, T., et al.: Tribological, oxidation and thermal conductivity studies of microwave synthesised molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanoparticles as nano-additives in diesel based engine oil. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 14108 (2022)
Nguyen, V.-H., et al.: Novel p–n heterojunction nanocomposite: TiO2 QDs/ZnBi2O4 photocatalyst with considerably enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible-light irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. C 124(50), 27519–27528 (2020)
Oladoye, P.O., et al., Methylene blue dye: Toxicity and potential technologies for elimination from (waste) water. Res. Eng., p. 100678 (2022)
Pak, S.: Controlled p-type doping of MoS2 monolayer by copper chloride. Nanomaterials 12(17), 2893 (2022)
Patnaik, R. Impact of industrialization on environment and sustainable solutions–reflections from a south Indian region. In: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2018. IOP Publishing. (2018)
Phung, H.N.T., Truong, N.D., Duong, P.A.: Influence of MoS2 deposition time on the photocatalytic activity of MoS2/V, N co-doped TiO2 heterostructure thin film in the visible light region. Curr. Appl. Phys. 18(6), 737–743 (2018)
Rashid, J., et al.: ZnO-nanoparticles thin films synthesized by RF sputtering for photocatalytic degradation of 2-chlorophenol in synthetic wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 23, 134–139 (2015)
Sajjadi, S.H., Goharshadi, E.K.: Highly monodispersed hematite cubes for removal of ionic dyes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 5(1), 1096–1106 (2017)
Samadi, M., Moshfegh, A.Z.: Recent developments of electrospinning-based photocatalysts in degradation of organic pollutants: principles and strategies. ACS Omega 7(50), 45867–45881 (2022)
Samuel, O., et al.: WO3–based photocatalysts: a review on synthesis, performance enhancement and photocatalytic memory for environmental applications. Ceram. Int. 48(5), 5845–5875 (2022)
Sarker, B., et al.: Surface and ground water pollution: causes and effects of urbanization and industrialization in South Asia. Scientific Rev 7(3), 32–41 (2021)
Scott, A.J.: Industrialization and urbanization: a geographical agenda. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 76(1), 25–37 (1986)
Sharma, M.D., Mahala, C., Modak, B., Pande, S., Basu, M.: Doping of MoS2 by “Cu” and “V”: an efficient strategy for the enhancement of hydrogen evolution activity. Langmuir 37(16), 4847–4858 (2021)
Sun, J., et al.: Synthesis methods of two-dimensional MoS2: a brief review. Crystals 7(7), 198 (2017)
Thakur, N., Thakur, N.: Removal of organic dyes and free radical assay by encapsulating polyvinylpyrrolidone and Tinospora Cordifolia in dual (Co–Cu) doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ. Pollut. 335, 122229 (2023)
Thakur, N., Kumar, A., Thakur, N.: Tinospora cordifolia and polyvinylpyrrolidone encapsulated dual doped Ni-Cu TiO2 emerging nanocatalyst for the removal of organic dyes from wastewater and its free radical assay activity. Hybrid Adv 4, 100086 (2023)
Thakur, N., et al., Catalytic efficiency of encapsulated coupled doped Zn-Ni TiO2 nanocatalyst for the removal of organic pollutants and free radical assay. Int J Environ Anal Chem, pp. 1–18. (2023)
Thakur, N., Thakur, N., Kumar, et al. Encapsulation of Tinospora cordifolia plant in Ni doped TiO2 nanoparticles for the degradation of malachite green dye. Nanofabrication, 8 (2023)
Thakur, N., Kumar, P., et al. Degradation of malachite green dye by capping polyvinylpyrrolidone and Azadirachta indica in hematite phase of Ni doped Fe2O3 nanoparticles via co-precipitation method. Nanofabrication, 8 (2023)
Turhan, K., et al.: Decolorization of textile basic dye in aqueous solution by ozone. Dyes Pigm. 92(3), 897–901 (2012)
Velusamy, S., et al.: A review on heavy metal ions and containing dyes removal through graphene oxide-based adsorption strategies for textile wastewater treatment. Chem. Rec. 21(7), 1570–1610 (2021)
Verma, V., et al.: A review on green synthesis of TiO2 NPs: photocatalysis and antimicrobial applications. Polymers 14(7), 1444 (2022)
Wang, S., et al.: Nanocrystalline MoS2 through directional growth along the (002) crystal plane under high pressure. Mater. Chem. Phys. 130(1–2), 170–174 (2011)
Wu, Z., et al.: MoS2 nanosheets: a designed structure with high active site density for the hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Catal. 3(9), 2101–2107 (2013)
Yang, Z., Goto, H., Matsumoto, M., Maeda, R.: Active micromixer for microfluidic systems using lead-zirconate-titanate (PZT)-generated ultrasonic vibration. ELECTROPHORESIS Int J 21(1), 116–119 (2000)
Yang, L., Yuan, X., Song, R., Liang, W.: Cu doped MoS2 nanosheets/NiS2 nanowires heterogeneous structure for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 181, 111540 (2023)
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2023R667), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MAJ, MF, MSM, contributed about conceptualization, methodology and original/initial draft, TI and SA contributed towards conceptualization, formal analysis and Supervision. NAZ, AE, IW, and HK contributed validation, editing, and review of final draft.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Iqbal, T., Jameel, M.A., Farooq, M. et al. Facile hydrothermal synthesis of Cu-doped MoS2 nanomaterial: a potential photocatalyst for degradation of MB dye. Opt Quant Electron 56, 156 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05759-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05759-9