Abstract
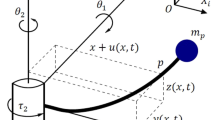
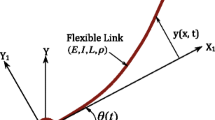
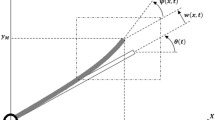
With the increasing demands for more flexibility, lighter weight, and larger working space of industrial robotic systems in many fields, the rigid–flexible coupled robotic systems attract more attention. In this work, the desired angular tracking and vibration suppression issues are investigated for the rigid–flexible coupled robotic systems (RFCRSs) in the presence of input quantization. The vibrating displacement is coupled nonlinear due to the coupling between two joints’ angular positions and flexible displacements. Using the assumed mode principle, the nonlinear infinite-dimension dynamics of rigid–flexible coupled robotic systems are reduced by ordinary differential equations. With the backstepping-based Lyapunov method, robust adaptive flexible prescribed performance control (FPPC) law is developed to track the given angular positions and to reduce the vibration oscillations. Besides, the robust adaptive update law is incorporated into the quantized FPPC for estimating the unknown parameters of logarithmic quantizers in the face of input quantization. In terms of the above robust adaptive FPPC control, the tracking errors of the RFCRSs eventually converge to a compact set in face of input quantization. At last, three comparison cases are implemented to verify the efficacy of the proposed robust adaptive FPPC strategy in comparison with the PD feedback law.


























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
He, W., He, X.Y., Ge, S.S.: Boundary output feedback control of a flexible string system with input saturation. Nonlinear Dyn. 80, 871–888 (2015)
Souza, A.G., Souza, L.C.G.: Design of a controller for a rigid–flexible satellite using the H-infinity method considering the parametric uncertainty. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 116, 641–650 (2019)
Liu, Z.J., Shi, J., He, Y., Zhao, Z.J., Lam, H.K.: Adaptive fuzzy control for a spatial flexible hose system with dynamic event-triggered mechanism. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 59(2), 1156–1167 (2023)
Wang, Y., Yu, F.J., Li, Q.Z., Chen, Y.: Dual-space configuration synthesis method for rigid-flexible coupled cable-driven parallel mechanisms. Ocean Eng. 271, 113753 (2023)
He, W., Meng, T.T., He, X.Y., Ge, S.Z.: Unified iterative learning control for flexible structures with input constraints. Automatica 96, 326–336 (2018)
Tian, L.F., Collins, C.: A dynamic recurrent neural network-based controller for a rigid-flexible manipulator system. Mechatronics 14(5), 471–490 (2004)
Lochan, K., Roy, B.K., Subudhi, B.: A review on two-link flexible manipulators. Annu. Rev. Control 42, 346–367 (2016)
Meng, T., He, W., He, X.: Tracking control of a flexible string system based on iterative learning control. IEEE Trans. Contr. Syst. Tech. 29(1), 436–443 (2021)
Zhou, X.Y., Tian, Y., Wang, H.P.: Neural network state observer-based robust adaptive fault-tolerant quantized iterative learning control for the rigid–flexible coupled robotic systems with unknown time delays. Appl. Math. Comput. 430, 127286 (2022)
Zhao, Z.J., Liu, Z.J., He, W., Hong, K.S., Li, H.X.: Boundary adaptive fault-tolerant control for a flexible Timoshenko arm with backlash-like hysteresis. Automatica 130, 109690 (2021)
Liu, Z.J., Zhao, Z., Ahn, C.K.: Boundary constrained control of flexible string systems subject to disturbances. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. II Exp. Br. 67(1), 112–116 (2020)
Zhang, S., Liu, R., Peng, K., He, W.: Boundary output feedback control for a flexible two-link manipulator system with high-gain observers. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Tech. 29(2), 835–840 (2021)
Cao, F.F., Liu, J.K.: Boundary control for a constrained two-link rigid-flexible manipulator with prescribed performance. Int. J. Control 91(5), 1091–1103 (2018)
Han, F., Jia, Y.: Sliding mode boundary control for a planar two-link rigid-flexible manipulator with input disturbances. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 18, 351–362 (2020)
Zhao, Z.J., He, X., Ahn, C.K.: Boundary disturbance observer-based control of a vibrating single-link flexible manipulator. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber. Syst. 51(4), 2382–2390 (2021)
Xie, D., Jian, K., Wen, W.: An element-free Galerkin approach for rigid-flexible coupling dynamics in 2D state. Appl. Math. Comput. 310, 149–168 (2017)
Hao, T., Wang, H., Xu, F., Wang, J., Miao, Y.: Uncalibrated visual servoing for a planar two link rigid-flexible manipulator without joint-space-velocity measurement. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber. Syst. 52(3), 1935–1947 (2022)
Meng, Q., Lai, X., Yan, Z., Wu, M.: Tip position control and vibration suppression of a planar two-link rigid–flexible underactuated manipulator. IEEE Trans. Cyber. 52(7), 6771–6783 (2022)
Gao, H., He, W., Zhou, C., Sun, C.: Neural network control of a two-link flexible robotic manipulator using assumed mode method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 15(2), 755–765 (2019)
Gao, H., He, W., Song, Y., Zhang, S., Sun, C.: Modeling and neural network control of a flexible beam with unknown spatiotemporally varying disturbance using assumed mode method. Neurocomputing 314, 458–467 (2018)
Meng, Q., Lai, X., Yan, Z., Su, C.Y., Wu, M.: Motion planning and adaptive neural tracking control of an uncertain two-link rigid-flexible manipulator with vibration amplitude constraint. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 33(8), 3814–3828 (2022)
Zhou, X.Y., Wang, H.P., Tian, Y., Zheng, G.: Neural network state observer-based robust adaptive iterative learning output feedback control for the rigid-flexible coupled robotic systems with unknown delays and backlash-like hysteresis. Nonlinear Dyn. 110, 1515–1542 (2022)
Liu, Z.J., Han, Z., He, W.: Adaptive fault-tolerant boundary control of an autonomous aerial refueling hose system with prescribed constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 19(4), 2678–2688 (2022)
Karayiannidis, Y., Doulgeri, Z.: Model-free robot joint position regulation and tracking with prescribed performance guarantees. Robot Auton. Syst. 60(2), 214–226 (2012)
Bechlioulis, C.P., Rovithakis, A.: Adaptive control with guaranteed transient and steady state tracking error bounds for strict feedback systems. Automatica 45(6), 532–538 (2016)
Kostarigka, A.K., Doulgeri, Z., Rovithakis, G.A.: Prescribed performance tracking for flexible joint robots with unknown dynamics and variable elasticity. Automatica 49(5), 1137–1147 (2013)
Shao, X., Hu, Q., Shi, Y., Jiang, B.: Fault-tolerant prescribed performance attitude tracking control for spacecraft under input saturation. IEEE Trans Control Syst. Tech. 28(2), 574–582 (2020)
Dimanidis, I.S., Bechlioulis, C.P., Rovithakis, G.A.: Output feedback approximation-free prescribed performance tracking control for uncertain MIMO nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 65(12), 5058–5069 (2020)
Jia, F.J., Wang, X.H., Zhou, X.Y.: Robust adaptive prescribed performance control for a class of nonlinear pure-feedback systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 29, 3971–3987 (2019)
Liu, A., Yu, L., Zhang, W., Chen, M.Z.Q.: Moving horizon estimation for networked systems with quantized measurements and packet dropouts. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 60(7), 1823–1834 (2013)
Wang, C.L., Wen, C.Y., Lin, Y., Wang, W.: Decentralized adaptive tracking control for a class of interconnected nonlinear systems with input quantization. Automatica 81, 359–368 (2017)
Brockett, R.W., Liberzon, D.: Quantized feedback stabilization of linear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 45(7), 1279–1289 (2000)
Yao, D.Y., Li, H.Y., Shi, Y.: Adaptive event-triggered sliding mode control for consensus tracking of nonlinear multi-agent systems with unknown perturbations. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 53(4), 2672–2684 (2023)
Xing, L., Wen, C., Zhu, Y., Su, H.: Output feedback control for uncertain nonlinear systems with input quantization. Automatica 65, 191–202 (2016)
Zhao, X.N., Zhang, S., Liu, Z.J., Wang, J., Gao, H.B.: Adaptive event-triggered boundary control for a flexible manipulator with input quantization. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 27(5), 3706–3716 (2021)
Ji, N., Liu, J.K.: Adaptive boundary control for flexible three-dimensional Euler-Bernoulli beam with input signal quantization. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 32, 1162–1181 (2018)
Cao, F.F., Liu, J.K.: Boundary vibration control for a two-link rigid-flexible manipulator with quantized input. J. Vib. Control 25(23–24), 2935–2945 (2019)
Yao, D.Y., Li, H.Y., Shi, Y.: Event-based average consensus of disturbed MASs via fully distributed sliding mode control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAC.2023.3317505
Yigit, A.S.: On the stability of PD control for a two-link rigid-flexible manipulator. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 116(2), 208–215 (1994)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant numbers [Grant Nos. 62173182, 61773212]; and the international science and technology innovation cooperation key project [Grant No. 2021YFE0102700];
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Wang, H. & Tian, Y. Robust adaptive flexible prescribed performance tracking and vibration control for rigid–flexible coupled robotic systems with input quantization. Nonlinear Dyn 112, 1951–1969 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-09139-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-09139-6