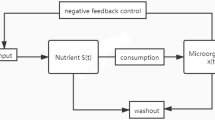
Abstract
Many turbidostat models are affected by environmental noise due to various complicated and uncertain factors, and Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process is a more effective and precise way. We formulate a stochastic turbidostat system incorporating Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process in this paper and develop dynamical behavior for the stochastic model, which includes the existence and uniqueness of globally positive equilibrium, sufficient conditions of the extinction, the existence of a unique stationary distribution and an expression of density function of quasi-stationary distribution around the positive solution of the deterministic model. The results indicate that the weaker volatility intensity can ensure the existence and uniqueness of the stationary distribution, and the stronger reversion speed can lead to the extinction of microorganisms. Numerical simulations verify the validity of the analysis results, which assess the influence of the speed of reversion and the intensity of volatility on the long-term behavior of microorganisms.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availablity statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Li, Z., Chen, L.: Periodic solution of a turbidostat model with impulsive state feedback control. Nonlinear Dyn. 58(3), 525–538 (2009)
Zhong, Z., Wang, T., Chen, L.: Dynamic analysis of a turbidostat model with the feedback control. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15(4), 1028–1035 (2010)
Yao, Y.: Dynamics of a delay turbidostat system with contois growth rate. Math. Biosci. Eng. 16(1), 56–77 (2018)
Yu, M., Lo, W.: Dynamics of microorganism cultivation with delay and stochastic perturbation. Nonlinear Dyn. 101(6), 501–519 (2020)
Yu, M., Lo, W.: Stochastic dynamics of populations with refuge in polluted turbidostat. Chaos Solitons Fractals 147(1), 110963 (2021)
Yu, M., Li, Z., Xiang, H., et al.: Dynamical analysis of a stochastic multispecies turbidostat model. Complexity (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4681205
Zhang, X., Yuan, R.: A stochastic chemostat model with mean-reverting Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process and Monod-Haldane response function. Appl. Math. Comput. (2021). 394: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2020.125833
Wang, W., Cai, Y., Ding, Z., et al.: A stochastic differential equation SIS epidemic model incorporating Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process. Physica A 509, 921–936 (2018)
Dixit, A., Pindyck, R.: Investment under Uncertainty. Princeton University Press, Princeton 39(5), 659–681 (1994)
Wu, F., Mao, X., Kan, C.: A highly sensitive mean-reverting process in finance and the Euler-Maruyama approximations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 348(1), 540–554 (2008)
Zhou, B., Jiang, D., Dai, Y., et al.: Stationary distribution and probability density function of a stochastic SVIS epidemic model with standard incidence and vaccination strategies. Chaos Solitons Fractals (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110601
Rudnicki, R., Pichór, K.: Influence of stochastic perturbation on prey-predator systems. Math. Biosci. 206(1), 108–119 (2007)
Bao, K., Rong, L., Zhang, Q.: Analysis of a stochastic SIRS model with interval parameters. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. B 24(9), 4827–4849 (2019)
Mao, X.: Stochastic differential equations and applications, 2nd edn. Horwood Publishing, Sawston (1997)
Rudnicki, R., Pichór, K., Tyran-Kamińska, M.: Markov semigroups and their applications. Lect. Notes Phys. 597, 215–238 (2002)
Pichór, K., Rudnicki, R.: Stability of Markov semigroups and applications to parabolic systems. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 215, 56–74 (1997)
Ben Arous, G., Léandre, R.: Décroissance exponentielle du noyau de la chaleur sur la diagonale (II). Probab. Theory Relat. Fields. 90, 377–402 (1991)
Higham, D.: An algorithmic introduction to numerical simulation of stochastic differential equations. SIAM Rev. 433, 525–546 (2001)
Acknowledgements
The research is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11871473), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Nos. ZR2019MA010, ZR2019MA006, ZR2020MA039) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 19CX02055A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DJ designed the research and methodology. XM wrote the original draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, X., Jiang, D., Hayat, T. et al. A stochastic turbidostat model with Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process: dynamics analysis and numerical simulations. Nonlinear Dyn 107, 2805–2817 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-07093-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-07093-9